Abstract
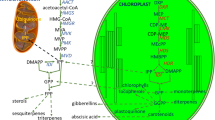
The components of rose essential oil are mainly monoterpene alcohols, predominantly synthesized through the methylerythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) pathway in plants. 1-Deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase (DXR) is specified to be a first committed enzyme of the MEP pathway. In order to understand better the role of DXR in the rose essential oil biosynthesis at the molecular level, the full-length cDNA of DXR sequence (designated as RhDXR) was isolated from an oil-bearing rose hybrid Rosa cv. Zizhi and characterized, and the expression profile of it was investigated. Essential oils of rose cv. Zizhi and the other five oil-bearing roses were distilled to evaluate the relationship between the expression of DXR gene and oil yield rate. The full-length cDNA of RhDXR was 1915 bp in length, comprised an open reading frame of 1419 bp, encoding an enzyme of 472 amino acids. A comparative analysis with DXRs of selected species from bacteria to higher plants revealed three conserved domains: a conserved cleavage site for plastids, an extended Prorich region, and a highly conserved NADPH oxidase-binding motif existing in the N-terminal region, like in other higher plant species. The relative expression levels of the DXR gene were determined in various tissues: receptacle, leaf, sepal, pistil, stamen, and petal (in the order of decreasing expression level), and at different flowering stages (flower bud, flower in half bloom, and flower in full bloom). Six cultivars could be classified into two groups according to flower color, and within each group there was a positive correlation between the expression level of DXR gene and oil yield rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DMAPP:
-
dimethylallyl diphosphate
- DXR:
-
1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase
- GAPDH:
-
glyceraldehyde-phosphate dehydrogenase
- IPP:
-
isopentenyl diphosphate
- MEP:
-
methylerythritol 4-phosphate
- MVA:
-
mevalonate pathway
References
Yang, D.F., Du, X.H., Liang, X., Han, R.L., Liang, Z.S., Liu, Y., Liu, F.H., and Zhao, J.J., Different roles of the mevalonate and methylerythritol phosphate pathways in cell growth and tanshinone production of Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots, PLoS One, 2012, vol. 7: e46797, doi 10.1371/journal.pone.0046797
Julliard, J.H. and Douce, R., Biosynthesis of the thiazole moiety of thiamin (vitamin B1) in higher plant chloroplasts, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1991, vol. 88, pp. 2042–2045.
Julliard, J.H., Biosynthesis of the pyridoxal ring (vitamin B6) in higher plant chloroplasts and its relationship with the biosynthesis of the thiazole ring (vitamin B1), C. R. Acad. Sci., III. Sci. Vie., 1992, vol. 314, pp. 285–290.
Himmeldirk, K., Kennedy, I.A., Hill, R.E., Sayer, B.G., and Spencer, I.D., Biosynthesis of vitamins B1 and B6 in E. coli, concurrent incorporation of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose into thiamin (B1) and pyridoxol (B6), Chem. Commun., 1996, vol. 10, pp. 1187–1188.
Kuzuyama, T., Shimizu, T., Takahashi, S., and Seto, H.F., A specific inhibitor of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase in the nonmevalonate pathway for terpenoid biosynthesis, Tetrahedron Lett., 1998, vol. 39, pp. 7913–7916.
Schwender, J., Muller, C., Zeidler, J., and Lichtenthaler, H.K., Cloning and heterologous expression of a cDNA encoding 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase of Arabidopsis thaliana, FEBS Lett., 1999, vol. 455, pp. 140–144.
Lange, B.M. and Croteau, R., Isoprenoid biosynthesis via the mevalonate-independent pathway in plants: cloning and heterologous expression of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase from peppermint, Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 1999, vol. 365, pp. 170–174.
Veau, B., Courtois, M., Oudin, A., Chenieux, J.C., Rideau, M., and Clastre, M., Cloning and expression of cDNAs encoding two enzymes of the MEP pathway in Catharanthus roseus, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2000, vol. 1517, pp. 159–163.
