Abstract
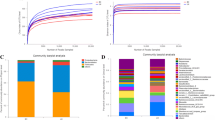
Thirty microbial phylotypes of microorganisms were found in the gastrointestinal tract of chicken belonging to the Hajseks White breed, and 38 phylotypes were found in the gastrointestinal tract of chicken belonging to the Hajseks Brown breed. The microbiome of the gastrointestinal tract of the chicken embryos of the Hajseks White breed was dominated by the typical representatives of avian intestinal microflora—bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae (47.3%), orders Actinomycetales (13.6%) and Bifidobacteriales (20.6%), and the family Lachnospiraceae (1.1%). The microbiome of the gastrointestinal tract of the chicken embryos of the Hajseks Brown breed was dominated by the pathogenic bacteria of the order Rickettsiales (94.8%). The metagenome of gastrointestinal tract of both breeds also contained a small number of genes of unidentified bacteria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Timoshko, M.A., Mikroflora pishchevaritel’nogo trakta sel’skokhozyaistvennykh zhivotnykh (The Microflora of the Digestive Tract of Farm Animals), Chisinau: Shtiintsa, 1990.
Van der Wielen, P.W.J.J., Keuzenkamp, D.A., Lipman, L.J.A., van Knapen, F., and Biesterveld, S., Spatial and temporal variation of the intestinal bacterial community in commercially raised broiler chickens during growth, Microbiol. Ecol., 2002, vol. 44, pp. 286–293.
Maiorka, A., Dahlke, F., and de Azevedo Morgulis, M.S.F., Broiler adaptation to post-hatching period, Ciencia Rural, 2006, vol. 36, pp. 701–708.
Mead, G.C., Microbes of the avian cecum: Types present and substrates utilized, J. Exp. Zool. Suppl., 1989, vol. 3, pp. 48–54.
Amit-Romach, E., Sklan, D., and Uni, Z., Microflora ecology of the chicken intestine using 16s ribosomal DNA primers, Poult. Sci., 2004, vol. 83, pp. 1093–1098.
Dibner, J.J., Richards, J.D., and Knight, C.D., Microbial imprinting in gut development and health, J. Appl. Poult. Res., 2008, vol. 17, pp. 174–188.
Kizerwetter-Swid, M. and Binek, M., Bacterial microflora of the chicken embryos and newly hatched chicken, J. Animal Feed Sci., 2008, vol. 17, pp. 224–232.
Babaca, Z., Isolation of bacterial pathogens from deadin-shell chicken embryos from local hatcheries, J. Veterinar. Sci. Technol., 2014, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 170–171.
Rossi, D.A., Fonseca, B.B., de Melo, R.T., Silva Felipe, G., Silva, P.L., Mendonca, E.P., Filgueiras, A.L., and Beletti, M.E., Transmission of campylobacter coli in chicken embryos, Brazil. J. Microbiol., 2012, vol. 43, no. 2, pp. 535–543.
Amann, R.I., Ludwig, W., and Schleifer, K.H., Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation, Microbiol. Rev., 1995, vol. 59, pp. 143–169.
Instruktsiya po sanitarno-mikrobiologicheskomu kontrolyu tushek, myasa ptitsy, ptitseproduktov, yaits i yaitseproduktov na ptitsevodcheskikh i pererabatyvayushchikh predpriyatiyakh (Instruction for the Sanitary-Microbiological Control of Carcasses, Poultry Meat, Poultry Products, Eggs, and Egg Products at Poultry Processing Plants), Moscow, approved by Goskomprod of USSR August 30, 1990.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F., and Maniatis, T., Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, Cold Spring Harbor, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press, 1989.
Nakphaichit, M., Thanomwongwattana, S., Phraephaisarn, C., Sakamoto, N., Keawsompong, S., Nakayama, J., and Nitisinprasert, S., The effect of including Lactobacillus reuteri KUB-AC5 during posthatch feeding on the growth and ileum microbiota of broiler chickens, Poult. Sci., 2011, vol. 12, no. 90, pp. 2753–2765.
Lowder, B.V. and Fitzgerald, J.R., Human origin for avian pathogenic Ataphylococcus aureus, Virulence, 2010, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 283–284.
Biberstein, E.L. and Hirsh, D.C., Bordetella in Veterinary Microbiology, Oxford, Reino Unido: Blackwell Sci., 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © L.A. Ilina, E.A. Yildirim, I.N. Nikonov, V.A. Filippova, G.Y. Laptev, N.I. Novikova, A.A. Grozina, T.N. Lenkova, V.A. Manukyan, I.A. Egorov, V.I. Fisinin, 2016, published in Doklady Akademii Nauk, 2016, Vol. 466, No. 4, pp. 482–486.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ilina, L.A., Yildirim, E.A., Nikonov, I.N. et al. Metagenomic bacterial community profiles of chicken embryo gastrointestinal tract by using T-RFLP analysis. Dokl Biochem Biophys 466, 47–51 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1607672916010130
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1607672916010130