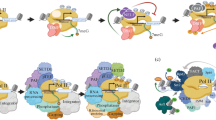
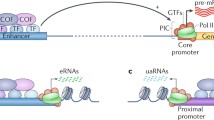
Abstract
Sequence-specific (regulatory) transcription factors are the proteins that recognize certain DNA sequences. They selectively regulate transcription levels of different sets of genes depending on the ontogeny stage, cell type, and external conditions. According to the established opinion, these proteins control the process of transcription at the stage of the RNA Pol II preinitiation complex assembly. However, according to the growing body of evidence, regulatory transcription factors can be also involved in the control of transcription elongation. This review focuses on systematization of such data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barboric, M., Nissen, R.M., Kanazawa, S., et al., NF-kappaB binds P-TEFb to stimulate transcriptional elongation by RNA polymerase II, Mol. Cell, 2001, vol. 8, pp. 327–337.
Bender, T.P., Thompson, C.B., and Kuehl, W.M., Differential expression of c-myb mRNA in murine B lymphomas by a block to transcription elongation, Science, 1987, vol. 237, pp. 1473–1476.
Bottardi, S., Zmiri, F.A., Bourgoin, V., et al., Ikaros interacts with P-TEFb and cooperates with GATA-1 to enhance transcription elongation, Nucleic Acids Res., 2011, vol. 39, pp. 3505–3519.
Buganim, Y., Faddah, D.A., and Jaenisch, R., Mechanisms and models of somatic cell reprogramming, Nat. Rev. Genet., 2013, vol. 14, pp. 427–439.
Charoensawan, V., Wilson, D., and Teichmann, S.A., Genomic repertoires of DNA-binding transcription factors across the tree of life, Nucleic Acids Res., 2010, vol. 38, pp. 7364–7377.
Chen, Y., Yamaguchi, Y., Tsugeno, Y., et al., DSIF, the Paf1 complex, and Tat-SF1 have nonredundant, cooperative roles in RNA polymerase II elongation, Genes Dev., 2009, vol. 23, pp. 2765–2777.
DeLaForest, A., Nagaoka, M. Si-Tayeb, K., et al., HNF4A is essential for specification of hepatic progenitors from human pluripotent stem cells, Development, 2011, vol. 138, pp. 4143–4153.
Dey, A., Chao, S.H., and Lane, D.P., HEXIM1 and the control of transcription elongation: from cancer and inflammation to AIDS and cardiac hypertrophy, Cell Cycle, 2007, vol. 6, pp. 1856–1863.
Diamant, G. and Dikstein, R., Transcriptional control by NF-κB: elongation in focus, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2013, vol. 1829, pp. 937–945.
Eberhardy, S.R. and Farnham, P.J., c-Myc mediates activation of the cad promoter via a post-RNA polymerase II recruitment mechanism, J. Biol. Chem., 2001, vol. 276, pp. 48562–48571.
Eberhardy, S.R. and Farnham, P.J., Myc recruits P-TEFb to mediate the final step in the transcriptional activation of the cad promoter, J. Biol. Chem., 2002, vol. 277, pp. 40156–40162.
Egloff, S., Szczepaniak, S.A., Dienstbier, M., et al., The integrator complex recognizes a new double mark on the RNA polymerase II carboxyl-terminal domain, J. Biol. Chem., 2010, vol. 285, pp. 20564–20569.
Fuda, N.J., Ardehali, M.B., and Lis, J.T., Defining mechanisms that regulate RNA polymerase II transcription in vivo, Nature, 2009, vol. 461, pp. 186–192.
Fuda, N.J. and Lis, J.T., A new player in Pol II pausing, EMBO J., 2013, vol. 32, pp. 1796–1808.
Glover-Cutter, K., Kim, S., Espinosa, J., and Bentley, D.L., RNA polymerase II pauses and associates with pre-mRNA processing factors at both ends of genes, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol, 2008, vol. 15, pp. 71–78.
Guenther, M.G., Levine, S.S., Boyer, L.A., et al., A chromatin landmark and transcription initiation at most promoters in human cells, Cell, 2007, vol. 130, pp. 77–88.
Guertin, M.J. and Lis, J.T., Chromatin landscape dictates HSF binding to target DNA elements, PLoS Genet., 2010, vol. 6, p. e1001114.
Hochheimer, A. and Tjian, R., Diversified transcription initiation complexes expand promoter selectivity and tissue-specific gene expression, Genes Dev., 2003, vol. 17, pp. 1309–1320.
Jiang, H., Zhang, F., Kurosu, T., and Peterlin, B.M., Runx1 binds positive transcription elongation factor b and represses transcriptional elongation by RNA polymerase II: possible mechanism of CD4 silencing, Mol. Cell. Biol., 2005, vol. 25, pp. 10675–10683.
