Abstract
Background
T4 esophageal cancer often portends a dismal prognosis even after surgical resection. Historical incomplete resections and poor survival rates often make surgery palliative rather than curative.
Methods
Using a comprehensive esophageal cancer database, we identified patients who underwent an esophagectomy for T4 tumors between 1994 and 2011. Neoadjuvant treatment (NT) and pathologic response variables were recorded, and response was denoted as complete response (pCR), partial response (pPR), and nonresponse (NR). Clinical and pathologic data were compared. Survival was calculated using Kaplan–Meier curves with log-rank tests for significance.
Results
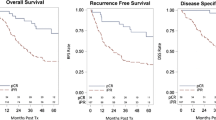
We identified 45 patients with T4 tumors all who underwent NT. The median age was 60 years (range, 31–79 years) with a median follow-up of 27 months (range, 0–122 months). There were 19 pCR (42 %), 22 pPR (49 %), and 4 NR (9 %). R0 resections were accomplished in 43 (96 %). There were 18 recurrences (40 %) with a median time to recurrence of 13.5 months (2.2–71 months). In this group pCR represented 7 (38.9 %), whereas pPR and NR represented 10 (55.5 %), and 1 (5.5 %) respectively. The overall and disease-free survival for all patients with T4 tumors were 35 and 36 %, respectively. Patients achieving a pCR had a 5 year overall and disease-free survival of 53 and 54 %, compared with pPR 23 and 28 %, while there were no 5 year survivors in the NR cohort.
Conclusion
We have demonstrated that neoadjuvant therapy and downstaging of T4 tumors leads to increased R0 resections and improvements in overall and disease-free survival.



Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300.
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Neyman N, Aminou R, Waldron W, et al. (eds). SEER cancer statistics review, 1975–2008. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2008/, based on November 2010 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, 2011.
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Meredith KL, Weber JM, Turaga KK, Siegel EM, McLoughlin J, Hoffe S, et al. Pathologic response after neoadjuvant therapy is the major determinant of survival in patients with esophageal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:1159–67.
Quint LE,and Bogot NR. Staging esophageal cancer. Cancer Imaging. 2008;8: S33–42.
Ikeda K, Ishida K, Sato N, Koeda K, Aoki K, Kimura Y, et al. Chemoradiotherapy followed by surgery for thoracic esophageal cancer potentially or actually involving adjacent organs. Dis Esophagus. 2001;14:197–201.
Forshaw MJ, Gossage JA, Chrystal K, Cheong K, Atkinson S, Botha A, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced carcinoma of the lower oesophagus and oesophago-gastric junction. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2006;32:1114–8.
Frechette E, Buck DA, Kaplan BJ, Chung TD, Shaw JE, Kachnic LA, et al. Esophageal cancer: outcomes of surgery, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and three-dimension conformal radiotherapy. J Surg Oncol. 2004;87:68–74.
Cordin J, Lehmann K, Schneider PM. Clinical staging of adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2010;182:73–83.
Bedenne L, Michel P, Bouche O, Milan C, Mariette C, Conroy T, et al. Chemoradiation followed by surgery compared with chemoradiation alone in squamous cancer of the esophagus: FFCD 9102. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:1160–8.
Kaneko K, Ito H, Konishi K, Kurahashi T, Ito T, Katagiri A, et al. Definitive chemoradiotherapy for patients with malignant stricture due to T3 or T4 squamous cell carcinoma of the oesophagus. Br J Cancer. 2003;88:18–24.
Kaneko K, Ito H, Konishi K, Kurahashi T, Katagiri A, Katayose K, et al. Implantation of self-expanding metallic stent for patients with malignant stricture after failure of definitive chemoradiotherapy for T3 or T4 esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Hepatogastroenterology. 2002;49:699–705.
Yamashita H, Okuma K, Seto Y, Mori K, Kobayashi S, Wakui R, et al. A retrospective comparison of clinical outcomes and quality of life measures between definitive chemoradiation alone and radical surgery for clinical stage II–III esophageal carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2009;100:435–41.
