Abstract
Background
Gliadel (polifeprosan 20 with carmustine [BCNU] implant) is commonly used for local delivery of BCNU to high-grade gliomas after resection and is associated with increased survival. Various complications of Gliadel wafers have been reported but not consistently reproduced. We set out to characterize Gliadel-associated morbidity in our 10-year experience with Gliadel wafers for treatment of malignant glioma.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed records of 1013 patients undergoing craniotomy for resection of malignant brain astrocytoma (World Health Organization grade III/IV disease). Perioperative morbidity occurring within 3 months of surgery was assessed for patients and compared between patients receiving versus not receiving Gliadel wafer. Overall survival was assessed for all patients.
Results
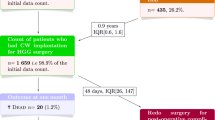
A total of 1013 craniotomies were performed for malignant brain astrocytoma. A total of 288 (28%) received Gliadel wafer (250 glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), 38 anaplastic astrocytoma/anaplastic oligodendroglioma (AA/AO), 166 primary resection, 122 revision resection). Compared with the non-Gliadel cohort, patients receiving Gliadel were older (55 ± 14 vs. 50 ± 17, P = .001) and more frequently underwent gross total resection (75% vs 36%, P < .01) but otherwise similar. Patients in Gliadel versus non-Gliadel cohorts had similar incidences of perioperative surgical site infection (2.8% vs. 1.8%, P = .33), cerebrospinal fluid leak (2.8% vs. 1.8%, P = .33), meninigitis (.3% vs. .3%, P = 1.00), incisional wound healing difficulty (.7% vs. .4%, P = .63), symptomatic malignant edema (2.1% vs. 2.3%, P = 1.00), 3-month seizure incidence (14.6% vs. 15.7%, P = .65), deep-vein thrombosis (6.3% vs. 5.2%, P = .53), and pulmonary embolism (PE) (4.9% vs. 3.7%, P = .41). For patients receiving Gliadel for GBM, median survival was 13.5 months after primary resection (20% alive at 2 years) and 11.3 months after revision resection (13% alive at 2 years). For patients receiving Gliadel for AA/AO, median survival was 57 months after primary resection (66% alive at 2 years) and 23.6 months after revision resection (47% alive at 2 years).
Conclusion
In our experience, use of Gliadel wafer was not associated with an increase in perioperative morbidity after surgical treatment of malignant astrocytoma.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fisher PG, Buffler PA. Malignant gliomas in 2005: where to go from here? JAMA 2005; 293:615–7.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin 2007; 57:43–66.
Reardon DA, Rich JN, Friedman HS, et al. Recent advances in the treatment of malignant astrocytoma. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24:1253–65.
Kornblith PL, Walker M. Chemotherapy for malignant gliomas. J Neurosurg 1988; 68:1–17.
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P. Genetic pathways to primary and secondary glioblastoma. Am J Pathol 2007; 170:1445–53.
Fine HA, Dear KB, Loeffler JS, et al. Meta-analysis of radiation therapy with and without adjuvant chemotherapy for malignant gliomas in adults. Cancer 1993; 71:2585–97.
Stupp R, Mason WP, Van den Bent MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 2005; 352:987–96.
Stewart LA. Chemotherapy in adult high-grade glioma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data from 12 randomised trials. Lancet 2002; 359:1011–8.
Mutter N, Stupp R. Temozolomide: a milestone in neuro-oncology and beyond? Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2006; 6:1187–204.
Patchell RA, Regine WF, Loeffler JS, et al. Radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy for brain metastases. JAMA 2006; 296:2089–90.
Ewend MG, Brem S, Gilbert M, et al. Treatment of single brain metastasis with resection, intracavity carmustine polymer wafers, and radiation therapy is safe and provides excellent local control. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13:3637–41.
Gururangan S, Cokgor L, Rich JN, et al. Phase I study of Gliadel wafers plus temozolomide in adults with recurrent supratentorial high-grade gliomas. Neuro Oncol 2001; 3:246–50.
Heery CR, Desjardins A, Quinn JA. Acute toxicity analysis of patients receiving surgery, Gliadel wafer implantation, and postoperative daily temozolomide with radiation therapy for primary high-grade glioma. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 2006; 24:11504.
La Rocca RV, Hodes J, Villanueva WG. A phase II study of radiation with concomitant and then sequential temozolomide (TMZ) in patients with newly diagnosed supratentorial high-grade malignant glioma who have undergone surgery with carmustine (BCNU) wafer insertion. Neuro Oncol 2006; 8:391–500.
Gaspar LE, Fisher BJ, Macdonald DR, et al. Supratentorial malignant glioma: patterns of recurrence and implications for external beam local treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1992; 24:55–7.
Guerin C, Laterra J, Hruban RH, et al. The glucose transporter and blood-brain barrier of human brain tumors. Ann Neurol 1990; 28:758–65.
Walker MD, Alexander E Jr, Hunt WE, et al. Evaluation of BCNU and/or radiotherapy in the treatment of anaplastic gliomas. A cooperative clinical trial. J Neurosurg 1978; 49:333–43.
Sandberg-Wollheim M, Malmstrom P, Stromblad LG, et al. A randomized study of chemotherapy with procarbazine, vincristine, and lomustine with and without radiation therapy for astrocytoma grades 3 and/or 4. Cancer 1991; 68:22–9.
