Abstract
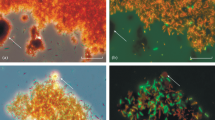
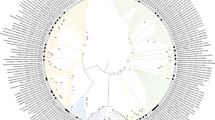
The genetic diversity of microbial communities that developed naturally within the system of ore heap–solution of heap leaching process has been studied. The difference in the microbial community structure is identified. It is found that phylotypes Serratia and Achromobacter dominated within the ore heap and Hydrogenophaga and Acinetobacter dominated in the solution. Phylogenetic analyses revealed that there are microorganisms among the closest homologues that are able to destruct toxic compounds and/or exhibit their enzyme activity at low temperature. It is shown that aerobic organoheterotrophs are the most promising for the isolation from autochthonous microbial communities of technogenic complexes in East Siberia, as well for studying their destructive potential and use in bioremediation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajithkumar, B., Ajithkumar, V.P., Iriye, R., Doi, Y., and Sakai, T., Spore-forming Serratia marcescens subsp. sakuensis subsp. nov., isolated from a domestic wastewater treatment tank, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2003, vol. 53, pp. 253–258.
Baxter, J. and Cummings, S.P., The current and future applications of microorganism in the bioremediation of cyanide contamination, Anton Leeuw Int. J., 2006, no. 1, pp. 1–17.
Belkova, N.L. and Andreeva, A.M., Vvedenie v molekulyarnuyu ekologiyu mikroorganizamov (The Introduction into Molecular Ecology of Microorganisms), Yaroslavl: Printkhaus, 2009.
Belykh, M.P., Petrov, S.V., Chikin, A.Yu., Stoyanov, I.N., and Belkova, N.L., Autochtonous microbial communities from gold-bearing ores heap leaching wastes: the way to solve the problem on environmental pollution, Izv. Isrkutsk. Gos. Univ., Ser.: Biol. Ekol., 2014, vol. 9, pp. 55–67.
Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology. The Proteobacteria, Brenner, D.J. and Krieg, N.R., Eds., New York: Springer-Verlag, 2005, vol. 2.
Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology. The Firmicutes, Vos, P., Garrity, G., Jones, D., Krieg, N.R., Ludwig, W., Eds., New York: Springer-Verlag, 2009, vol. 3.
Brodie, E.L., DeSantis, T.Z., Joyner, D.C., Baek, S.M., Larsen, J.T., Andersen, G.L., Hazen, T.C., Richardson, P.M., Herman, D.J., Tokunaga, T.K., Wan, J.M., and Firestone, M.K., Application of a high-density oligonucleotide microarray approach to study bacterial population dynamics during uranium reduction and reoxidation, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2006, vol. 72, no. 9, pp. 6288–6298.
Collins, M.D., Lund, B.M., Farrow, J.A.E., and Schleiref, K.H., Chemotaxonomic study of an alkalophilic bacterium, Exiguobacterium aurantiacum gen. nov., sp. nov., J. Gen. Microbiol., 1983, vol. 129, pp. 2037–2042.
Grigor’eva, N.V., Smirnova, Yu.V., Terekhova, S.V., and Karavaiko, G.I., Isolation of an aboriginal bacterial community capable of utilizing cyanide, thiocyanate, and ammonia from metallurgical plant wastewater, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2008, vol. 44, no. 5, pp. 502–506.
Harris, R. and Knowles, C.J., Isolation and growth of a Pseudomonas species that utilizes cyanide as a source of nitrogen, J. Gen. Microbiol., 1983, vol. 129, pp. 1005–1011.
Ji, L.Y., Zhang, W.W., Yu, D., Cao, Y.R., and Xu, H., Effect of heavy metal-solubilizing microorganisms on zinc and cadmium extractions from heavy metal contaminated soil with Tricholoma lobynsis, World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2012, vol. 28, no. 1, pp. 293–301.
Kumar, V., Kumar, V., and Bhalla, T.C., In vitro cyanide degradation by Serretia marcescens RL2b, Int. J. Environ. Sci., 2013, vol. 3, no. 6, pp. 1969–1979.
Maniyam, M.N., Sjahrir, F., and Ibrahim, A.L., Bioremediation of cyanide by optimized resting cells of Rhodococcus strains isolated from Peninsular Malaysia, Int. J. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., 2011, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 98–101.
Mirizadeh, S., Yaghmaei, S., and Ghobadi Nejad, Z., Biodegradation of cyanide by a new isolated strain under alkaline conditions and optimization by response surface methodology (RSM), J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng., 2014, vol. 12, no. 85, pp. 1–9.
