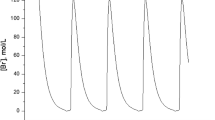
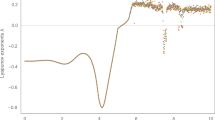
Abstract.
This paper presents an overview of some techniques and concepts coming from dynamical system theory and used for the analysis of dynamical neural networks models. In a first section, we describe the dynamics of the neuron, starting from the Hodgkin-Huxley description, which is somehow the canonical description for the “biological neuron”. We discuss some models reducing the Hodgkin-Huxley model to a two dimensional dynamical system, keeping one of the main feature of the neuron: its excitability. We present then examples of phase diagram and bifurcation analysis for the Hodgin-Huxley equations. Finally, we end this section by a dynamical system analysis for the nervous flux propagation along the axon. We then consider neuron couplings, with a brief description of synapses, synaptic plasticity and learning, in a second section. We also briefly discuss the delicate issue of causal action from one neuron to another when complex feedback effects and non linear dynamics are involved. The third section presents the limit of weak coupling and the use of normal forms technics to handle this situation. We consider then several examples of recurrent models with different type of synaptic interactions (symmetric, cooperative, random). We introduce various techniques coming from statistical physics and dynamical systems theory. A last section is devoted to a detailed example of recurrent model where we go in deep in the analysis of the dynamics and discuss the effect of learning on the neuron dynamics. We also present recent methods allowing the analysis of the non linear effects of the neural dynamics on signal propagation and causal action. An appendix, presenting the main notions of dynamical systems theory useful for the comprehension of the chapter, has been added for the convenience of the reader.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Abeles, Firing rates and well-timed events, in Models of Neural Networks II, edited by E. Domany, K. Schulten, J.L. van Hemmen (Springer, New York, 1994), Chap. 3
D. Amit, H. Gutfreund, H. Sompolinsky, Phys. Rev. A 32, 1007 (1985); D. Amit, H. Gutfreund, H. Sompolinsky, Phys. Rev. Lett. 55, 1530 (1985)
L.F. Abbott, S.B. Nelson, Nat. Neurosci. 3, 1178 (2000)
L.F. Abbott, T.B. Kepler, Model neurons: from Hodgkin–Huxley to Hopfield, in Statistical Mechanics of Neural Networks, edited by L. Garrido (Springer, Berlin, 1990)
L.F. Abbott, C. van Vreeswijk, Phys. Rev. E 48, 1483 (1993)
E.D. Adrian, J. Physiol. (Lond.) 61, 49 (1926)
E.D. Adrian, The Basis of Sensation (W.W. Norton, New York, 1928)
S. Amari, IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cyb. SMC-2, 5 (1972)
S. Amari, A Method of Statistical Neurodynamics (Kybernetik, 1974)
S. Amari, K. Yoshida, K. Kanatani, SIAM J. Appl. Math. 33, 95 (1977)
D.J. Amit, Modelling Brain Functions: The World of Attractor Neural Networks (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1989)
V. Arnold, Équations Différentielles Ordinaires (Éditions Mir, Moscou)
