Abstract
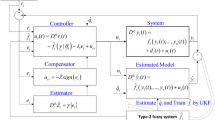
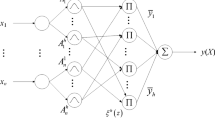
The rise of artificial intelligence has revolutionized all aspects of today's life. Neural networks, which are a stepping stone in the search for artificial intelligence, considerably affect the pace of advances in this field. Therefore, developing trustable tools for their modeling and control is of crucial importance. Motivated by this, we propose an intelligent controller for neural networks. Although the proposed approach is based on the sliding mode concept, it is chatter-free and provides smooth results. A type 2 fuzzy observer is applied to estimate the unknown function of the chaotic neural networks and enhance the performance of the proposed controller. This way, the proposed controller will act smartly in unseen conditions. The offered disturbance observer possesses an updating mechanism that modifies the type 2 fuzzy observer’s weights. Using the Lyapunov stability method, the analysis of stability is performed, and it is guaranteed that the proposed control scheme is asymptotically stable. Finally, the simulation results are presented to show the effectiveness of the offered method for the chaotic variable-order fractional neural networks under uncertainties and unknown external disturbances.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.J. Hopfield, Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational abilities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 79(8), 2554–2558 (1982)
L.O. Chua, L. Yang, Cellular neural networks: applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 35(10), 1273–1290 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1109/31.7601
M.A. Cohen, S. Grossberg, Absolute stability of global pattern formation and parallel memory storage by competitive neural networks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. SMC-13(5), 815–826 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.1983.6313075
H. Jahanshahi et al., Simulation and experimental validation of a non-equilibrium chaotic system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 143, 110539 (2021)
H. Jahanshahi et al., On the dynamical investigation and synchronization of variable-order fractional neural networks: the Hopfield-like neural network model. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-022-00450-8
B. Wang et al., Tracking control and stabilization of a fractional financial risk system using novel active finite-time fault-tolerant controls. Fractals 29(6), 2150155–2150177 (2021)
H. Jahanshahi, A. Yousefpour, Z. Wei, R. Alcaraz, S. Bekiros, A financial hyperchaotic system with coexisting attractors: dynamic investigation, entropy analysis, control and synchronization. Chaos Solitons Fractals 126, 66–77 (2019)
S. Soradi-Zeid, H. Jahanshahi, A. Yousefpour, S. Bekiros, King algorithm: a novel optimization approach based on variable-order fractional calculus with application in chaotic financial systems. Chaos Solitons Fractals 132, 109569 (2020)
B. Wang et al., Incorporating fast and intelligent control technique into ecology: a Chebyshev neural network-based terminal sliding mode approach for fractional chaotic ecological systems. Ecol. Complex. 47, 100943 (2021)
H. Wang, X.-J. Zhu, S.-W. Gao, Z.-Y. Chen, Singular observer approach for chaotic synchronization and private communication. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 16(3), 1517–1523 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2010.06.021
S. Vaidyanathan, Adaptive synchronization of novel 3-D chemical chaotic reactor systems. Parameters 1, 4 (2015)
H.D.I. Abarbanel, R. Brown, J.J. Sidorowich, LSh. Tsimring, The analysis of observed chaotic data in physical systems. Rev. Mod. Phys. 65(4), 1331–1392 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.65.1331
V. Sundarapandian, I. Pehlivan, Analysis, control, synchronization, and circuit design of a novel chaotic system. Math. Comput. Model. 55(7), 1904–1915 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcm.2011.11.048
A. El-Gohary, Chaos and optimal control of cancer self-remission and tumor system steady states. Chaos Solitons Fractals 37(5), 1305–1316 (2008)
C.R. Mirasso, P. Colet, P. Garcia-Fernandez, Synchronization of chaotic semiconductor lasers: application to encoded communications. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 8(2), 299–301 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1109/68.484273
H. Lin, C. Wang, Q. Deng, C. Xu, Z. Deng, C. Zhou, Review on chaotic dynamics of memristive neuron and neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 106(1), 959–973 (2021)
G. Maddodi, A. Awad, D. Awad, M. Awad, B. Lee, A new image encryption algorithm based on heterogeneous chaotic neural network generator and dna encoding. Multimed. Tools Appl. 77(19), 24701–24725 (2018)
K. Aihara, T. Takabe, M. Toyoda, Chaotic neural networks. Phys. Lett. A 144(6–7), 333–340 (1990)
L. Cui, C. Chen, J. Jin, F. Yu, Dynamic analysis and FPGA implementation of new chaotic neural network and optimization of traveling salesman problem. Complexity 2021, 5521192 (2021)
C.-J. Cheng, C.-B. Cheng, An asymmetric image cryptosystem based on the adaptive synchronization of an uncertain unified chaotic system and a cellular neural network. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 18(10), 2825–2837 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2013.02.011
D. Rickles, P. Hawe, A. Shiell, A simple guide to chaos and complexity. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 61(11), 933–937 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1136/jech.2006.054254
