Abstract
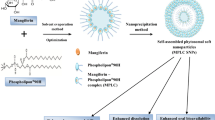
The aim of this research was to formulate Marsupsin–phospholipid complex (M–P Complex) in attempt to increase the bioavailability of marsupsin and to characterize this new formulation along with its evaluation. Marsupsin–phospholipid complex was formulated by mechanical dispersion method. In this new formulation, complex formation was confirmed by carrying out transmission electron microscopy (TEM), IR, 1H-NMR and RP-HPLC analysis. TEM showed M–P Complex diameter range of 0.05–0.5 μm. The entrapment efficiency of M–P Complex was found to be 44%. In vitro release study revealed its first order release profile. Mean blood serum concentration vs time curve of marsupsin was of first order after oral administration of M–P Complex in albino rabbits which clearly showed remarkably increased bioavailability of M–P Complex than standardized marsupsin. The average value of C max and T max of M–P Complex were found to be 3.02 mg/ml and 10.2 h, respectively. Hence the findings demonstrate that complexing marsupsin with phospholipids results in better oral bioavailability and improved biological response than free form of standardized marsupsin.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Tripathi. Charak Samhita 2. Varanasi, India, Chaukhamba Surbharati Prakashan, 2005.
D. Adinarayana, and K. Syamasundar. A new sesquiterpene alcohol from Pterocarpus marsupium. Phytochemistry 21(5):1083–1085 (1982).
R. Maurya, R. B. Ray, F. K. Duah, D. J. Slatkin, and P. L. SchiffJr. Constituents of Pterocarpus marsupium. J. Nat. Prod. 47:179–181 (1984).
J. Bruneton. Pharmacognosy Phytochemistry Medicinal Plants. France, Lavoisier Publication, 1999.
P. Morazzoni, and E. Bombardelli. Anti-inflammatory activity of some Gingko biloba constituents and of their phospholipids-complexes. Fitoterapia LXVII(3):263 (1996).
E. Bombardelli, and M. J. Magistretti, inventors. Pharmaceutical Compositions containing flavanolignans and phospholipids as active principles. EP0209037, Jan 21, 1987.
K. A. Connors. A Text book of Pharmaceutical Analysis. Singapore: A Wiley-Interscience Publication John Wiley and Sons, 1999.
J Novakonic, K Nesmerak, and H Nova. An HPTLC method for the determination and the purity control of ciprofloxacin HCL in coated tablets. J Pharm Bio Ana. 2001;957–964.
P. Krishna, and S. Sarasija. Standard curve of stilbene. Indian Drugs 34(2):227–228 (1997).
S. P. Vyas, and R. K. Khar. Targeted and Control Drug Delivery, New Delhi, India, CBS Publishers & Distributors, 2002.
M. Manconi, C. Sinico, D. Valenti, G. Loy, and A. M. Fadda. Niosomes as carriers for tretinoin. I.Preparation and properties. Int. J. Pharm. 234:237–248 (2002).
F. Kvasnicka, B. Biba, R. Sevcik, M. Voldrich, and J. Kratka. Analysis of the active compounds of silymarin. J. Chromatography A. 990:239–245 (2003).
A. Maitra, T. Banerjee, S. Mitra, A. K. Singh, and R. K. Sharma. Preparation, characterization and biodistribution of ultrafine chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 243:93–105 (2002).
M. A. Schubert, M. Harms, and C. C. Mueller-Goymann. Structural investigation on lipid nanoparticles containing high amounts of lecithin. European J. Pharm. Sci. 27:226–236 (2006).
R. G. Rengel, K. Barisic, Z. Pavelic, T. Z. Grubisic, I. Cepelak, and J. F. Gricic. High efficiency entrapment of superoxide dismutase into mucoadhesive chitosan-coated liposomes. European J. Pharm. Sci. 15:441–448 (2002).
X. Yanyu, S. Yunmei, C. Zhipeng, and P. Oineng. The preparation of silybin-phospholipid complex and the study on its pharmacokinetics in rats. Int. J. Pharm. 307:77–82 (2006).
B. Jayakar, and B. Suresh. Antihyperglycaemic and hypoglycaemic activity of Aporosa lindleyana in normal and alloxan induced diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmcol. 84:247–249 (2003).
M. Manickam, M. Ramanatham, M. A. Jahromi, J. P. N. Chonsouria, and A. B. Ray. Antihypoglycaemic activity of phenolics from Pterocarpus marsupium. J. Nat. Prod. 60:609–610 (1997).
F. Ahmad, P. Khalid, M. Chaubey, A. K. Rastogi, and J. R. Kidwai. Hypoglycaemic activity of Pterocarpus marsupium wood. J. Ethnopharmacol. 35:71–75 (1991).
J. A. Abdel, I. A. Abdel, and M. H. H. Al-Hakiem. Hypoglycaemic and antihyperglycemic effects of Trigonella foenum-graecum leaf in normal and allaxon induced diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 58:149–155 (1997).
R. Maurya, S. S. Handa, and R. Singh. 8-(C-beta-d-glucopyranosyl)-7,3′,4′-trihydroxyflavone, process of isolation thereof, pharmaceutical composition and method for the treatment of diabetes. US Patent 6777392. August 17, 2004.
A. D. Skoog, J. F. Holler, and A. T. Nieman. Principle of instrumental analysis. USA, Saunders college publishing, 1997.
R. Maurya, and R. B. Ray. Marsupsin, A new Benzofuranone from Pterocarpus marsupium Roxb. Heterocycles 19(11):2103–2106 (1982).
J. Mathew, and A. V. SubbaRao. Marsupol: A novel isoflavonoid glycol from Pterocarpus marsupium. Phytochemistry 21(7):1837–1838 (1982).
Indena Company. Phytosome a technical revolution in phytomedicine Website Available at: http://www.indena.com/pdf/ephytosome.pdf. Accessed January 7, 2006.
B. Gabetta, G. Pifferi, and E. Bombardelli. Complexes of flavanolignans with phospholipids, preparation thereof and associated pharmaceutical compositions. US Patent 4764508. August 16, 1988.
Silibinol Company, Pterocarpus marsupium, the source of Silbinolâ website available at: http://www.silbinol.com/precStudies.htm accessed may 20, 2007.
M. Manickam, M. Ramanatham, M. A. Jahromi, J. P. N. Chonsouria, and A. B. Ray. Antihyperglycaemic activity of phenolics from Pterocarpus marsupium. J. Nat. Prod. 60:609–610 (1997).
Acknowledgments
The authors are obliged to Dr. V. B. Gupta, Director B. R. Nahata college of Pharmacy for his valuable support during this research. Authors are also thankful to CDRI Lucknow and All India institute of medical sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi for support in analytical portion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sikarwar, M.S., Sharma, S., Jain, A.K. et al. Preparation, Characterization and Evaluation of Marsupsin–Phospholipid Complex. AAPS PharmSciTech 9, 129–137 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-007-9020-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-007-9020-x