Abstract
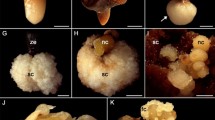
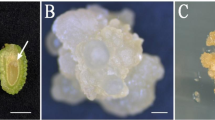
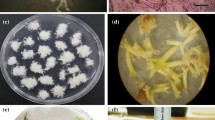
Zygotic embryos and megagametophytes of Pinus pumila for cultivation in vitro were transferred in 1/2 LV medium supplemented with growth regulators 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) and benzylaminopurine (6-BAP) to induce somatic embryogenesis. Four stably proliferating cell lines from two genotypes were derived. The cell lines differed in the number of globular somatic embryos and the weight of embryogenic calli. Cells of these lines were multiplied as a result of somatic polyembryogenesis via cleavage. In the nutrient medium for maturation, mature somatic embryos were obtained. However, somatic embryos of not all embryogenic cell lines reached maturation. In this study, plantlets were obtained in an in vitro culture for the first time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Von Arnold, S., Sabala, I., Bozhkov, P., et al., Developmental pathways of somatic embryogenesis, Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult., 2002, vol. 69, pp. 233–249.
Arya, S., Kalia, R.K., and Arya, I.D., Induction of somatic embryogenesis in Pinus roxburghii Sarg, Plant Cell Rep., 2000, vol. 19, pp. 775–780.
Batygina, T.B., Embryogenesis and morphogenesis of germ and somatic embryos, Fiziol. Rast., 1999, vol. 46, no. 6, pp. 884–898.
Becwar, M.R., Nagmani, R., and Wann, S.R., Initiation embryogenic cultures and somatic embryo development in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda), Can J. For. Res., 1990, vol. 20, pp. 810–817.
Becwar, M.R., Park, Y.-S., Corderro, J.P., and Pullman, G.S., Genetic control of somatic embryogenesis initiation in loblolly pine and implications for breeding, Tree Genet Genom., 2006, vol. 2, pp. 1–9.
Belorussova, A.S. and Tret’yakova, I.N., Patterns of somatic embryo formation in Siberian larch: embryological aspects, Russ. J. Dev. Biol., 2008, vol. 39, no. 2, pp. 83–91.
Bercetche, J. and Paques, M., Somatic Embryogenesis in Maritime Pine (Pinus pinaster) Somatic Embryogenesis in Woody Plants, Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1995.
Bonga, J.M. and von Aderkas, P., Recalcitrance in clonal propagation, in particular of conifers, Plant Cell. Tiss. Organ Cult., 2010, vol. 100, pp. 241–254.
Bozhkov, R.V., Ahn, I.S., and Park, Ya., Two alternative pathways of somatic embryo origin from polyembryonic mature stored seeds of Pinus koriensis, Can. J. Bot., 1997, vol. 85, pp. 509–512.
Carneros, E., Celestino, C., Klimaszewska, K., Parky, S., Toribio, M., and Bonga, J.M., Plant regeneration in stone pine (Pinus pinea L.) by somatic embryogenesis, Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult., 2009, vol. 98, pp. 165–178.
Cyr, D.R., Conifer somatic embryogenesis. I. Development, Dendrobiology, 2002, vol. 48, pp. 31–39.
Finer, J.J., Kriebel, H.B., and Becwar, M.R., Initiation of embryogenic callus and suspension cultures of eastern white pine (Pinus strobus L.), Plant Cell Rep., 1989, vol. 8, pp. 203–206.
Garin, E., Isabel, N., and Plourde, A., Screening of large numbers of seed families of Pinus strobus L. for somatic embryogenesis from immature zygotic embryos, Plant Cell Rep., 1998, vol. 18, pp. 37–43.
Gupta, P.K. and Dursan, D.J., Biotechnology of somatic polyembryogenesis and plantlet regeneration in loblolly pine, Bio/Technology, 1987, vol. 5, pp. 147–151.
Klimaszewska, K., Park, Y.S., Overton, C., Mac Eacheron, I., and Bonga, J.M., Optimized somatic embryogenesis in Pinus strobus L. in vitro cell, Dev. Biol.-Plant, 2001, vol. 37, pp. 392–399.
Laine, E. and David, D., Somatic embryogenesis in immature embryos and protoplasts of Pinus caribaea, Plant Sci., 1990, vol. 69, pp. 215–224.
Lelu, M.A., Klimaszewska, M.A., and Charest, P.J., Somatic embryogenesis from immature and mature zygotic embryos and from cotyledons and needles of somatic plantlets of Larix, Can. J. For. Res., 1994, vol. 24, pp. 100–106.
Lelu, M.A., Bastien, C., Drugeault, A., Gouez, M.L., and Klimaszewska, K., Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet development in Pinus sylvestris and Pinus pinaster on medium with and without plant growth regulators, Physiol. Plant., 1999, vol. 105, pp. 719–728.
