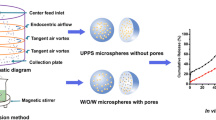
Abstract
Coaxial electrostatic spray technology has received extensive attention in fabricating micro/nanoparticles for drug delivery. However, there are few reports on applying this technology in preparing albumin nanoparticles. In this study, the bufalin (BF) and nintedanib (NDNB) co-loaded ursodeoxycholic acid and p-biguanides benzoic acid decorated albumin sub-microparticles (BN-DUB subMPs) were fabricated by coaxial electrostatic spray technology and optimized by central composite design. Five percent of albumin (contained 0.7% polyethylene oxide) solution was selected as the shell solution which ejected through outer axis with the flow rate of 0.07 mm/min, while the core solution which contained by BF and NDNB ethanol solution was ejected through inner axis with the flow rate of 0.05 mm/min. In vitro cell studies revealed that the modified albumin possessed good biocompatibility. What’s more, the BN-DUB subMPs enhanced the inhibitory effect on the growth of LLC cells efficiently. The pharmacokinetics study showed that the t1/2 and AUC0-t of BN-DUB subMPs increased significantly compared with that of the drug solution, which indicated the improved in vivo stability of modified albumin nanoparticles. Thus, this study provided a novel and simple technical platform for the development of albumin-based drug carriers.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hao L, Zhou Q, Piao Y, Zhou Z, Tang J, Shen Y. Albumin-binding prodrugs via reversible iminoboronate forming nanoparticles for cancer drug delivery. J Control Release. 2021;330:362–71.
Salehiabar M, Nosrati H, Javani E, Aliakbarzadeh F, Kheiri Manjili H, Davaran S, et al. Production of biological nanoparticles from bovine serum albumin as controlled release carrier for curcumin delivery. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;115:83–9.
Li C, Zhang D, Guo H, Hao L, Zheng D, Liu G, et al. Preparation and characterization of galactosylated bovine serum albumin nanoparticles for liver-targeted delivery of oridonin. Int J Pharm. 2013;448(1):79–86.
Dong Y, Fu R, Yang J, Ma P, Liang L, Mi Y, et al. Folic acid-modified ginsenoside Rg5-loaded bovine serum albumin nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy in vitro and in vivo. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:6971–88.
Zhang W, Xia L, Ren X, Cui M, Liu T, Ling C, et al. The improved targeting of an aspirin prodrug albumin-based nanosystem for visualizing and inhibiting lung metastasis of breast cancer. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(21):5941–54.
Hou W, Xia F, Alfranca G, Yan H, Zhi X, Liu Y, et al. Nanoparticles for multi-modality cancer diagnosis: simple protocol for self-assembly of gold nanoclusters mediated by gadolinium ions. Biomaterials. 2017;120:103–14.
Kakkar V, Wani SUD, Gautam SP, Qadrie ZL. Role of microspheres in novel drug delivery systems: preparation methods and applications. Int J Curr Pharm Res. 2020;12:10–5.
Manoharan C, Singh J. Insulin loaded PLGA microspheres: effect of zinc salts on encapsulation, release, and stability. J Pharm Sci. 2009;98(2):529–42.
Ye BY, An CW, Wang JY, Geng XH. Formation and properties of HMX-based microspheres via spray drying. RSC Adv. 2017;7:35411–6.
Ferrado JB, Perez AA, Visentini FF, Islan GA, Castro GR, Santiago LG. Formation and characterization of self-assembled bovine serum albumin nanoparticles as chrysin delivery systems. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019;173:43–51.
Li Y, Zhao X, Zu Y, Zhang Y. Preparation and characterization of paclitaxel nanosuspension using novel emulsification method by combining high speed homogenizer and high pressure homogenization. Int J Pharm. 2015;490(1–2):324–33.
Kohane DS, Tse JY, Yeo Y, Padera R, Shubina M, Langer R. Biodegradable polymeric microspheres and nanospheres for drug delivery in the peritoneum. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006;77(2):351–61.
Vandervoort J, Ludwig A. Biocompatible stabilizers in the preparation of PLGA nanoparticles: a factorial design study. Int J Pharm. 2002;238(1–2):77–92.
Kovács AN, Varga N, Gombár G, Hornok V, Csapó E. Novel feasibilities for preparation of serum albumin-based core-shell nanoparticles in flow conditions. J Flow Chem. 2020;42.