Juven-Gershon, T. and Kadonaga, J.T., Regulation of gene expression via the core promoter and the basal transcriptional machinery, Dev. Biol., 2010, vol. 339, pp. 225–229.
Keys, J.R., Tallack, M.R., Zhan, Y., et al., A mechanism for Ikaros regulation of human globin gene switching, Br. J. Haematol., 2008, vol. 141, pp. 398–406.
Kim, S.I., Bultman, S.J., and Kiefer, C.M., BRG1 requirement for long-range interaction of a locus control region with a downstream promoter, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2009, vol. 106, pp. 2259–2264.
Kwak, H., Fuda, N.J., Core, L.J., and Lis, J.T., Precise maps of RNA polymerase reveal how promoters direct initiation and pausing, Science, 2013, vol. 339, pp. 950–953.
Lee, D.K., Duan, H.O., and Chang, C., Androgen receptor interacts with the positive elongation factor P-TEFb and enhances the efficiency of transcriptional elongation, J. Biol. Chem., 2001, vol. 27, pp. 9978–9984.
Lenasi, T. and Barboric, M., P-TEFb stimulates transcription elongation and pre-mRNA splicing through multilateral mechanisms, RNA Biol., 2010, vol. 7, pp. 145–150.
Lis, J.T., Mason, P., Peng, J., et al., P-TEFb kinase recruitment and function at heat shock loci, Genes Dev., 2000, vol. 14, pp. 792–803.
Lüscher, B. and Vervoorts, J., Regulation of gene transcription by the oncoprotein MYC, Gene, 2012, vol. 494, pp. 145–160.
Mahajan, M.C., Karmakar, S., and Weissman, S., Control of beta globin genes, J. Cell Biochem., 2007, vol. 102, pp. 801–810.
Mandal, S.S., Chu, C., Wada, T., et al., Functional interactions of RNA-capping enzyme with factors that positively and negatively regulate promoter escape by RNA polymerase II, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2004, vol. 101, pp. 7572–7577.
Markova, E.N., Petrova, N.V., Razin, S.V., and Kantidze, O.L., Transcription factor RUNX1, Mol. Biol. (Moscow), 2012, vol. 46, no. 6, pp. 755–767.
Merkulova, T.I., Anan’ko, E.A., Ignat’eva, E.V., and Kolchanov, N.A., Transcription regulatory codes of eukaryotic genomes, Russ. J. Genet., 2013, vol. 49, no. 1, pp. 29–45.
Miltenberger, R.J., Sukow, K.A., and Farnham, P.J., An E-box-mediated increase in cad transcription at the G1/S-phase boundary is suppressed by inhibitory c-Myc mutants, Mol. Cell. Biol., 1995, vol. 15, pp. 2527–2535.
Min, I.M., Waterfall, J.J., Core, L.J., et al., Regulating RNA polymerase pausing and transcription elongation in embryonic stem cells, Genes Dev., 2011, vol. 25, pp. 742–754.
Mitra, P., Pereira, L.A., Drabsch, Y., et al., Estrogen receptor-αrecruits P-TEFb to overcome transcriptional pausing in intron 1 of the MYB gene, Nucleic Acids Res., 2012, vol. 40, pp. 5988–6000.
Nechaev, S. and Adelman, K., Pol II waiting in the starting gates: Regulating the transition from transcription initiation into productive elongation, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2011, vol. 1809, pp. 34–45.
Nissen, R.M. and Yamamoto, K.R., The glucocorticoid receptor inhibits NFkappaB by interfering with serine-2 phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II carboxyterminal domain, Genes Dev., 2000, vol. 14, pp. 2314–2329.
Nowak, D.E., Tian, B., Jamaluddin, M., et al., RelA Ser276 phosphorylation is required for activation of a subset of NF-kappaB-dependent genes by recruiting cyclin-dependent kinase 9/cyclin T1 complexes, Mol. Cell. Biol., 2008, vol. 28, pp. 3623–3638.
Osmanbeyoglu, H.U., Lu, K.N., Oesterreich, S., et al., Estrogen represses gene expression through reconfiguring chromatin structures, Nucleic Acids Res., 2013, vol. 41, pp. 8061–8071.
Oven, I., Brdickova, N., Kohoutek, J., et al., AIRE recruits P-TEFb for transcriptional elongation of target genes in medullary thymic epithelial cells, Mol. Cell. Biol., 2007, vol. 27, pp. 8815–8823.
Peterlin, B.M. and Price, D.H., Controlling the elongation phase of transcription with P-TEFb, Mol. Cell, 2006, vol. 23, pp. 297–305.
