Abstract
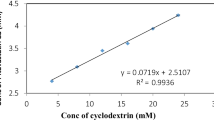
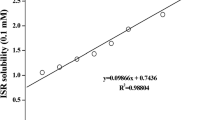
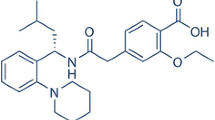
The aim of this study was to improve the solubility and oral bioavailability of clozapine (CLZ), a poorly water-soluble drug subjected to substantial first-pass metabolism, employing cyclodextrin complexation technique. The inclusion complexes were prepared by an evaporation method. Phase solubility studies, differential scanning calorimetry, X-ray powder diffraction, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy were used to evaluate the complexation of CLZ with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD) and the formation of true inclusion complexes. Characterization and dissolution studies were carried out to evaluate the orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs) containing CLZ/HP-β-CD complexes prepared by direct compression. Finally, the bioavailability studies of the prepared ODTs were performed by oral administration to rabbits. The ODTs showed a higher in vitro dissolution rate and bioavailability compared with the commercial tablets. It is evident from the results herein that the developed ODTs provide a promising drug delivery system in drug development, owing to their excellent performance of a rapid onset of action, improved bioavailability, and good patient compliance.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Sweetman SC. Martindale: the complete drug reference. 36th ed. London: Pharmaceutical Press; 2009. p. 768–71.
Lindenberg M, Kopp S, Dressman JB. Classification of orally administered drugs on the World Health Organization Model list of Essential Medicines according to the biopharmaceutics classification system. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2004;58:265–78.
Gerald KM. AHFS drug information. Bethesda: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists Press; 2004. p. 2273–85.
Seager H. Drug delivery products and the Zydis fast dissolving dosage forms. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1998;50:375–82.
Badgujar BP, Mundada AS. The technologies used for developing orally disintegrating tablets: a review. Acta Pharm. 2011;61:117–39.
Goel H, Rai P, Rana V, Tiwary AK. Orally disintegrating systems: innovations in formulation and technology. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2008;2:258–74.
Szejtli J. Introduction and general overview of cyclodextrin chemistry. Chem Rev. 1998;98:1743–54.
Uekama K, Hirayama F, Irie T. Cyclodextrin drug carrier systems. Chem Rev. 1998;98:2045–76.
Misiuk W, Zalewska M. Investigation of inclusion complex of trazodone hydrochloride with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Carbohydr Polym. 2009;77:482–8.
Gould S, Scott RC. 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD): a toxicology review. Food Chem Toxicol. 2005;43:1451–9.
Higuchi T, Connors KA. Phase solubility techniques. Adv Anal Chem Instrum. 1965;4:117–212.
Yadav VR, Suresh S, Devi K, Yadav S. Effect of cyclodextrin complexation of curcumin on its solubility and antiangiogenic and anti-inflammatory activity in rat colitis model. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2009;10:752–62.
Jain SK, Shukla M, Shrivastava V. Development and in vitro evaluation of ibuprofen mouth dissolving tablets using solid dispersion technique. Chem Pharm Bull. 2010;58:1037–42.
Rajitha K, Shravan KY, Adukondalu D, Ramesh G, Madhusudan Y. Formulation and evaluation of orally disintegrating tablets of buspirone. Int J Pharm Sci Nanotechnol. 2009;1:372–4.
US Food and Drug Administration. In vivo bioequivalence guidances. Pharmacopeial Forum. 1993;19:6501–8.
Loftsson T, Brewster ME. Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins. 1. Drug solubilization and stabilization. J Pharm Sci. 1996;85:1017–25.
Zornoza A, Martı́n C, Sánchez M, Vélaz I, Piquer A. Inclusion complexation of glisentide with α-, β- and γ-cyclodextrins. Int J Pharm. 1998;169:239–44.
Fernandes CM, Teresa Vieira M, Veiga FJ. Physicochemical characterization and in vitro dissolution behavior of nicardipine-cyclodextrins inclusion compounds. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2002;15:79–88.
Carrier RL, Miller LA, Ahmed I. The utility of cyclodextrins for enhancing oral bioavailability. J Control Release. 2007;123:78–99.
Cirri M, Righi MF, Maestrelli F, Mura P, Valleri M. Development of glyburide fast-dissolving tablets based on the combined use of cyclodextrins and polymers. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2009;35:73–82.
Cirri M, Rangoni C, Maestrelli F, Corti G, Mura P. Development of fast-dissolving tablets of flurbiprofen-cyclodextrin complexes. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2005;31:697–707.
Williams RO, Mahaguna V, Sriwongjanya M. Characterization of an inclusion complex of cholesterol and hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 1998;46:355–60.
Veiga F, Fernandes C, Maincent P. Influence of the preparation method on the physicochemical properties of tolbutamide/cyclodextrin binary systems. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2001;27:523–32.
Dali MM, Moench PA, Mathias NR, Stetsko PI, Heran CL, Smith RL. A rabbit model for sublingual drug delivery: comparison with human pharmacokinetic studies of propranolol, verapamil and captopril. J Pharm Sci. 2006;95:37–44.
Odou P, Barthelemy C, Chatelier D, Luyckx M, Brunet C, Dine T, et al. Pharmacokinetics of midazolam: comparison of sublingual and intravenous routes in rabbit. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 1999;24:1–7.
Nie S, Fan X, Peng Y, Yang X, Wang C, Pan W. In vitro and in vivo studies on the complexes of vinpocetine with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Arch Pharm Res. 2006;30:991–1001.
Bekers O, Uijtendaal EV, Beijnen JH, Buit A, Under-berg WJM. Cyclodextrins in the pharmaceutical field. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1991;17:1503–49.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are grateful to the College Students Innovation Project for the R&D of Novel Drugs (program no. J1030830) for supporting the present research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, F., Wang, L., Zhang, W. et al. Formulation and In Vivo Evaluation of Orally Disintegrating Tablets of Clozapine/Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes. AAPS PharmSciTech 14, 854–860 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-013-9973-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-013-9973-x