Abstract
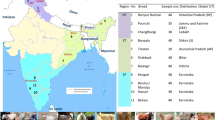
The purpose of this study was to assess genetic diversity, genetic differentiation relationship and population structure among 10 Chinese sheep populations using 5 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in MC1R gene. The genetic diversity indices suggested that the intra-population variation levels of Chinese Merino and Large-tailed Han breeds were lowest than Kazakh Fat-Rumped. Chinese sheep breeds have maintained a high intra-population variation levels (95.23%). The genetic differentiation patterns and genetic relationships among Chinese sheep breeds displayed a high consistency with the traditional classification. The cluster trees were constructed by UPMGA method. The results showed that Chinese indigenous sheep populations have distinct genetic differentiation. The inter-population variation levels in Chinese sheep populations indicated three geographically independent domestication events have occurred. The Bayesian cluster analyses also showed a reliable clustering pattern, which revealed three major clusters in Chinese indigenous sheep populations (Mongolian group, Kazakh group and Tibetan group), except for Duolang and Minxian Black-fur. There were probably caused by different breeding history, geography isolation and different levels of inbreeding. The findings supported the related records in literature, ten sheep populations originated on different time stage from the primogenitor population and communicated genetically with each other in the process of natural and artificial selection, and in different ecological environment. It is concluded that Chinese indigenous sheep have higher genetic variation and diversity, genetic differentiation exist between Chinese sheep populations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zheng, P.L., Zhang, Z.G., Chen, W.H., et al., The Editorial Section of Sheep and Goat Breeds in China, Sheep and Goat Breeds in China, Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, 1989.
National Consultative Committee, Country Report for the Preparation of SoW-AnGR Report on Domestic Animal Genetic Resources in China, Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2004.
Guo, J., Du, L.X., Ma, Y.H., et al., A novel maternal lineage revealed in sheep (Ovis aries), Anim. Genet., 2005, vol. 36, no. 4, pp. 331–336.
Niu, L.L., Li, H.B., Ma, Y.H., et al., Genetic variability and individual assignment of Chinese indigenous sheep populations (Ovis aries) using microsatellites, Anim. Genet., 2012, vol. 43, no. 1, pp. 108–111.
Zhong, T., Han, J.L., Guo, J., et al., Genetic diversity of Chinese indigenous sheep breeds inferred from microsatellite markers, Small. Ruminant. Res., 2010, vol. 90, nos. 1–3, pp. 88–94.
Zhong, T., Han, J.L., Guo, J., et al., Tracing genetic differentiation of Chinese Mongolian sheep using microsatellites, Anim. Genet., 2011, vol. 42, no. 5, pp. 563–565.
Chen, S.Y., Duan, Z.Y., Sha, T., et al., Origin, genetic diversity, and population structure of Chinese domestic sheep, Gene, 2006, vol. 376, no. 2, pp. 216–223.
Fang, M.Y., Larson, G., Ribeiro, H.S., et al., Contrasting mode of evolution at a coat color locus in wild and domestic pigs, PLoS Genet., 2009, vol. 5, no. 1. e1000341
Searle, A.G., Comparative Genetics of Coat Colour in Mammals, London: Logos, 1968.
Andersson, L., Melanocortin receptor variants with phenotypic effects in horse, pig, and chicken, Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 2003, vol. 91, pp. 313–318.
Li, J., Yang, H., Li, J.R., et al., Artificial selection of the melanocortin receptor 1 gene in Chinese domestic pigs during domestication, Heredity, 2010, vol. 105, no. 3, pp. 274–281.
Anderson, T.M., von Holdt, B.M., Candille, S.I., et al., Molecular and evolutionary history of melanism in North American gray wolves, Science, 2009, vol. 323, no. 5919, pp. 1339–1343.
Yeh, F.C., Yang, R.C., and Boyle, T., POPGENE: Microsoft Windows-Based Freeware for Population Genetic Analysis: Release 1.31, Edmonton: Univ. Alberta, 1999.
Manly, B.F.J., The Statistics of Natural Selection, Chapman and Hall, 1985.
Stephens, M., Smith, N.J., and Donnelly, P., A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data, Am. J. Hum. Genet., 2001, vol. 68, no. 4, pp. 978–989.
Rozas, J., Sanchez-DelBarrio, J.C., Messeguer, X., et al., DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods, Bioinformatics, 2003, vol. 19, no. 18, pp. 2496–2497.
Nei, M., Genetic distance between populations, Am. Nat., 1972, vol. 106, no. 949, pp. 283–292.
Pritchard, J.K., Stephens, M., and Donnelly, P., Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data, Genetics, 2000, vol. 155, no. 2, pp. 945–959.
Rosenberg, N.A., Distruct: a program for the graphical display of population structure, Mol. Ecol. Notes, 2004, vol. 4, pp. 137–138.
Våge, D.I., Klungland, H., Lu, D., et al., Molecular and pharmacological characterization of dominant black coat color in sheep, Mamm. Genome, 1999, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 39–43.
Fontanesi, L., Beretti, F., Riggio, V., et al., Sequence characterization of the melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) gene in sheep with different coat colors and identification of the putative allele at the ovine Extension locus, Small. Ruminant. Res., 2010, vol. 91, nos. 2–3, pp. 200–207.
Lawson, H.L.J., Santucci, F.B.K., Townsend, S., et al., Genetic structure of European sheep breeds, Heredity, 2007, vol. 99, no. 6, pp. 620–631.
Xie, C.X., History of Raising Cattle, Sheep and Goat in China (Attached History of Raising Deer), Agricultural Publishing House of China, 1985, pp. 144–150, 173–179.
Shan, N.S., Primary discuss of history for Han sheep, in China Semifine-Wool, 1983, no. 3, pp. 15–17.
Zhao, Q.J., Ma, Y.H., Guan, W.J., et al., Microsatellite analysis of genetic diversity and phylogenetic relation-ship of 8 Tibetan sheep populations in China, Anim. Biotechnol. Bull., 2006, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 503–507.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, G.L., Fu, D.L., Lang, X. et al. Genetic variation of 5 SNPs of MC1R gene in Chinese indigenous sheep breeds. Russ J Genet 50, 1048–1059 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795414100159
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795414100159