Poss, Z.C., Ebmeier, C.C., and Taatjes, D.J., The mediator complex and transcription regulation, Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol., 2013.
Rahl, P.B., Lin, C.Y., Seila, A.C., et al., C-myc regulates transcriptional pause release, Cell, 2010, vol. 141, pp. 432–445.
Roeder, R.G., Transcriptional regulation and the role of diverse coactivators in animal cells, FEBS Lett., 2005, vol. 579, pp. 909–915.
Saunders, A., Core, L.J., Sutcliffe, C., et al., Extensive polymerase pausing during Drosophila axis patterning enables high-level and pliable transcription, Genes Dev., 2013, vol. 27, pp. 1146–1158.
Sawada, S., Scarborough, J.D., Killeen, N., and Littman, D.R., A lineage-specific transcriptional silencer regulates CD4 gene expression during T lymphocyte development, Cell, 1994, vol. 77, pp. 917–929.
Sharma, M., George, A.A., Singh, B.N., et al., Regulation of transcript elongation through cooperative and ordered recruitment of cofactors, J. Biol. Chem., 2007, vol. 282, pp. 20887–20896.
Takahashi, K. and Yamanaka, S., Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors, Cell, 2006, vol. 126, pp. 663–676.
Taniuchi, I., Osato, M., Egawa, T., et al., Differential requirements for Runx proteins in CD4 repression and epigenetic silencing during T lymphocyte development, Cell, 2002, vol. 111, pp. 621–633.
Taube, R., Lin, X., Irwin, D., et al., Interaction between P-TEFb and the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase ii activates transcriptional elongation from sites upstream or downstream of target genes, Mol. Cell Biol., 2002, vol. 22, pp. 321–331.
Thompson, M.A., Flegg, R., Westin, E.H., and Ramsay, R.G., Microsatellite deletions in the c-myb transcriptional attenuator region associated with over-expression in colon tumour cell lines, Oncogene, 1997, vol. 14, pp. 1715–1723.
Trotter, K.W. and Archer, T.K., The BRG1 transcriptional coregulator, Nucl. Recept. Signal, 2008, vol. 6, p. e004.
Vaquerizas, J.M., Kummerfeld, S.K., Teichmann, S.A., and Luscombe, N.M., A census of human transcription factors: function, expression and evolution, Nat. Rev. Genet., 2009, vol. 10, pp. 252–263.
Watson, R.J., A transcriptional arrest mechanism involved in controlling constitutive levels of mouse c-myc mRNA, Oncogene, 1988, vol. 2, pp. 267–272.
Wernig, M., Meissner, A., Foreman, R., et al., In vitro reprogramming of fibroblasts into a pluripotent ES-cell-like state, Nature, 2007, vol. 448, pp. 318–324.
White, U.A. and Stephens, J.M., Transcriptional factors that promote formation of white adipose tissue, Mol. Cell. Endocrinol., 2010, vol. 318, pp. 10–14.
Wittmann, B.M., Fujinaga, K., Deng, H., Ogba, N., and Montano, M.M., The breast cell growth inhibitor, estrogen down regulated gene 1, modulates a novel functional interaction between estrogen receptor alpha and transcriptional elongation factor cyclin T1, Oncogene, 2005, vol. 24, pp. 5576–5588.
Yamaguchi, Y., Shibata, H., and Handa, H., Transcription elongation factors DSIF and NELF: promoter-proximal pausing and beyond, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2013, vol. 1829, pp. 98–104.
Zhang, H.M., Chen, H., Liu, W., et al., Animal TFDB: a comprehensive animal transcription factor database, Nucleic Acids Res., 2012, vol. 40, pp. D144–D149.
Zhang, D. and Glass, C., Towards an under standing of cell-specific functions of signal-dependent transcription factors, J. Mol. Endocrinol., 2013.
Zhong, H., Voll, R.E., and Ghosh, S Phosphorylation of NF-kappa B p65 by PKA stimulates transcriptional activity by promoting a novel bivalent interaction with the coactivator CBP/p300, Mol. Cell, 1998, vol. 1, pp. 661–671.
Zumer, K., Saksela, K., and Peterlin, B.M., The mechanism of tissue-restricted antigen gene expression by AIRE, J. Immunol., 2013, vol. 190, pp. 2479–2482.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.M. Merkulov, T.I. Merkulova, 2014, published in Vavilovskii Zhurnal Genetiki i Selektsii, 2014, Vol. 18, No. 2, pp. 329–337.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Merkulov, V.M., Merkulova, T.I. Regulatory transcription factors can control the process of transcription at the stage of pre-mRNA elongation. Russ J Genet Appl Res 4, 549–555 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079059714060124
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079059714060124