Lelu-Walter, M.A., Bernier-Cardou, M., and Klimaszewska, K., tClonal plant production from selfand crosspollinated seed families of Pinus sylvestris (L.) through somatic embryogenesis, {iPlant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult.}, 2008, vol. 92, pp. 31–45.
Lelu-Walter, M.-A., Thompson, D., Harvengt, L., Sanchez, L., Toribio, M., and Paques, L., Somatic embryogenesis in forestry with a focus on Europe: stateof-the-art, benefits, challenges and future direction, Tree Genet. Genom., 2013, vol. 9, pp. 883–899.
Litvay, J., Verma, D.C., and Johnson, M.A., Influence of a loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) culture medium and its components on growth and somatic embryogenesis of the wild carrot (Daucus carota L.), Plant Cell Rep., 1985, no. 4, pp. 325–328.
Niskanen, A-M., Lu, J., Seitz, S., Keinonen, K., Von Weissenberg, K., and Pappinen, A., Effect of parent genotype on somatic embryogenesis in Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris), Tree Physiol., 2004, vol. 24, p. 29.
Noskova, N.E., Sirenko, A.S., and Noskova, M.A., Obtaining stable embryogenic cell lines in Siberian dwarf pine Pinus pumila (Pall.) by somatic embryogenesis, in Materialy mezhdunarodnoi zaochnoi nauchnoi konferentsii “Problemy sovremennoi agrarnoi nauki” (15 oktyabrya 2011 g. (Proceedings of International Extramural Scientific Conference “Problems of Modern Agricultural Science” (October 15, 2011), Krasnoyarsk, 2012, pp. 64–66.
Park, Y.-S., Lelu-Walter, M.A., Initiation, Park Y.S., and Lelu-Walter, M.A., Initiation of somatic embryogenesis in Pinus banksiana, P. pinaster, and P. sylvestris at three laboratories in Canada and France, Plant Cell Organ Cult., 2006, vol. 86, pp. 87–101.
Percy, R.E., Klimaszewska, K., and Cyr, D.R., Evaluation of somatic embryogenesis for clonal propagation of western white pine, Can J. For Res., 2000, vol. 30, pp. 1867–1876.
Rokitskii, P.F., Biologicheskaya statistika (Biological Statistics), Minsk: Vysshaya shkola, 1973.
Pullman, G.S. and Bucalo, K., Pine somatic embryogenesis using zygotic embryos as explants, Plant Embryo Cultures: Methods in Molecular Biology, 2011, vol. 710, pp. 267–291.
Salajova, T., Jasik, J., and Kormutak, A., Somatic embryogenesis in Pinus nigra Arn., in Somatic Embryogenesis in Woody Plants, Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1995, pp. 207–220.
Stasolla, C. and Yeung, E.C., Recent advances in conifer somatic embryogenesis: improving somatic embryo quality, Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult., 2003, vol. 74, no. 1, pp. 15–35.
Tret’yakova, I.N., Embriologiya khvoinykh: fiziologicheskie aspekty (Embryology of Conifers: Physiological Aspects), Novosibirsk: Nauka, 1990.
Tret’yakova, I.N., Embryogenic cell lines and somatic embryogenesis in an vitro culture of Siberian larch, Dokl. Biol. Sci., 2013, vol. 450, no. 1, pp. 122–125.
Tret’yakova, I.N. and Voroshilova, E.V., Embryo initiation from Pinus sibirica megagametophytes in in vitro culture, Russ. J. Dev. Biol., 2014, vol. 45, no. 2, pp. 93–100.
Tretyakova, I., Voroshilova, E., Ivanitskya, A., Shuvaev, D., and Park, M., The embryogenic lines and somatic embryogenesis of coniferous species in Siberia, in Proceedings of 2nd International Conference of IUFRO “Integrating Vegetative Propagation, Biotechnologies and Genetic Improvement for Tree Production and Sustainable Forest Management,” June 25–28, 2012, Brno, Cheswick republic, pp. 71–79.
Tret’yakova, I.N., Voroshilova, E.V., and Shuvaev, D.N., Callusogenesis and somatic embryogenesis induction in hybrid embryos from the seeds of Pinus sibirica, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2014, vol. 61, no. 2, pp. 274–280.
Vondrakova, Z., Eliasova, K., Fischerova, L., and Vagner, M., The role of auxins in somatic embryogenesis of Abies alba, Cent. Rur. J. Biol., 2011, vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 587–5965.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © I.N. Tret’yakova, D.N. Shuvaev, 2015, published in Ontogenez, 2015, Vol. 46, No. 5, pp. 327–337.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tret’yakova, I.N., Shuvaev, D.N. Somatic embryogenesis in Pinus pumila and productivity of embryogenic lines during long-term cultivation in vitro. Russ J Dev Biol 46, 276–285 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062360415050070
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062360415050070