Wei Y, Wang Y, Xia D, Guo S, Wang F, Zhang X, et al. Thermosensitive liposomal codelivery of HSA-paclitaxel and HSA-ellagic acid complexes for enhanced drug perfusion and efficacy against pancreatic cancer. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(30):25138–51.
Stein NC, Mulac D, Fabian J, Herrmann FC, Langer K. Nanoparticle albumin-bound mTHPC for photodynamic therapy: preparation and comprehensive characterization of a promising drug delivery system. Int J Pharm. 2020;582:119347.
Pu W, Fu D, Xia H, Wang Z. Preparation of hollow polyurethane microspheres with tunable surface structures via electrospraying technology. RSC Adv. 2017;7:49828–37.
Thomasin C, Merkle HP, Gander B. Drug microencapsulation by PLA/PLGA coacervation in the light of thermodynamics. 2. Parameters determining microsphere formation. J Pharm Sci. 1998;87(3):269–75.
Nath SD, Son S, Sadiasa A, Min YK, Lee BT. Preparation and characterization of PLGA microspheres by the electrospraying method for delivering simvastatin for bone regeneration. Int J Pharm. 2013;443(1–2):87–94.
Zhang M, Ma Y, Li R, Zeng J, Li Z, Tang Y, et al. RhBMP-2-loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres fabricated by coaxial electrospraying for protein delivery. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2017;28(18):2205–19.
Wu Y, Liao IC, Kennedy SJ, Du J, Wang J, Leong KW, et al. Electrosprayed core-shell microspheres for protein delivery. Chem Commun (Camb). 2010;46(26):4743–5.
Wang M, Wang Y, Omari-Siaw E, Wang S, Zhu Y, Xu X. Reduced burst release and enhanced oral bioavailability in shikimic acid-loaded polylactic acid submicron particles by coaxial electrospray. J Pharm Sci. 2016;105(8):2427–36.
Xu Y, Hanna MA. Morphological and structural properties of two-phase coaxial jet electrosprayed BSA-PLA capsules. J Microencapsul. 2008;25(7):469–77.
Yu DG, Zheng XL, Yang Y, Li XY, Williams GR, Zhao M. Immediate release of helicid from nanoparticles produced by modified coaxial electrospraying. Appl Surf Sci. 2019;473:148–55.
Parhizkar M, Reardon PJ, Knowles JC, Browning RJ, Stride E, Barbara PR, et al. Electrohydrodynamic encapsulation of cisplatin in poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery. Nanomedicine. 2016;12(7):1919–29.
Almería B, Gomez A. Electrospray synthesis of monodisperse polymer particles in a broad (60 nm-2 μm) diameter range: guiding principles and formulation recipes. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2014;417:121–30.
Regev O, Khalfin R, Zussman E, Cohen Y. About the albumin structure in solution and related electro-spinnability issues. Int J Biol Macromol. 2010;47(2):261–5.
Nosrati H, Abbasi R, Charmi J, Rakhshbahar A, Aliakbarzadeh F, Danafar H, et al. Folic acid conjugated bovine serum albumin: an efficient smart and tumor targeted biomacromolecule for inhibition folate receptor positive cancer cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;117:1125–32.
Jose P, Sundar K, Anjali CH, Ravindran A. Metformin-loaded BSA nanoparticles in cancer therapy: a new perspective for an old antidiabetic drug. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015;71(2):627–36.
Stanzl EG, Trantow BM, Vargas JR, Wender PA. Fifteen years of cell-penetrating, guanidinium-rich molecular transporters: basic science, research tools, and clinical applications. Acc Chem Res. 2013;46(12):2944–54.
Vance DE, Li Z, Jacobs RL. Hepatic phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase, unexpected roles in animal biochemistry and physiology. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(46):33237–41.
Zhao H, Zhao D, Jin H, Li H, Yang X, Zhuang L, et al. Bufalin reverses intrinsic and acquired drug resistance to cisplatin through the AKT signaling pathway in gastric cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(2):1817–22.
Wu SH, Bau DT, Hsiao YT, Lu KW, Hsia TC, Lien JC, et al. Bufalin induces apoptosis in vitro and has antitumor activity against human lung cancer xenografts in vivo. Environ Toxicol. 2017;32(4):1305–17.
Xu Y, Tang L, Chen P, Chen M, Zheng M, Shi F, et al. Tumor-targeted delivery of bufalin-loaded modified albumin-polymer hybrid for enhanced antitumor therapy and attenuated hemolysis toxicity and cardiotoxicity. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021;22(4):137.
