Abstract
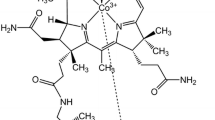
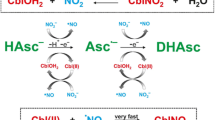
The degradation kinetics of 5 × 10−5 M cyanocobalamin (B12) and hydroxocobalamin (B12b) in the presence of ascorbic acid (AH2) was studied in the pH range of 1.0–8.0. B12 is degraded to B12b which undergoes oxidation to corrin ring cleavage products. B12b alone is directly oxidized to the ring cleavage products. B12 and B12b in degraded solutions were simultaneously assayed by a two-component spectrometric method at 525 and 550 nm without interference from AH2. Both degrade by first-order kinetics and the values of the rate constants at pH 1.0–8.0 range from 0.08 to 1.05 × 10−5 s−1 and 0.22–7.62 × 10−5 s−1, respectively, in the presence of 0.25 × 10−3 M AH2. The t 1/2 values of B12 and B12b range from 13.7 to 137.5 h and 2.5–87.5 h, respectively. The second-order rate constants for the interaction of AH2 with B12 and B12b are 0.05–0.28 × 10−2 and 1.10–30.08 × 10−2 M−1 s−1, respectively, indicating a greater effect of AH2 on B12b compared to that of B12. The k obs–pH profiles for both B12 and B12b show the highest rates of degradation around pH 5. The degradation of B12 and B12b by AH2 is affected by the catalytic effect of phosphate ions on the oxidation of AH2 in the pH range 6.0–8.0.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith EL. Purification of anti-pernicious anemia factors from liver. Nature. 1948;161:638.
Rickes EL, Brink NG, Koniuszy FR, Wood TR, Folkers K. Crystalline vitamin B12. Science. 1948;107:396–7.
Banerjee R, Ragsdale SW. The many faces of vitamin B12: catalysis by cobalamin-dependent enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2003;72:209–47.
Green R, Miller JW. Vitamin B12. In: Zempleni J, Rucker RB, McCormick DB, Suttie JW, editors. Handbook of vitamins. 4th ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2007. p. 413–57.
British Pharmacopoeia, 2013. Monographs on cyanocobalamin and hydroxocobalamin. London, UK: Her Majesty’s Stationary Office, Electronic version; 2013.
Baxter N, Horsford J, Wokes F, Norris FW, Fernandes SJG. Cyanocobalamin and hydroxocobalamin in vitamer B12 injections. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1953;5:723–36.
Hayward GC, Hill HAO, Pratt JM, Vanston NJ, Williams RJP. The chemistry of vitamin B12. Part IV. The thermodynamic trans-effect. J Chem Soc. 1965;6485–93.
Vogler A, Hirschmann R, Otto H, Kunkely H. Photochemistry of biologically important transition metal complexes. I. Cyanocobalamin and related corrin complexes of rhodium(III). Ber Bunsenges Physik Chem. 1976;80:420–4.
Connors KA, Amidon GL, Stella VJ. Chemical stability of pharmaceuticals a handbook for pharmacists. 2nd ed. New York: John Willey; 1986. p. 377–84.
Ahmad I, Hussain W, Fareedi AA. Photolysis of cyanocobalamin in aqueous solution. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1992;10:9–15.
Ahmad I, Hussain W. Stability of cyanocobalamin solutions in sunlight and artificial light. Pak J Pharm Sci. 1993;6:23–8.
Macek TJ. Stability problems with some vitamins in pharmaceuticals. Am J Pharm. 1960;132:433–55.
Kirschbaum J. Cyanocobalamin. In: Florey K, editor. Analytical profiles of drug substances, vol. 10. New York: Academic; 1981. p. 183–288.
DeRitter E. Vitamins in pharmaceutical formulations. J Pharm Sci. 1982;71:1073–96.
Heathcote J, Wills BA. Hydrolytic destruction of thiamine, especially in the presence of cyanocobalamin. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1962;14:232–6.
Doerge RF, Ravin LJ, Caldwell HC. Effect of the thiazole moiety of thiamine hydrochloride and selected model compounds on cyanocobalamin stability. J Pharm Sci. 1965;54:1038–41.
Mukherjee SL, Sen SP. Stability of vitamin B12. Part II. Protection by an iron salt against destruction by aneurine and nicotinamide. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1959;11:26–31.
Ahmad I, Ansari IA, Ismail T. Effect of nicotinamide on the photolysis of cyanocobalamin in aqueous solution. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2003;31:369–74.