J. Kurths, S. Boccaletti, C. Grebogi, Y.-C. Lai, Introduction: control and synchronization in chaotic dynamical systems. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 13(1), 126–127 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1554606
J. Xiao, S. Zhong, S. Wen, Improved approach to the problem of the global Mittag–Leffler synchronization for fractional-order multidimension-valued BAM neural networks based on new inequalities. Neural Netw. 133, 87–100 (2021)
J. Xiao, Y. Li, S. Wen, Mittag–Leffler synchronization and stability analysis for neural networks in the fractional-order multi-dimension field. Knowl. Based Syst. 231, 107404 (2021)
Y. Liu, R. Tang, C. Zhou, Z. Xiang, X. Yang, Event-triggered leader-following consensus of multiple mechanical systems with switched dynamics. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 51(16), 3563–3572 (2020)
J. Xiao, J. Cheng, K. Shi, R. Zhang, A general approach to fixed-time synchronization problem for fractional-order multi-dimension-valued fuzzy neural networks based on memristor. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 30, 968–977 (2021)
A. Sharifi, A. Sharafian, Q. Ai, Adaptive MLP neural network controller for consensus tracking of multi-agent systems with application to synchronous generators. Expert Syst. Appl. 184, 115460 (2021)
J. Xiao, J. Cao, J. Cheng, S. Wen, R. Zhang, S. Zhong, Novel inequalities to global Mittag–Leffler synchronization and stability analysis of fractional-order quaternion-valued neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 32(8), 3700–3709 (2020)
A. Sharafian, V. Bagheri, W. Zhang, RBF neural network sliding mode consensus of multiagent systems with unknown dynamical model of leader-follower agents. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 16(2), 749–758 (2018)
A. Sharafian, A. Sharifi, W. Zhang, Different types of sliding mode controller for nonlinear fractional multi-agent system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 131, 109481 (2020)
H. Yatimi, E. Aroudam, Assessment and control of a photovoltaic energy storage system based on the robust sliding mode MPPT controller. Sol. Energy 139, 557–568 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2016.10.038
S. Mobayen, An LMI-based robust controller design using global nonlinear sliding surfaces and application to chaotic systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 79(2), 1075–1084 (2015)
A. Yousefpour, H. Jahanshahi, Fast disturbance-observer-based robust integral terminal sliding mode control of a hyperchaotic memristor oscillator. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 228(10), 2247–2268 (2019)
A. Yousefpour, A.H. Hosseinloo, M.R.H. Yazdi, A. Bahrami, Disturbance observer-based terminal sliding mode control for effective performance of a nonlinear vibration energy harvester. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 31(12), 1495–1510 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1177/1045389X20922903
S. Wang et al., Synchronization of a non-equilibrium four-dimensional chaotic system using a disturbance-observer-based adaptive terminal sliding mode control method. Entropy 22(3), 271 (2020)
M. Chen, W. Chen, Sliding mode control for a class of uncertain nonlinear system based on disturbance observer. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 24(1), 51–64 (2010)
A. Sharafian, R. Ghasemi, Fractional neural observer design for a class of nonlinear fractional chaotic systems. Neural Comput. Appl. 31(4), 1201–1213 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-3153-y
A. Mohammadzadeh, S. Ghaemi, O. Kaynak, S. Khanmohammadi, Observer-based method for synchronization of uncertain fractional order chaotic systems by the use of a general type-2 fuzzy system. Appl. Soft Comput. 49, 544–560 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2016.08.016
S.-S. Zhou et al., Discrete-time macroeconomic system: bifurcation analysis and synchronization using fuzzy-based activation feedback control. Chaos Solitons Fractals 142, 110378 (2021)
Y.-L. Wang, H. Jahanshahi, S. Bekiros, F. Bezzina, Y.-M. Chu, A.A. Aly, Deep recurrent neural networks with finite-time terminal sliding mode control for a chaotic fractional-order financial system with market confidence. Chaos Solitons Fractals 146, 110881 (2021)
S. Bekiros, H. Jahanshahi, F. Bezzina, A.A. Aly, A novel fuzzy mixed H2/H∞ optimal controller for hyperchaotic financial systems. Chaos Solitons Fractals 146, 110878 (2021)
Z. Liu et al., Fuzzy adaptive control technique for a new fractional-order supply chain system. Phys. Scr. 96(12), 124017 (2021)
H.-B. Bao, J.-D. Cao, Projective synchronization of fractional-order memristor-based neural networks. Neural Netw. 63, 1–9 (2015)
F. Jarad, T. Abdeljawad, D. Baleanu, Stability of q-fractional non-autonomous systems. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 14(1), 780–784 (2013)
C.T. Leondes, Fuzzy theory systems (Academic Press, Cambridge, 1999)
H.A. Hagras, A hierarchical type-2 fuzzy logic control architecture for autonomous mobile robots. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 12(4), 524–539 (2004)
Y. Li, Y. Chen, I. Podlubny, Stability of fractional-order nonlinear dynamic systems: Lyapunov direct method and generalized Mittag–Leffler stability. Comput. Math. Appl. 59(5), 1810–1821 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.camwa.2009.08.019
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yousefpour, A., Yasami, A., Beigi, A. et al. On the development of an intelligent controller for neural networks: a type 2 fuzzy and chatter-free approach for variable-order fractional cases. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 231, 2045–2057 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-022-00612-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-022-00612-8