Abstract
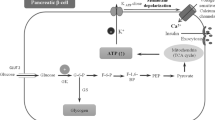
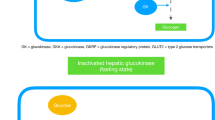
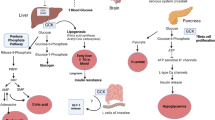
The impairment of glucose homeostasis leads to hyperglycemia and type-2 diabetes mellitus. Glucokinase (GK), an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate in pancreatic ß-cells, liver hepatocytes, specific hypothalamic neurons, and intestine enterocytes, is a key regulator of glucose homeostasis. In hepatocytes, GK controls the glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis and inhibits the glucose synthesis via the gluconeogenesis pathway. Glucokinase regulatory protein (GKRP) synthesized in hepatocytes acts as an endogenous GK inhibitor. During fasting, GKRP binds GK, inactivates it, and transports it into the cell nucleus, thus isolating it from the hepatocyte carbohydrate metabolism. In the beginning of the 2000s, the research was mainly focused on the development and trials of the small molecule GK activators as potential antidiabetic glucose-lowering drugs. However, the use of such substances increased the risk of hypoglycemia, and clinical studies of most synthetic GK activators are currently discontinued. Allosteric inhibitors of the GK–GKRP interaction are coming as alternative agents increasing the GK activity that can substitute GKA. In this review, we discuss the recent advances and the current state of art in the development of potential antidiabetic drugs targeted to GK as a key regulator of glucose homeostasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization Diabetes Fact Sheet No. 312 (Updated November 2014).
Slingerland A.S. 2006. Monogenic diabetes in children and young adults: challenges for researcher, clinician and patient. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 7, 171–185.
Vaxillaire M., Froguel P. 2008. Monogenic diabetes in the young, pharmacogenetics and relevance to multifactorial forms of type 2 diabetes. Endocr. Rev. 29, 254–264.
Ellard S., Beards F., Allen L.I., Shepherd M., Ballantyne E., Harvey R., Hattersley A.T. 2000. A high prevalence of glucokinase mutations in gestational diabetic subjects selected by clinical criteria. Diabetologia. 43, 250–253.
Osbak K.K., Colclough K., Saint-Martin C., Beer N.L., Bellanné- Chantelot C., Ellard S., Gloyn A.L. 2009. Update on mutations in glucokinase (GCK), which cause maturity onset diabetes of the young, permanent neonatal diabetes, and hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. Hum. Mutat. 30, 1512–1526.
Glaser B., Kesavan P., Haymen M., Davis E., Cuesta A., Buchs A., Stanley C.A., Thornton P.S., Permutt M.A., Matschinsky F.M., Herold K.C. 1998. Familial hyperinsulinism caused by an activating glucokinase mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 338, 226–230.
Sayed S., Langdon D.R., Odili S., Chen P., Buettger C., Schiffman A.B., Suchi M., Taub R., Grimsby J., Matschinsky F.M., Stanley C.A. 2009. Extremes of clinical and enzymatic phenotypes in children with hyperinsulinism due to glucokinase activating mutations. Diabetes. 58, 1419–1427.
Christesen H.B., Jacobsen B.B., Odili S., Buettger C., Cuesta-Munoz A., Hansen T., Brusgaard K., Massa O., Magnuson M.A., Shiota C., Matschinsky F.M., Barbetti F. 2002. The second activating glucokinase mutation (A456V): implications for glucose homeostasis and diabetes therapy. Diabetes. 51, 1240–1246.
Gloyn A.L., Noordam K., Willemsen M.A., Ellard S., Lam W.W., Campbell I.W., Midgley P., Shiota C., Buettger C., Magnuson M.A., Matschinsky F.M., Hattersley A.T. 2003. Insights into the biochemical and genetic basis of glucokinase activation from naturally occurring hypoglycaemia mutations. Diabetes. 52, 2433–2440.
Cuesta-Muñoz A.L., Huopio H., Otonkoski T., Gomez-Zumaquero J.M., Näntö-Salonen K., Rahier J., López-Enriquez S., García-Gimeno M.A., Sanz P., Soriguer F.C. 2004. Severe persistent hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia due to a de novo glucokinase mutation. Diabetes. 53, 2164–2168.