Gong, Y.F., Liao, Z.H., Chen, M., Zuo, K.J., Guo, L., Tan, Q.M., Huang, Z.S., Kai, G.Y., Sun, X.F., Tan, F., and Tang, K.X., Molecular cloning and characterization of a 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase gene from Ginkgo biloba, DNA Sequence, 2005, vol. 16, pp. 111–120.
Yao, H.Y., Gong, Y.F., Zuo, K.J., Ling, H., Qiu, C.X., Zhang, F., Wang, Y.C., Pi, Y., Liu, X., Sun, X.F., and Tang, K., Molecular cloning, expression profiling and functional analysis of a DXR gene encoding 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase from Camptotheca acuminate, J. Plant Physiol., 2008, vol. 165, pp. 203–213.
Mahmoud, S.S. and Croteau, R.B., Metabolic engineering of essential oil yield and composition in mint by altering expression of deoxyxylulose phosphate reductoisomerase and menthofuran synthase, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2001, vol. 98, pp. 8915–8920.
Thompson, J.D., Gibson, T.J., Plewniak, F., Higgins, D.G., and Jeanmougin, F., The CLUSTAL-X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools, Nucleic Acids Res., 1997, vol. 25, pp. 4876–4882.
Scalliet, G., Lionnet, C., le Bechec, M., Dutron, L., Jean-Louis, M., Baudino, S., Bergougnoux, V., Jullien, F., Chambrier, P., Vergne, P., Dumas, C., Cock, J.M., and Hugueney, P., Role of petal specific orcinol O-methyltransferases in the evolution of rose scent, Plant Physiol., 2006, vol. 140, pp. 18–29.
Kenneth, J.L. and Schmittgen, T.D., Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method, Methods, 2001, vol. 25, pp. 402–408.
Carretero-Paulet, L., Ahumada, I., Cunillera, N., Rodríguez-Concepción, M., Ferrer, A., Boronat, A., and Campos, N., Expression and molecular analysis of the Arabidopsis DXR gene encoding 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase, the first committed enzyme of the 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway, Plant Physiol., 2002, vol. 129, pp. 1581–1591.
Takahashi, S., Kuzuyama, T., Watanabe, H., and Seto, H., A 1-Deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase catalyzing the formation of 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate in an alternative nonmevalonate pathway for terpenoid biosynthesis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1998, vol. 95, pp. 9879–9884.
Proteau, P.J., 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase: an overview, Bioorganic Chem., 2004, vol. 32, pp. 483–493.
Wan, X.R. and Li, L., Pathways and related enzymes of ABA biosynthesis in higher plants, Chinese Bull. Bot., 2004, vol. 21, pp. 352–359.
Cooper, C.M., Davies, N.W., and Menary, R.C., Changes in some carotenoids and apocarotenoids during flower development in Boronia megastigma (Nees.), J. Agric. Food Chem., 2009, vol. 57, pp. 1513–1520.
Eugster, C.H. and Märki-Fischer, E., The chemistry of rose pigments, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl., 1991, vol. 30, pp. 654–672.
Li, W.X., A study on the chemical component and properties of’ Ku-shui’ rose, J. Teachers College, Qingdao Univ., 1997, vol. 14, pp. 34–37 [in Chinese].
Tang, L., Li, Z.J., Zhao, L., Wang, X.Y., and Wang, Z., Comparison of two pH methods for determining anthocyanins from flower petals of rose, Food Sci., 2009, vol. 30, pp. 310–313 [in Chinese].
Li, Z.J., Study of the extraction process and properties of anthocyanin from Pingyin roses, Master thesis, Shandong Normal University, 2010 [in Chinese].
Suzuki, M., Matsumoto, S., Fleischmann, H.P., Shimada, H., Yamano, Y., Ito, M., and Watanabe, N., Identification of β-damascenone progenitors and their biogenesis in rose flowers (Rosa damascena Mill.), ACS Symp. Ser., 2002, vol. 802, pp. 89–101.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This text was submitted by the authors in English.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Yao, L. Cloning and expression profile of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase gene from an oil-bearing rose. Russ J Plant Physiol 61, 548–555 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443714040207
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443714040207