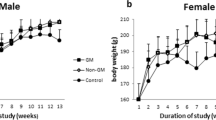
Abstract
Genetic engineering is considered as background for crop protection against pest damage by adding new genes inside the grains. Rice, like other cereals is included in gene engineering experiments. The questions about possible gene transfer related to food safety appear. It is important to find any additional genes or fragments in animal tissues after consumption of genetically modified (GM) food. Therefore, in this study, the remaining of CryIA(b) gene and P35 were assessed in the liver of rats fed with GM rice. This work presents an experimental study with the intervention of GM rice feeding by Sprague Dawley rats. Overall, 20 male and 20 female SD rats were fed by pellets made by GM rice in 50% of needed carbohydrate for 90 days. Then, sampling was done from rats liver. DNA extraction was done based on the protocol. The quality and quantity of the extracted DNA was done by agarose gel electrophoresis and spectrophotometry, respectively. Detection of GM genes residues, including CryIA(b), P35, and T35 was done by Polymerase Chain Reaction using specific primer pairs. The results were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis alongside with 50 bp DNA ladder. The results were compared with the ones in control groups with feeding by standard pellet of non-modified rice. All amplification tests were done in triplicates. Analysis of the amplification of P35, CryIA(b) and T35 showed no residues inside the liver tissue. The results showed no significant difference in the presence of transgenic gene of cryIA(b), T35, and P35 in the liver tissue between the control and experiment groups. Therefore, this study rejects the possibility of gene settle of GM rice gene residues in liver tissue of the animal model studied.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Seck, P.A., Diagne, A., Mohanty, S., and Wopereis, M.C., Crops that feed the world: 7. Rice, Food Secur., 2012, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 7—24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-012-0168-1
Choi, H., Moon, J.-K., Park, B.-S., et al., Comparative nutritional analysis for genetically modified rice, Iksan483 and Milyang204, and nontransgenic counterparts, J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem., 2012, vol. 55, pp. 19—26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13765-012-0004-5
Séralini, G.-E., Clair, E., Mesnage, R., et al., Retracted: long term toxicity of a Roundup herbicide and a Roundup-tolerant genetically modified maize, Elsevier, 2012. Séralini, G.E., Clair, E., Mesnage, R., et al., Republished study: long-term toxicity of a Roundup herbicide and a Roundup-tolerant genetically modified maize, Environ. Sci. Eur., 2014, vol. 26, p. 14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-014-0014-5
Ezzaher, A., Genetically modified foods against hunger in developing countries, J. Food Qual. Hazards Control, 2015, vol. 2, no. 4, p. 111.
Estruch, J.J., Carozzi, N.B., Desai, N., et al., Transgenic plants: an emerging approach to pest control, Nat. Biotechnol., 1997, vol. 15, no. 2, p. 137. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0297-137
Matteson, P.C., Insect pest management in tropical Asian irrigated rice, Annu. Rev. Entomol., 2000, vol. 45, no. 1, pp. 549—574.
Alderborn, A., Sundström, J., Soeria-Atmadja, D., et al., Genetically modified plants for non-food or non-feed purposes: straightforward screening for their appearance in food and feed, Food Chem. Toxicol., 2010, vol. 48, no. 2, pp. 453—464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2009.10.049
Zhang, W. and Shi, F., Do genetically modified crops affect animal reproduction? A review of the ongoing debate, Animal, 2011, vol. 5, no. 7, pp. 1048—1059. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1751731110002776
Panchin, A.Y. and Tuzhikov, A.I., Published GMO studies find no evidence of harm when corrected for multiple comparisons, Crit. Rev. Biotechnol., 2017, vol. 37, no. 2, pp. 213—217. https://doi.org/10.3109/07388551.2015.1130684
Kumar, P.A., Sharma, R.P., and Malik, V.S., The insecticidal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis, Adv. Appl. Microbiol., 1996, vol. 42, pp. 1—43.