Ahmad I, Hussain W. Multicomponent spectrophotometric assay of cyanocobalamin, hydroxocobalamin and riboflavin. Pak J Pharm Sci. 1992;5:121–7.
Ahmad I, Hafeez A, Akhter N, Vaid FHM, Qadeer K. Effect of riboflavin on the photolysis of cyanocobalamin in aqueous solution. Open Anal Chem J. 2012;6:22–7.
Juzeniene A, Nizauskaite Z. Photodegradation of cobalamins in aqueous solutions and in human blood. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol. 2013;122:7–14.
Ansari A, Vaid FHM, Ahmad I. Spectral study of photolysis of aqueous cyanocobalamin solutions in presence of vitamins B and C. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2004;17:93–9.
Ichikawa M, Ide N, Shiraishi S, Ono K. Effect of various halide salts on the incompatibility of cyanocobalamin and ascorbic acid in aqueous solution. Chem Pharm Bull. 2005;53:688–90.
Frost DV, Lapidus M, Plaut KA, Scherfling E, Fricke HH. Differential stability of various analogs of cobalamin to vitamin C. Science. 1952;116:119–21.
Marcus M, Prabhudesai M, Wassef S. Stability of vitamin B12 in the presence of ascorbic acid in food and serum: restoration by cyanide of apparent loss. Am J Clin Nutr. 1980;33:137–43.
Newmark HL, Scheiner MS, Marcus M, Prabhudesai M. Stability of vitamin B12 in the presence of ascorbic acid. Am J Clin Nutr. 1976;29:645–9.
Herbert V, Jacob E. Destruction of vitamin B by ascorbic acid. JAMA. 1974;230:241–2.
Trenner NR, Buhs RP, Bacher FA, Gakenheimer WC. A note concerning the incompatibility of vitamin B12 and ascorbic acid. J Am Pharm Assoc. 1950;39:361.
Campbell JA, McLaughlan JM, Chapman DG. A method for the differentiation of hydroxocobalamin from cyanocobalamin employing the ascorbic acid reaction. J Am Pharm Assoc. 1952;41:479–81.
Hutchins HH, Cravioto PJ, Macek TJ. A comparison of the stability of cyanocobalamin and its analogs in ascorbate solution. J Am Pharm Assoc. 1956;45:806–8.
Ahmad I, Hussain W. Stability of cyanocobalamin in parenteral preparations. Pak J Pharm Sci. 1993;6:53–9.
Hogenkamp HPC. The interaction between vitamin B12 and vitamin C. Am J Clin Nutr. 1980;33:1–3.
Kuehl Jr FA, Shunk CH, Moore M, Folkers K. Vitamin B12. XXV. 3,3-Dimethyl-2,5-dioxopyrrolidine-4-propionamide: a new degradation product. J Am Chem Soc. 1955;77:4418–9.
Marcus AD, Stanley JL. Stability of the cobalamin moiety in buffered aqueous solutions of hydroxocobalamin. J Pharm Sci. 1964;53:91–4.
Zuck DA, Conine JW. Stabilization of vitamin B12 I. Complex cyanides. J Pharm Sci. 1963;52:59–63.
Conine JW, Zuck DA. Stabilization of vitamin B12. II. Alpha-Hydroxynitriles. J Pharm Sci. 1963;52:63–6.
Pratt JM. The chemistry of vitamin B12. Part II. Photochemical reactions. J Chem Soc. 1964;5154–60.
Sinko PJ. Martin’s physical pharmacy and pharmaceutical sciences. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2006. p. 205–6. 416–25.
Cima L, Mantovan R. Cyanocobalamin and hydroxocobalamin separation by thin-layer chromatography. Farmaco Ed Prat. 1962;17:473–81.
Covello M, Schettino O. Determination by chromatospectrophotometry of hydroxo- and cyanocobalamin combined with other medicaments in various pharmaceutical forms. Farmaco Ed Prat. 1964;19:38–51.
Ganshirt H, Malzacher A. Separation of several vitamins of the B group and C by chromatography. Naturwiss. 1960;47:279–80.
Bolliger HR, Konig A. Water-soluble vitamins. In: Stahl E, editor. Thin-layer chromatography. Berlin: Springer; 1969. p. 304–6.
Moffat C, Osselton MD, Widdop B. Clark’s analysis of drugs and poisons. 4th ed. London, UK: Pharmaceutical Press; 2011. p. 1173, 1500.