V. Arnold, Chapitre Supplémentaire de la Théorie des Équations Différentielles Ordinaires (Éditions Mir, Moscou)
V. Arnold, A. Avez, Problèmes Ergodiques de la Mécanique Classique (Gauthier-Vilars, 1967)
A. Babloyantz, C. Nicolis, J.M. Salazar, Phys. Lett. A 111, 152 (1985)
A. Babloyantz, A. Destexhe, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 3513 (1986)
A. Babloyantz, A. Destexhe, edited by M. Candill, C. Butler, Proc. IEEE. First Int. Conf. Neural Networks 4, 31 (1987)
A. Babloyantz, A. Destexhe, edited by M. Markus, S. Muller, G. Nicolis, Springer Ser. Synerg. 39, 307 (1988)
P. Bak, How Nature Works: The Science of Self-organized Criticality (Springer-Verlag, 1996; Oxford University Press, 1997)
Ph. Blanchard, B. Cessac, T. Krüger, J. Stat. Phys. 88, 307 (1997)
Ph. Blanchard, B. Cessac, T. Krüger, J. Stat. Phys. 98, 375 (2000)
D.H. Chialvo, P. Bak, Neuroscience 90, 1137 (1999)
H. Berry, M. Quoy, Structure and Dynamics of Random Recurrent Neural Networks, 2005 (submitted)
G.Q. Bi, M.M. Poo, J. Neurosci. 18, 10464 (1998)
G. Basti, A. Perrone, IEEE I, 657 (1989)
M. Benaim, Dynamiques d'activation et dynamiques d'apprentissage des réseaux de neurones, Thèse de doctorat, Toulouse (1992)
W. Bialek, F. Rieke, R.R. de Ruyter van Stevenick, D. Warland, Science 252, 1854 (1991)
K. Binder, A. Young, Rev. Mod. Phys. 58, 801 (1986)
L. Boltzmann, Lectures on Gas Theory (Dover, New York, 1995), Translation by S. Brush
A.J. Bray, M.A. Moore, J. Phys. C 13, L469 (1980)
A. Roxin, N. Brunel, D. Hansel, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2005 (in press)
Carr, Applications of Center Manifold Theory (Springer-Verlag, New-York; Heidelberg, Berlin, 1981)
See e.g. the web site http://elegans.swmed.edu/ and references therein
B. Cessac, B. Doyon, M. Quoy, M. Samuelides, Physica D 74, 24 (1994)
B. Cessac, J. Phys. A 27, L927 (1994)
B. Cessac, Europhys. Lett. 26, 577 (1994)
B. Cessac, Propriétés statistiques des dynamiques de réseaux neuromimétiques, Thèse Université Paul Sabatier, Toulouse, 1994
B. Cessac, J. Phys. I (France) 5, 409 (1995)
B. Cessac, Ph. Blanchard, T. Krüger, J.L. Meunier, J. Stat. Phys. 115, 1283 (2004)
B. Cessac, J.A. Sepulchre, Phys. Rev. E 70, 056111 (2004)
B. Cessac, J.A. Sepulchre, Chaos. 16, 013104 (2006)
B. Cessac, J.A. Sepulchre, Physica D, 2007 (to appear)
B. Cessac, Dynamical and topological effects of hebbian learning in a simple neural network model (in preparation)
B. Cessac, Some remarks about a discrete time neural network model with spiking neurons: Spontaneous dynamics (in preparation)
B. Cessac, Some remarks about a discrete time neural network model with spiking neurons: synaptic plasticiy and thermodynamic formalism (in preparation)
Carpenter (1977)
J.P. Changeux, S. Dehaene, Cognition 33, 63 (1989)
N. Chernov, R. Markarian, Am. Math. Soc. (2006)
D.R.J. Chillingworth, Differentiable Toplogy with a View to Applications (Pitman, London, 1976)
M.A. Cohen, S. Grossberg, IEEE Trans. Syst., Man Cybernet. SMC-13 (1983)
M. Cosnard, J. Demongeot, K. Lausberg, K. Lott, Attractors, Confiners, and Fractal Dimensions: Applications in Neuromodelling (Wuerz Publishing Ltd., 1993) in Math. Appl. Biol. Med.