Song, H., He, X., Zou, S., et al., A 90-day subchronic feeding study of genetically modified rice expressing Cry1Ab protein in Sprague—Dawley rats, Transgenic Res., 2015, vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 295—308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-014-9844-6
Cao, S., He, X., Xu, W., et al., Safety assessment of transgenic Bacillus thuringiensis rice T1c-19 in Sprague—Dawley rats from metabonomics and bacterial profile perspectives, IUBMB Life, 2012, vol. 64, no. 3, pp. 242—250. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.601
Li, Z., Gao, Y., Zhang, M., et al., Effects of a diet containing genetically modified rice expressing the Cry1Ab/1 Ac protein (Bacillus thuringiensis toxin) on broiler chickens, Arch. Anim. Nutr., 2015, vol. 69, no. 6, pp. 487—498. https://doi.org/10.1080/1745039X.2015.1087749
Brookes, G. and Barfoot, P., Economic impact of GM crops: the global income and production effects 1996—2012, GM Crops Food, 2014, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 65—75. https://doi.org/10.4161/gmcr.28098
Brookes, G. and Barfoot, P., Farm income and production impacts of using GM crop technology 1996—2015, GM Crops Food, 2017, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 156—193. https://doi.org/10.1080/21645698.2017.1317919
Bhullar, N.K. and Gruissem, W., Nutritional enhancement of rice for human health: the contribution of biotechnology, Biotechnol. Adv., 2013, vol. 31, no. 1, pp. 50—57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2012.02.001
Marenkova, T.V. and Deineko, E.V., Hybridological analysis of inheritance of mosaic nptII gene expression in transgenic tobacco plants, Russ. J. Genet., 2016, vol. 52, no. 6, pp. 557—564. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795416060089
Marenkova, T.V. and Deineko, E.V., Transgenic plants as a model for studying epigenetic regulation of gene expression, Vavilovskii Zh. Genet. Sel., 2015, vol. 19, no. 5, pp. 545—551. https://doi.org/10.18699/VJ15.071
Trifonova, E.A., Savel’eva, A.V., Romanova, A.V., et al., Transgenic expression of Serratia marcescens native and mutant nucleases modulates tobacco mosaic virus resistance in Nicotiana tabacum L., Russ. J. Genet., 2015, vol. 51, no. 7, pp. 715—719. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795415070133
Zhirnov, I.V., Trifonova, E.A., Romanova, A.V., et al., Induced expression of Serratia marcescens ribonuclease III gene in transgenic Nicotiana tabacum L. cv. SR1 tobacco plants, Russ. J. Genet., 2016, vol. 52, no. 11, pp. 1137—1141. https://doi.org/10.1134/S102279541611017X
Fujimoto, H., Itoh, K., Yamamoto, M., et al., Insect resistant rice generated by introduction of a modified delta-endotoxin gene of Bacillus thuringiensis, Biotechnology (New York), 1993, vol. 11, no. 10, pp. 1151—1155.
Ghareyazie, B., Alinia, F., Menguito, C.A., et al., Enhanced resistance to two stem borers in an aromatic rice containing a synthetic cryIA(b) gene, Mol. Breed., 1997, vol. 3, no. 5, pp. 401—414. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009695324100
International Service for the Acquisition of Agri-biotech Applications (ISAAA). http://www.isaaa.org/ gmapprovaldatabase/event/default.asp?EventID=221. Accessed February 2, 2019.
Yavari, B., Sarami, S., Shahgaldi, S., et al., If there is really a notable concern about allergenicity of genetically modified foods?, J. Food Qual. Hazards Control, 2016, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 3—9.
Wang, Y., Wei, B., Tian, Y., et al., Evaluation of the potential effect of transgenic rice expressing Cry1Ab on the hematology and enzyme activity in organs of female Swiss rats, PLoS One, 2013, vol. 8, no. 11. e80424.
Spisák, S., Solymosi, N., Ittzés, P., et al., Complete genes may pass from food to human blood, PLoS One, 2013, vol. 8, no. 7. e69805. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0069805
EFSA GMO Panel Working Group on Animal Feeding Trials, Safety and nutritional assessment of GM plants and derived food and feed: the role of animal feeding trials, Food Chem Toxicol., 2008, vol. 46, suppl. 1, pp. S2—S70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2008.02.008
Zou, S., Huang, K., Xu, W., et al., Safety assessment of lepidopteran insect-protected transgenic rice with cry2A* gene, Transgenic Res., 2016, vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 163—172.
Schrøder, M., Poulsen, M., Wilcks, A., et al., A 90-day safety study of genetically modified rice expressing Cry1Ab protein (Bacillus thuringiensis toxin) in Wistar rats, Food Chem. Toxicol., 2007, vol. 45, no. 3, pp. 339—349.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2006.09.001
Hammond, B., Dudek, R., Lemen, J., and Nemeth, M., Results of a 90-day safety assurance study with rats fed grain from corn borer-protected corn, Food Chem. Toxicol., 2006, vol. 44, no. 7, pp. 1092—1099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2006.01.003
Tan, X., Zhou, X., Tang, Y., et al., Immunotoxicological evaluation of genetically modified rice expressing Cry1Ab/Ac protein (TT51-1) by a 6-month feeding study on cynomolgus monkeys, PLoS One, 2016, vol. 11, no. 9. e0163879. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0163879
Mao, J., Sun, X., Cheng, J.H., et al., A 52-week safety study in cynomolgus macaques for genetically modified rice expressing Cry1Ab/1Ac protein, Food Chem. Toxicol., 2016, vol. 95, pp. 1—11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2016.06.015
Opara, C.N., Elijah, A.I., Adamu, L.G., and Uzochukwu, S.V., Screening for genetically modified maize in raw and processed foods sold commercially in Southern Nigeria boarder states, Appl. Food Biotechnol., 2016, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 150—158.