Christesen H.B., Tribble N.D., Molven A., Siddiqui J., Sandal T., Brusgaard K., Ellard S., Njølstad P.R., Alm J., Brock Jacobsen B., Hussain K., Gloyn A.L. 2008. Activating glucokinase (GCK) mutations as a cause of medically responsive congenital hyperinsulinism: Prevalence in children and characterisation of a novel GCK mutation. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 159, 27–34.
Grimsby J., Sarabu R., Corbett W.L., Haynes N.E., Bizzarro F.T., Coffey J.W., Guertin K.R., Hilliard D.W., Kester R.F., Mahaney P.E., Marcus L., Qi L., Spence C.L., Tengi J., Magnuson M.A., Chu C.A., Dvorozniak M.T., Matschinsky F.M., Grippo J.F. 2003. Allosteric activators of glucokinase: Potential role in diabetes therapy. Science. 301, 370–373.
Sarabu R., Berhtel S.J., Kester R.F., Tilley J.W. 2008. Glucokinase activators as new type 2 diabetes therapeutic agents. Expert Opin. Ther. Pathol. 18, 759–768.
Sarabu R., Berhtel S.J., Kester R.F., Tilley J.W. 2011. Novel glucokinase activators: A patent review (2008–2010). Expert Opin. Ther. Pathol. 21, 13–33.
Filipski K.J., Futasugi K., Pfefferkorn J.A., Stevens B.D. 2012. Glucokinase activators. Pharm. Pathol. Anal. 1, 301–311.
Filipski K.J., Pfefferkorn J.A. 2014. Glucokinase activators and disruptors of the glucokinase–glucokinase regulatory protein interaction: 2011–2014. Expert Opin. Ther. Pathol. 24, 875–891.
Matschinsky F.M. 2013. GKAs for diabetes therapy: why no clinically useful drug after two decades of trying? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 34, 90–99.
Hale C., Lloyd D.J., Pellacani A., Veniant M.M. 2015. Molecular targeting of the GK-GKRP pathway in diabetes. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets. 19, 129–139.
Van Schaftingen E. 1989. A protein from rat liver confers to glucokinase the property of being antagonistically regulated by fructose 6-phosphate and fructose 1phosphate. Eur. J. Biochem. 179, 179–184.
Van Schaftingen E., Vandercammen A., Detheux M., Davies D.R. 1992. The regulatory protein of liver glucokinase. Adv. Enzyme Regul. 32, 133–148.
Vandercammen A., van Schaftingen E. 1990. The mechanism by which rat liver glucokinase is inhibited by the regulatory protein. Eur. J. Biochem. 191, 483–489.
Toyoda Y., Miwa I., Satake S., Anai M., Oka Y. 1995. Nuclear location of the regulatory protein of glucokinase in rat liver and translocation of the regulator to the cytoplasm in response to high glucose. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 215, 467–473.
Shiota C., Coffey J., Grimsby J., Grippo J.F., Magnuson M.A. 1999. Nuclear import of hepatic glucokinase depends upon glucokinase regulatory protein, whereas export is due to a nuclear export signal sequence in glucokinase. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 37125–37130.
Veiga-da-Cunha M., Van Schaftingen E. 2002. Identification of fructose 6-phosphateand fructose 1-phosphate-binding residues in the regulatory protein of glucokinase. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 8466–8473.
Grimsby J., Coffey J.W., Dvorozniak M.T., Magram J., Li G., Matschinsky F.M., Shiota C., Kaur S., Magnuson M.A., Grippo J.F. 2000. Characterization of glucokinase regulatory protein-deficient mice. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 7826–7831.
Farrelly D., Brown K.S., Tieman A., Ren J., Lira S.A., Hagan D., Gregg R., Mookhtiar K.A., Hariharan N. 1999. Mice mutant for glucokinase regulatory protein exhibit decreased liver glucokinase: A sequestration mechanism in metabolic regulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 96, 14511–14516.