Itoh Y, Fuwa N, Matsumoto A, Asano A, Morita K. Outcomes of radiotherapy for inoperable locally advanced (T4) esophageal cancer-retrospective analysis. Radiat Med. 2001;19:231–5.
Matsubara T, Ueda M, Kokudo N, Takahashi T, Muto T, Yanagisawa A. Role of esophagectomy in treatment of esophageal carcinoma with clinical evidence of adjacent organ invasion. World J Surg. 2001;25:279–84.
Sherman CA, Turrisi AT, Wallace MB, Reed CE. Locally advanced esophageal cancer. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2002;3:475–85.
Tachibana M, Dhar DK, Kinugasa S, Yoshimura H, Shibakita M, Ohno S, et al. Surgical treatment for locally advanced (T4) squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus. Dysphagia. 2002;17:255–61.
Fockens P, Kisman K, Merkus MP, van Lanschot JJ, Obertop H, Tytgat GN. The prognosis of esophageal carcinoma staged irresectable (T4) by endosonography. J Am Coll Surg. 1998;186:17–23.
Tabira Y, Yasunaga M, Nakano KY, Sakaguchi T, Nagamoto N, Matsushita H, et al. All pathological T4 esophageal carcinomas should be categorized as stage IV. Hepatogastroenterology. 2002;49:694–8.
Malaisrie SC, Untch B, Aranha GV, Mohideen N, Hantel A, Pickleman J. Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced esophageal cancer: experience at a single institution. Arch Surg. 2004;139:532–8; discussion 538–9.
Oken M, Creech R, Tormey D, Horton J, Davis TE, McFadden ET, et al. Toxicity and response criteria of the eastern cooperative oncology group. Am J Clin Oncol. 1982;5:649–55.
Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, Fritz A, Balch CM, Haller DG, (eds), A American joint committee on cancer: jcc cancer staging manual. 6th ed. New York, NY: Springer; 2002.
Cordin J, Lehmann K, Schneider PM. Clinical staging of adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2010;182:73–83.
Rasanen JV, Sihvo EI, Knuuti MJ, Minn HR, Luostarinen ME, Laippala P, et al. Prospective analysis of accuracy of positron emission tomography, computed tomography, and endoscopic ultrasonography in staging of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and the esophagogastric junction. Ann Surg Oncol. 2003;10:954–60.
Smith BR, Chang KJ, Lee JG, Nguyen NT. Staging accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound based on pathologic analysis after minimally invasive esophagectomy. Am Surg. 2010;76:1228–31.
Yen TJ, Chung CS, Wu YW, Yen RF, Cheng MF, Lee JM, et al. Comparative study between endoscopic ultrasonography and positron emission tomography-computed tomography in staging patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Esophagus. 2012;25:40–7.
Puli SR, Reddy JB, Bechtold ML, Antillon D, Ibdah JA, Antillon MR. Staging accuracy of esophageal cancer by endoscopic ultrasound: a meta-analysis and systematic review. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:1479–90.
Kutup A, Link BC, Schurr PG, Strate T, Kaifi JT, Bubenheim M, et al. Quality control of endoscopic ultrasound in preoperative staging of esophageal cancer. Endoscopy. 2007;39:715–9.
Lightdale CJ, Kulkarni KG. Role of endoscopic ultrasonography in the staging and follow-up of esophageal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:4483–9.
Makino T, Doki Y. Treatment of T4 esophageal cancer. Definitive chemo-Radiotherapy vs chemo-radiotherapy followed by surgery. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;17:221–8.
Donahue JM, Nichols FC, Li Z, Schomas DA, Allen MS, Cassivi SD, et al. Complete pathologic response after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for esophageal cancer is associated with enhanced survival. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;87:392–9.
Noguchi T, Moriyama H, Wada S, Takeno S, Wakisaka M, Mori H, et al. Resection surgery with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy improves outcomes of patients with T4 esophageal carcinoma. Dis Esophagus. 2003;16:94–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pimiento, J.M., Weber, J., Hoffe, S.E. et al. Outcomes Associated with Surgery for T4 Esophageal Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 20, 2706–2712 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-013-2885-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-013-2885-x