Zaulet, M., Rusu, L., Kevorkian, S., et al., Detection and quantification of GMO and sequencing of the DNA amplified products, Rom. Biotechnol. Lett., 2009, vol. 14, no. 5, pp. 4733—4746.
Debode, F., Janssen, E., and Berben, G., Development of 10 new screening PCR assays for GMO detection targeting promoters (pFMV, pNOS, pSSuAra, pTA29, pUbi, pRice actin) and terminators (t35S, tE9, tOCS, tg7), Eur. Food Res. Technol., 2013, vol. 236, no. 4, pp. 659—669. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-013-1921-1
International Organization for Standardization, Foodstuffs: Methods of Analysis for the Detection of Genetically Modified Organisms and Derived Products: Qualitative Nucleic Acid Based Methods, Amendment 1: (ISO 21569:2005/Amd1:2013), 2013.
Phipps, R., Deaville, E.R., and Maddison, B.C., Detection of transgenic and endogenous plant DNA in rumen fluid, duodenal digesta, milk, blood, and feces of lactating dairy cows, J. Dairy Sci., 2003, vol. 86, no. 12, pp. 4070—4078. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(03)74019-3
Einspanier, R., Bieser, B., Reischl, J., and Prelle, K., First identification of caldesmon transcripts in bovine oviduct epithelial cells in vitro by means of an RNA differential display technique examining culture-induced expression changes, Reprod. Domest. Anim., 2001, vol. 36, no. 5, pp. 230—235.
Nemeth, A., Wurz, A., Artim, L., et al., Sensitive PCR analysis of animal tissue samples for fragments of endogenous and transgenic plant DNA, J. Agric. Food Chem., 2004, vol. 52, no. 20, pp. 6129—6135. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf049567f
Tony, M., Butschke, A., Broll, H., et al., Safety assessment of Bt 176 maize in broiler nutrition: degradation of maize-DNA and its metabolic fate, Arch. Anim. Nutr., 2003, vol. 57, no. 4, pp. 235—252.
Oraby, H.A.S., Kandil, M.M.H., Hassan, A.A.M., and Al-Sharawi, H.A., Addressing the issue of horizontal gene transfer from a diet containing genetically modified components into rat tissues, Afr. J. Biotechnol., 2014, vol. 13, no. 48, pp. 4410—4418. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB2014.14088
Mazza, R., Soave, M., Morlacchini, M., et al., Assessing the transfer of genetically modified DNA from feed to animal tissues, Transgenic Res., 2005, vol. 14, no. 5, pp. 775—784. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-005-0009-5
Panchin, A.Y., Toxicity of Roundup-tolerant genetically modified maize is not supported by statistical test, Food Chem. Toxicol., 2013, vol. 53, p. 475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2012.10.039
Zhao, K., Ren, F., Han, F., et al., Edible safety assessment of genetically modified rice T1C-1 for Sprague Dawley rats through horizontal gene transfer, allergenicity and intestinal microbiota, PLoS One, 2016, vol. 11, no. 10. e0163352. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0163352
Haddad, N., Johnson, N., Kathariou, S., et al., Next generation microbiological risk assessment—potential of omics data for hazard characterisation, Int. J. Food Microbiol., 2018, vol. 287, pp. 28—39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.04.015
Peng, C., Chen, X., Wang, X., et al., Comparative analysis of miRNA expression profiles in transgenic and non-transgenic rice using miRNA-Seq, Sci. Rep., 2018, vol. 8, no. 1, p. 338. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-18723-x
Michno, J.M. and Stupar, R.M., The importance of genotype identity, genetic heterogeneity, and bioinformatic handling for properly assessing genomic variation in transgenic plants, BMC Biotechnol., 2018, vol. 18, no. 1, p. 38. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-018-0447-9
Wang, F., Dang, C., Chang, X., et al., Variation among conventional cultivars could be used as a criterion for environmental safety assessment of Bt rice on nontarget arthropods, Sci. Rep., 2017, vol. 7, p. 41918. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41918
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This article is part of a thesis of Master’s degree. This study has been done in the Research Center of Food Safety and Hygiene, School of Health, Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences, Yazd. The authors appreciate from Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences, Yazd, Iran for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shirdeli, M., Orlov, Y.L., Eslami, G. et al. Testing Safety of Genetically Modified Products of Rice: Case Study on Sprague Dawley Rats. Russ J Genet 55, 962–968 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795419080131
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795419080131