A. Crisanti, H. Sompolinsky, Phys. Rev. A 36, 4922 (1987)
A. Crisanti, H.J. Sommers, H. Sompolinsky, Chaos in Neural Networks: Chaotic solutions, 1990 (preprint)
J. Cronin, Mathematical Aspects of Hodgkin–Huxley Theory (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1987)
O. David, K.J. Friston, NeuroImage 20, 1743 (2003)
E. Dauce, M. Quoy, B. Cessac, B. Doyon, M. Samuelides, Neural Netw. 11, 521 (1998)
E. Daucé, Adaptation dynamique et apprentissage dans des réseaux de neurones récurrents aléatoires, thèse troisième cycle (Toulouse, 2000)
A. Guillot, E. Daucé (Éds), Approche Dynamique de la Cognition Artificielle (Lavoisier, Paris, 2002)
A.M.O. De Almeida, D.J. Thouless, J. Phys. A 11, 983 (1978)
B. Doyon, B. Cessac, M. Quoy, M. Samuelides, Acta Biotheoretica. 42, 215 (1994)
S. Doi, S. Kumagai, Non linear dynamics of small scale biophysical neural networks, in Biophysical Neural Networks, edited by R.R. Poznanski (Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., Larchmont, NY, 2001), p. 261
Y. Dudai, The Neurobiology of Memory (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1989)
B. Doyon, B. Cessac, M. Quoy, M. Samuelides, Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 3, 279 (1993)
J.P. Eckmann, D. Ruelle, Rev. Mod. Phys. 57, 617 (1985)
R. Eckhorn, R. Bauer, W. Jordan, M. Brosch, W. Kruse, M. Munk, H.J. Reitboeck, Biol. Cybernet. 60, 121 (1988)
A. Edelman, The circular law and the probability that a random matrix has k real eigenvalues, 1 (1993)
A. Edwards, J. Phys. A 11, 983 (1978)
G.B. Ermentrout, N. Kopell, SIAM J. Math. Anal. 15, 215 (1984)
W.J. Freeman Biol. Cyber. 56 (1987) 139-150
W.J. Freeman, Y. Yao, B. Burke, Neural Netw. 1, 277-288 (1988)
R. FitzHugh, Biophys. J. 1, 445-466 (1961)
R.M. Fitzsimonds, H.J. Song, M.M. Poo, Nature 31 (1997); 388 (6641), 427-8
A. Bovier, V. Gayrard, J. Stat. Phys. 69, 597-627 (1993)
D. Gallez, A. Babloyantz, Biol. Cybern. 64, 381-392 (1991)
J.M. Gambaudo, C. Tresser, Transition vers le chaos pour des applications continues de degré un du cercle, in Le chaos, théorie et expériences, Collection CEA (1988)
S. Geman, Ann. Prob. 8, 252-261 (1980)
The Genesis simulator, http://www.genesis-sim.org/GENESIS/genesis.html
W. Gerstner, W.M. Kistler, Spiking Neuron Models. Single Neurons, Populations, Plasticity (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2002)
V.L. Girko, Theor. Prob. Appl. 29, 694-706 (1984)
J.-L. Gouzé, J. Biol. Syst. 6, 11–15 (1998)
C.M. Gray, W. Singer, Neurosci. Suppl. 1301P (1987)
C.M. Gray, P. Koenig, A.K. Engel, W. Singer, Nature 338, 334-337 (1989)
F. Grimbert, O. Faugeras, Neural Comput. (2006) to appear
J. Guckenheimer, P. Holmes, Non Linear Oscillations, Dynamical Systems, and Bifurcation of Vector Fields (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1983)
J. Guckenheimer, I.S. Labouriau, Bull. Math. Biol. 55, 937-952 (1993)
J. Guckenheimer, O. Ricardo, SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 1, 105-114 (2002)
J. Guckenheimer, P. Worfolk, Dynamical systems: Some computational problems, NATO ASI, Bifurcations and Periodic Orbits of Vector Fields, Conference Proceedings and http://arxiv.org/abs/chao-dyn/9304010' (1993)
B. Hassard, J. Theoret. Biol. 71, 401-420 (1978)
D.O. Hebb, The Organization of Behaviour (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1949)
B. Hille, Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes, 2nd edn. (Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Mass, 1992)