Fung LK, Ewend MG, Sills A, et al. Pharmacokinetics of interstitial delivery of carmustine, 4-hydroperoxycyclophosphamide, and paclitaxel from a biodegradable polymer implant in the monkey brain. Cancer Res 1998; 58:672–84.
Tamargo RJ, Epstein JI, Reinhard CS, et al. Brain biocompatibility of a biodegradable, controlled-release polymer in rats. J Biomed Mater Res 1989; 23:253–66.
Brem H, Tamargo RJ, Olivi A, et al. Biodegradable polymers for controlled delivery of chemotherapy with and without radiation therapy in the monkey brain. J Neurosurg 1994; 80:283–90.
Ewend MG, Williams JA, Tabassi K, et al. Local delivery of chemotherapy and concurrent external beam radiotherapy prolongs survival in metastatic brain tumor models. Cancer Res 1996; 56:5217–23.
Ewend MG, Sampath P, Williams JA, et al. Local delivery of chemotherapy prolongs survival in experimental brain metastases from breast carcinoma. Neurosurgery 1998; 43:1185–93.
Withrow SJ, Liptak JM, Straw RC, et al. Biodegradable cisplatin polymer in limb-sparing surgery for canine osteosarcoma. Ann Surg Oncol 2004; 11:705–13.
Brem H, Langer R. Polymer-based drug delivery to the brain. Sci Med 1996; 3:2–11.
Brem H, Mahaley MS Jr, Vick NA, et al. Interstitial chemotherapy with drug polymer implants for the treatment of recurrent gliomas. J Neurosurg 1991; 74:441–6.
Brem H, Piantadosi S, Burger PC, et al. Placebo-controlled trial of safety and efficacy of intraoperative controlled delivery by biodegradable polymers of chemotherapy for recurrent gliomas. The Polymer-brain Tumor Treatment Group. Lancet 1995; 345:1008–12.
Sipos EP, Tyler B, Piantadosi S, et al. Optimizing interstitial delivery of BCNU from controlled release polymers for the treatment of brain tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1997; 39:383–9.
Olivi A, Grossman SA, Tatter S, et al. Dose escalation of carmustine in surgically implanted polymers in patients with recurrent malignant glioma: a New Approaches to Brain Tumor Therapy CNS Consortium trial. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21:1845–9.
Valtonen S, Timonen U, Toivanen P, et al. Interstitial chemotherapy with carmustine-loaded polymers for high-grade gliomas: a randomized double-blind study. Neurosurgery 1997; 41:44–8.
Westphal M, Hilt DC, Bortey E, et al. A phase 3 trial of local chemotherapy with biodegradable carmustine (BCNU) wafers (Gliadel wafers) in patients with primary malignant glioma. Neuro Oncol 2003; 5:79–88.
Whittle IR, Lyles S, Walker M. Gliadel therapy given for first resection of malignant glioma: a single centre study of the potential use of Gliadel. Br J Neurosurg 2003; 17:352–4.
Lawson HC, Sampath P, Bohan E, et al. Interstitial chemotherapy for malignant gliomas: the Johns Hopkins experience. J Neurooncol 2007; 83:61–70.
Limentani SA, Asher A, Heafner M, et al. A phase I trial of surgery, Gliadel wafer implantation, and immediate postoperative carboplatin in combination with radiation therapy for primary anaplastic astrocytoma or glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol 2005; 72:241–4.
Kleinberg LR, Weingart J, Burger P, et al. Clinical course and pathologic findings after Gliadel and radiotherapy for newly diagnosed malignant glioma: implications for patient management. Cancer Invest 2004; 22:1–9.
Brem H, Ewend MG, Piantadosi S, et al. The safety of interstitial chemotherapy with BCNU-loaded polymer followed by radiation therapy in the treatment of newly diagnosed malignant gliomas: phase I trial. J Neurooncol 1995; 26:111–23.
Westphal M, Ram Z, Riddle V, et al. Gliadel wafer in initial surgery for malignant glioma: long-term follow-up of a multicenter controlled trial. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2006; 148:269–75.
Bohan E, Brem H. Treatment of brain tumors by local delivery of chemotherapy via biodegradable polymers. Hosp Pharm Rep 1997; 12–6
Engelhard HH. Tumor bed cyst formation after BCNU wafer implantation: report of two cases. Surg Neurol 2000; 53:220–4.
McGirt MJ, Villavicencio AT, Bulsara KR, et al. Management of tumor bed cysts after chemotherapeutic wafer implantation. Report of four cases. J Neurosurg 2002; 96:941–5.
Weber EL, Goebel EA. Cerebral edema associated with Gliadel wafers: two case studies. Neuro Oncol 2005; 7:84–9.
Subach BR, Witham TF, Kondziolka D, et al. Morbidity and survival after 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea wafer implantation for recurrent glioblastoma: a retrospective case-matched cohort series. Neurosurgery 1999; 45:17–22.
LaRocca R, Hodes J, Villanueva W, et al. A phase II study of radiation with concomitant and then sequential temozolomide (TMZ) in patients with newly diagnosed supratentorial high-grade malignant glioma who have undergone surgery with carmustine (BCNU) wafer insertion. Presented at the 11th Scientific Meeting of the Society for Neuro-Oncology, 2006
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Attenello, F.J., Mukherjee, D., Datoo, G. et al. Use of Gliadel (BCNU) Wafer in the Surgical Treatment of Malignant Glioma: A 10-Year Institutional Experience. Ann Surg Oncol 15, 2887–2893 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-008-0048-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-008-0048-2