O’Neil MJ. The merck index, 15th ed. Cambridge, UK: The Royal Society of Chemistry; 2013. Electronic version.
Lexa D, Saveant JM, Zickler J. Electrochemistry of vitamin B12. 5. Cyanocobalamins. J Am Chem Soc. 1980;102:2654–63.
Loy HW, Haggerty JF, Kline OL. Stability of vitamin B12 and B12b. J Assoc Offic Agr Chemists. 1952;35:169–74.
Carstensen JT. Kinetic pH profiles. In: Carstensen JT, Rhodes CT, editors. Drug stability principles and practices. 3rd ed. New York: Marcel Dekker; 2000. p. 57–111.
Hill HAO, Pratt JM, Williams RJP. The corphyrins. J Theor Biol. 1962;3:423–5.
Allwood MC, Kearney MC. Compatibility and stability of additives in parenteral nutrition admixtures. Nutrition. 1998;14:697–706.
Linn Jr DE, Gould ES. Electron transfer. 92. Reductions of vitamin B12a (hydroxocobalamin) with formate and related formyl species. Inorg Chem. 1988;27:1625–8.
Varia SA, Schuller S, Stella VJ. Phenytoin prodrugs IV: hydrolysis of various 3-(hydroxymethyl)phenytoin esters. J Pharm Sci. 1984;73:1074–80.
Powell MF. Enhanced stability of codeine sulfate: effect of pH, buffer, and temperature on the degradation of codeine in aqueous solution. J Pharm Sci. 1986;75:901–3.
Carney CF. Solution stability of ciclosidomine. J Pharm Sci. 1987;76:393–7.
Pramar Y, Gupta VD. Preformulation studies of spironolactone: effect of pH, two buffer species, ionic strength, and temperature on stability. J Pharm Sci. 1991;80:551–3.
Hoitink MA, Beijnen JH, Bult A, van der Houwen OAGJ, Nijholt J, Underberg WJM. Degradation kinetics of gonadorelin in aqueous solution. J Pharm Sci. 1996;85:1053–9.
Ahmad I, Fasihullah Q, Vaid FHM. A study of simultaneous photolysis and photoaddition reactions of riboflavin in aqueous solution. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol. 2004;75:13–20.
Ahmad I, Fasihullah Q, Vaid FHM. Effect of phosphate buffer on photodegradation reactions of riboflavin in aqueous solution. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol. 2005;78:229–34.
Ahmad I, Fasihullah Q, Vaid FHM. Effect of light intensity and wavelengths on photodegradation reactions of riboflavin in aqueous solution. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol. 2006;82:21–7.
Ahmad I, Ahmed S, Sheraz MA, Vaid FHM, Ansari IA. Effect of divalent anions on photodegradation kinetics and pathways of riboflavin in aqueous solution. Int J Pharm. 2010;390:174–82.
Ahmad I, Mirza T, Iqbal K, Ahmed S, Sheraz MA, Vaid FHM. Effect of pH, buffer and viscosity on the photolysis of formylmethylflavin: a kinetic study. Aust J Chem. 2013;66:579–85.
Blaug SM, Hajratwala B. Kinetics of aerobic oxidation of ascorbic acid. J Pharm Sci. 1972;61:556–62.
Rogers AR, Yacomeni JA. The effect of pH on the aerobic degradation of ascorbic acid solutions. J Pharm Pharmcol. 1971;23:218S.
Fasman GD. CRC handbook of biochemistry and molecular biology, vol. 1. 3rd ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 1976. p. 122.
Beiler JM, Moss JN, Martin GJ. Formation of a competitive antagonist of vitamin B12 by oxidation. Science. 1951;114:122–3.
Abu-Soud HM, Maitra D, Byun J, Souza CE, Banerjee J, Saed GM, et al. The reaction of HOCl and cyanocobalamin: corrin destruction and the liberation of cyanogen chloride. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012;52:616–25.
Lexa D, Saveant JM, Zickler J. Electrochemistry of vitamin B12. 2. Redox and acid-base equilibria in the B12a/B12r system. J Am Chem Soc. 1977;99:2786–90.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, I., Qadeer, K., Zahid, S. et al. Effect of Ascorbic Acid on the Degradation of Cyanocobalamin and Hydroxocobalamin in Aqueous Solution: A Kinetic Study. AAPS PharmSciTech 15, 1324–1333 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-014-0160-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-014-0160-5