L.J. Graham, The Surf-Hippo Neuron Simulation System, http://www.neurophys.biomedicale.univ-paris5.fr/~graham/surf-hippo-files/Surf-Hippo.README.html
M.W. Hirsch Neural Networks 2, 331-349 (1989)
A.L. Hodgkin, A.F. Huxley, J. Physiol. (Lond.) 116, 449-472 (1952)
A.L. Hodgkin, A.F. Huxley, J. Physiol. (Lond.) 117, 500-544 (1952)
J.J. Hopfield, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79, 2554-2558 (1981)
J.J. Hopfield, Nature 376, 33-36 (1995)
J.J. Hopfield, Tank, Biol. Cybern. 52, 141-152 (1985)
F.C. Hoppensteadt, E.M. Izhikevich, Weakly Connected Neural Networks (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1997)
G. Iooss, A. Chenciner, ARMA 69, 109-198 (1979)
E.M. Izhikevich, Bifurcations in brain dynamics, Ph.D. thesis, Department of Mathematics, Michigan State University (1996)
J.J. Jack, D. Noble, R.W. Tsien, Electric current flow in excitable cells (Clarendon Press, Oxford 1975)
B.H. Jansen, G. Rit, Biol. Cybern. 73, 357-366 (1995)
A. Katok, B. Hasselblatt, Introduction to the Modern Theory of Dynamical Systems (Kluwer, 1998)
J. Keener, J. Sneyd, Mathematical Physiology, volume 8 of Interdisciplinary Applied Mathematics (Springer, New York, 1998)
T.B. Kepler, L.F. Abbott, E. Marder, Biol. Cybern. 66, 381-387 (1992)
S.R. Kelso, A.H. Ganong, T.H. Brown, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 5326-5330 (1986)
C. Koch, Biophysics of Computation (Oxford University Press, New York, 1999)
C. Koch, O. Bernander, R.J. Douglas, J. Comput. Neurosci. 2, 63-82 (1995)
J.P. Lasalle, J. Diff. Eq. 4, 57-65 (1968)
I.S. Labouriau, SIAM J., Math. Anal. 20, 1-12 (1989)
F.H. Lopes da Silva, A. van Rotterdam, P Barts, E. van Heusden, W. Burr, Model of neuronal populations, the basic mechanism of rhythmicity, in Progress in brain research, edited by M.A. Corner, D.F. Swaab (Elsevier, Amsterdam) 45, 281-308 (1976)
W.S. Mac Cullogh, W. Pitts, Bull. Math. Biophys. 5, 115-133 (1943)
R.S. MacKay, C. Tresser, Physica D 19, 206-237 (1986)
C.M. Marcus, R.M. Westrevelt, Phys. Rev. A 40, 501-504 (1989)
J.E. Marsden, M. Mac Craken, in The Hopf Bifurcation and Its Applications (Springer-Verlag, New York; Heidelberg, Berlin, 1976)
M.V. Mascagni, A.S. Sherman, Numerical methods for neuronal modeling, in edited by Methods in Neuronal Modeling Christof Koch Idan Segev (MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1998)
M. Mézard, G. Parisi, M.A. Virasoro, Spin-glass Theory and Beyond (Singapore World Scientific, 1987)
J. Milnor, Com. Math. Phys. 99, 177 (1985)
L. Molgedey, J. Schuchardt, H.G. Schuster, Phys. Rev. Let. 69, 3717-3719 (1992)
C. Morris, H. Lecar, Biophys. J. 35, 193-213 (1981)
E.F. Mishchenko, N.Kh. Rozov, Differential Equations with Small Parameters and Relaxation Oscillations, Translated from Russian by F.M.C. Goodspeed (Plenum, New York, 1980)
J.S. Nagumo, S. Arimoto, S. Yoshizawa, Proc. IRE 50, 2061-2070 (1962)
M. Nelson, Rinzel, J. The Hodgkin-Huxley model, in The Book of Genesis, edited by J.M. Bower, Beeman, Chap. 4 (Springer, New York, 1995), pp. 27-51
G. Parisi, J. Phys. A. 19, L675-680 (1988)
H. Poincaré, Oeuvres complètes, Jacques Gabay
M.W. Oram, M.C. Wiener, R. Lestienne, B.J. Richmond, J. Neurophysiol. 81, 3021-3033 (1999)
M. Pollicott, Invent. Math. 81, 413-426 (1985); D. Ruelle, J. Diff. Geom. 25, 99-116 (1987)