Epstein Shochet G, Israeli-Shani L, Koslow M, Shitrit D. Nintedanib (BIBF 1120) blocks the tumor promoting signals of lung fibroblast soluble microenvironment. Lung Cancer. 2016;96:7–14.
Hilberg F, Tontsch-Grunt U, Baum A, Le AT, Doebele RC, Lieb S, et al. Triple angiokinase inhibitor nintedanib directly inhibits tumor cell growth and induces tumor shrinkage via blocking oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinases. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018;364(3):494–503.
Hilberg F, Roth GJ, Krssak M, Kautschitsch S, Sommergruber W, Tontsch-Grunt U, et al. BIBF 1120: triple angiokinase inhibitor with sustained receptor blockade and good antitumor efficacy. Cancer Res. 2008;68(12):4774–82.
Kudo K, Arao T, Tanaka K, Nagai T, Furuta K, Sakai K, et al. Antitumor activity of BIBF 1120, a triple angiokinase inhibitor, and use of VEGFR2+pTyr+ peripheral blood leukocytes as a pharmacodynamic biomarker in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(6):1373–81.
Xu Y, Liu Y, Liu Q, Lu S, Chen X, Xu W, Shi F. Co-delivery of bufalin and nintedanib via albumin sub-microspheres for synergistic cancer therapy. J Control Release. 2021 ;1:S0168–3659(21)00463–6.
Böhlen P, Stein S, Dairman W, Udenfriend S. Fluorometric assay of proteins in the nanogram range. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973;155(1):213–20.
Dezhampanah H, Firouzi R, Shoeili ZM, Binazir R. Intermolecular investigation on interaction of two ternary copper(II) Schiff base complexes with bovine serum albumin. J Mol Struct. 2020;1205:127557.
Buddanavar AT, Nandibewoor ST. Multi-spectroscopic characterization of bovine serum albumin upon interaction with atomoxetine. J Pharm Anal. 2017;7(3):148–55.
Kowalczyk T, Nowicka A, Elbaum D, Kowalewski TA. Electrospinning of bovine serum albumin. Optimization and the use for production of biosensors. Biomacromolecules. 2008; 9(7):2087–2090.
Hu K, Li J, Shen Y, Lu W, Gao X, Zhang Q, et al. Lactoferrin-conjugated PEG–PLA nanoparticles with improved brain delivery: in vitro and in vivo evaluations. J Control Release. 2009;134(1):55–61.
Cui Y, Zhang Y, Tang X. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of ofloxacin sustained release pellets. Int J Pharm. 2008;360(1–2):47–52.
Tikhonova TN, Shirshin EA, Romanchuk AY, Fadeev VV. The role of colloid particles in the albumin-lanthanides interaction: the study of aggregation mechanisms. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016;146:507–13.
Peng M, Darko KO, Tao T, Huang Y, Su Q, He C, et al. Combination of metformin with chemotherapeutic drugs via different molecular mechanisms. Cancer Treat Rev. 2017;54:24–33.
Zhao Y, Wang W, Guo S, Wang Y, Miao L, Xiong Y, et al. PolyMetformin combines carrier and anticancer activities for in vivo siRNA delivery. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11822.
Zhang D, Li D, Shang L, He Z, Sun J. Transporter-targeted cholic acid-cytarabine conjugates for improved oral absorption. Int J Pharm. 2016;511(1):161–9.
Gause KT, Yan Y, Cui J, O’Brien-Simpson NM, Lenzo JC, Reynolds EC, et al. Physicochemical and immunological assessment of engineered pure protein particles with different redox states. ACS Nano. 2015;9(3):2433–44.
Geng T, Zhao X, Ma M, Zhu G, Yin L. Resveratrol-loaded albumin nanoparticles with prolonged blood circulation and improved biocompatibility for highly effective targeted pancreatic tumor therapy. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2017;12(1):437.
Funding
This research was supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2017M610309, 2019T120403).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Peng Chen: conceptualization, writing — original draft, methodology.
Shengzhe Lu: investigation, validation, data curation.
Bin Pan: formal analysis, writing — reviewing and editing.
Ying Xu: funding acquisition, project administration, supervision, writing — reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, P., Lu, S., Pan, B. et al. Development, Optimization, and Pharmacokinetics Study of Bufalin/Nintedanib Co-loaded Modified Albumin Sub-microparticles Fabricated by Coaxial Electrostatic Spray Technology. AAPS PharmSciTech 23, 13 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-021-02163-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-021-02163-y