Nekrasov, B.V., Osnovy obshchei khimii (Fundamentals of General Chemistry), Nekrasov, B.V., Ed., Moscow: Khimiya, 1973, vol. 2.
Nishimura, Y., Ino, T., and Iizuka, H., Acinetobacter radioresistens sp. nov. isolated from cotton and soil, Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol., 1988, vol. 38, pp. 209–211.
Perumal, M., Prabakaran, J.J., and Kamaraj, M., Isolation and characterization of potential cyanide degrading Bacillus nealsonii from different industrial effluents, Int. J. Chem. Tech. Res., 2013, vol. 5, no. 5, pp. 2357–2364.
Petrova, S., Andronov, E., Pinaev, A., and Pershina, E., The prospective use of molecular and genetic analyses in soil ecology, Vestn. Orlovsk. Gos. Agrar. Univ., 2010, vol. 26, no. 5, pp. 45–48.
Pinevich, A.V., Mikrobiologiya. Biologiya prokariotov (Microbiology. Biology of Prokaryotes), Pinevich, A.V., Eds., St. Petersburg: S.-Peterb. Gos. Univ., 2006, vol. 1.
Spring, S., Wagner, M., Schumann, P., and Kämpfer, P., Malikia granosa gen. nov.,sp. nov.,a novel polyhydroxyalkanoate- and polyphosphate-accumulating bacterium isolated from activated sludge, and reclassification of Pseudomonas spinosa as Malikia spinosa comb. nov., Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 55, pp. 621–629.
Thomassin-Lacroix, E.J., Yu, Z., Eriksson, M., Reimer, K.J., and Mohn, W.W., DNA-based and culture- based characterization of a hydrocarbon-degrading consortium enriched from Arctic soil, Can. J. Microbiol., 2001, vol. 47, no. 12, pp. 1107–1115.
Vandammea, P., Moore, E. R.B., Cnockaert, M., Peeters, Ch., Svensson-Stadler, L., Houf, K., Spilker, T., and LiPuma, J.J., Classification of Achromobacter genogroups 2,5,7 and 14 as Achromobacter insuavis sp. nov.,Achromobacter aegrifaciens sp. nov.,Achromobacter anxifer sp. nov. and Achromobacter dolens sp. nov.,respectively, Syst. Appl. Microbiol., 2013, vol. 36, no. 7, pp. 474–482.
Willems, A., Busse, J., Goor, M., Pot, B., Falsen, E., Jantzen, E., Hoste, B., Gillis, M., Kersters, K., Auling, G., and Ley, Y J.D., Hydrogenophaga, a new genus of hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria that includes Hydrogenophaga flava comb. nov. (formerly Pseudomonas flava), Hydrogenophaga palleronii (formerly Pseudomonas palleronii), Hydrogenophaga pseudoflava (formerly Pseudomonas pseudoflava and “Pseudomonas carboxydoflava”), and Hydrogenophaga taeniospiralis (formerly Pseudomonas taeniospiralis), Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 1989, vol. 39, no. 3, pp. 319–333.
Wood, A.P., Kelly, D.P., McDonald, I.R., Jordan, S.L., Morgan, T.D., Khan, S., Murrell, J.C., and Borodina, E., A novel pink-pigmented facultative methylotroph, Methylobacterium thiocyanatum sp. nov., capable of growth on thiocyanate or cyanate as sole nitrogen sources, Arch. Microbiol., 1998, vol. 169, no. 2, pp. 148–158.
Yoon, J.H., Kang, S.J., Ryu, S.H., Jeon, Ch. O., and Oh, T.K., Hydrogenophaga bisanensis sp. nov., isolated from wastewater of a textile dye works, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2008, vol. 58, pp. 393–397.
Zhang, C., Jia, L., Wang, S., Qu, J., Li, K., Xu, L., Shi, Y., and Yan, Y., Biodegradation of beta-cypermethrin by two Serratia spp. with different cell surface hydrophobicity, Bioresour. Technol., 2010, vol. 101, no. 10, pp. 3423–3429.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © M.P. Belykh, S.V. Petrov, A.Ju. Chikin, N.L. Belkova, 2016, published in Sibirskii Ekologicheskii Zhurnal, 2016, No. 5, pp. 684–696.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belykh, M.P., Petrov, S.V., Chikin, A.J. et al. Genetic diversity of bacteria adapted to cyanide-bearing compounds in the technogenic ecosystems as detected by 16S rDNA sequences. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 9, 563–573 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995425516050012
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995425516050012