F. Rieke, D. Warland, R. de Ruyter van Steveninck, W. Bialek, Spikes – Exploring the Neural Code (MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1996)
J. Rinzel, Excitation dynamics: insights from simplified membrane models. Federation Proc. 44, 2944-2946 (1985)
J. Rinzel, G.B. Ermentrout, Analysis of neuronal excitability and oscillations, Methods in Neuronal Modeling, edited by C. Koch, I. Segev (MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1989)
J. Rinzel, R. Miller, Math. Biosci. 49, 22-59 (1980)
D. Ruelle, Elements of Differentiable Dynamics and Bifurcation Theory (Academic Press, 1989)
D. Ruelle, F. Takens, Commun. Math. Phys. 20, 167-192 (1971)
D. Ruelle, J. Stat. Phys. 95, 393-468 (1999)
M. Samuelides, B. Doyon, B. Cessac, M. Quoy, Math. of Neural Networks, 312-317 (1996)
O. Moynot, M. Samuelides, Probab. Theory Relat. Fields 123, 41-75 (2002)
M. Quoy, Apprentissage dans les réseaux neuromimétiques à dynamique de base chaotique, Thèse ENSAE, Toulouse, 1994
M. Quoy, B. Doyon, M. Samuelides, Hebbian Learning in Discrete Time Chaotic Neural Networks (WCNN, Washington DC, 1995)
M. Quoy, E. Daucé, Visual and motor learning using a chaotic recurrent neural network: application to the control of a mobile robot, in Neural Computation (Berlin, 2000)
E. Daucé, M. Quoy, Random Recurrent Neural Networks for Autonomous System Design (SAB Paris, France, 2000)
E. Daucé, M. Quoy, B. Doyon, Biol. Cybern. 87, 185-198 (2002)
C.A. Skarda, W.J. Freeman, Behav. Brain Sci. 10, 161-195 (1987)
M.N. Shadlen, W.T. Newsome, Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 4, 569-579 (1994)
D. Sherrington, An introduction and overview is given of the theory of spin glasses and its application, cond-mat/9806289 (1998)
C. Soulé, ComPlexUs, 1, 123-133 (2003)
Ya.G. Sinai, Russ. Math. Surveys, 27, 21-69 (1972); D. Ruelle, Thermodynamic formalism (Addison-Wesley Reading, Massachusetts, 1978); R. Bowen, Lect. Notes. Math. 470 (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1975)
D. Sherrington, S. Kirkpatrick, Phys. Rev. Let. 35, 1792 (1975)
S. Smale J. Math. Biol. 3, 5-7 (1976)
H.L. Smith, SIAM Rev. 30, 87-113 (1988)
W.R. Softky, Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 5, 239-247 (1995)
H. Sompolinsky, A. Crisanti, H.J. Sommers, Phys. Rev. Lett. 61, 259-262 (1988)
R. Thomas, On the relation between the logical structure of systems and their ability to generate multiple steady states or sustained oscillations, in Numerical Methods in the Study of Critical Phenomena, of Springer-Verlag in Synergetics 9, 180-193 (1981)
D.J. Thouless, P.W. Anderson, R.J. Palmer, Philos. Mag. 35, 593-601 (1977)
S. Thorpe, D. Fize, C. Marlot, Nature 381, 520-522 (1996)
M. Viana, Stochastic dynamics of deterministic systems
G. Boffeta, G. Lacorata, S. Musacchio, A. Vulpiani, Chaos, 13, 806 (2003) and references therein
R.F. Williams, Publ. Math. IHES 43, 169 (1974)
M. Yoshioka, Chaos synchronization in gap-junction-coupled neurons, ArXiv nlin.CD/0505054 (2005)
M. Samuelides, B. Cessac, Eur. Phys. J. Special Topics 142, 89-122 (2007)
L. Perrinet, Eur. Phys. J. Special Topics 142, 163-225 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cessac, B., Samuelides, M. From neuron to neural networks dynamics. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 142, 7–88 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2007-00058-2
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2007-00058-2