Pino M.F., Kim K.-A., Shelton K.D., Lindner J., Odili S., Li C., Collins H.W., Shiota M., Matschinsky F.M., Magnuson M.A. 2007. Glucokinase thermolability and hepatic regulatory protein binding are essential factors for predicting the blood glucose phenotype of missense mutations. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 13906–13916.
Ling Y., Li X., Gu Q., Chen H., Lu D., Gao X. 2011. Associations of common polymorphisms in GCKR with type 2 diabetes and related traits in a Han Chinese population: A case-control study. BMC Med. Genet. doi 10.1186/1471-2350-12-66
Horvatovich K., Bokor S., Polgar N., Kisfali P., Hadarits F., Jaromi L. Csongei V., Repasy J., Molnar D., Melegh B. 2011. Functional glucokinase regulator gene variants have inverse effects on triglyceride and glucose levels, and decrease the risk of obesity in children. Diabetes Metab. 37, 432–439.
Pollin T.I., Jablonski K.A., Mc Ateer J.B., Saxena R., Kathiresan S., Kahn S.E., Goldberg R.B., Altshuler D., Florez J.C; Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. 2011. Triglyceride response to an intensive lifestyle intervention is enhanced in carriers of the GCKR Pro446Leu polymorphism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 96, E1142–E1147.
Rees M.G., Wincovitch S., Schultz J., Waterstradt R., Beer N.L., Baltrusch S., Collins F.S., Gloyn A.L. 2012. Cellular characterisation of the GCKR P446L variant associated with type 2 diabetes risk. Diabetologia. 55, 114–122.
Rees M.G., Ng D., Ruppert S., Turner C., Beer N.L., Swift A.J., Morken M.A., Below J.E., Blech I.; NISC Comparative Sequencing Program, Mullikin J.C., Mc Carthy M.I., Biesecker L.G., Gloyn A.L., Collins F.S. 2012. Correlation of rare coding variants in the gene encoding human glucokinase regulatory protein with phenotypic, cellular, and kinetic outcomes. J. Clin. Invest. 122, 205–217.
Orho-Melander M., Melander O., Guiducci C., Perez Martinez P., Corella D., Roos C., Tewhey R., Rieder M.J,. Hall J., Abecasis G., Tai E.S., Welch C., Arnett D.K., Lyssenko V., Lindholm E., Saxena R., de Bakker P.I., Burtt N., Voight B.F., Hirschhorn J.N., Tucker K.L., Hedner T., Tuomi T., Isomaa B., Eriksson K.F., Taskinen M.R., Wahlstrand B., Hughes T.E., Parnell L.D., Lai C.Q., Berglund G., Peltonen L., Vartiainen E., Jousilahti P., Havulinna A.S., Salomaa V., Nilsson P., Groop L., Altshuler D., Ordovas J.M., Kathiresan S. 2008. Common missense variant in the glucokinase regulatory protein gene is associated with increased plasma triglyceride and C-reactive protein but lower fasting glucose concentrations. Diabetes. 57, 3112–3121.
Ridker P.M., Pare G., Parker A., Zee R.Y., Danik J.S., Buring J.E., Kwiatkowski D., Cook N.R., Miletich J.P., Chasman D.I. 2008. Loci related to metabolic-syndrome pathways including LEPR, HNF1A, IL6R, and GCKR associate with plasma C-reactive protein: The Women’s Genome Health Study. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 82, 1185–1192.
Saxena R., Hivert M.F., Langenberg C., et al. 2010. Genetic variation in GIPR influences the glucose and insulin responses to an oral glucose challenge. Nat. Genet. 42, 142–148.
Illig T., Gieger C., Zhai G., Römisch- Margl W., Wang Sattler R., Prehn C., Altmaier E., Kastenmüller G., Kato B.S., Mewes H.W., Meitinger T., de Angelis M.H., Kronenberg F., Soranzo N., Wichmann H.E., Spector T.D., Adamski J., Suhre K. 2010. A genome-wide perspective of genetic variation in human metabolism. Nat. Genet. 42, 137–141.
Ingelsson E., Langenberg C., Hivert M.F., et al. 2010. Detailed physiologic characterization reveals diverse mechanisms for novel genetic loci regulating glucose and insulin metabolism in humans. Diabetes. 59, 1266–1275.
Dupuis J., Langenberg C., Prokopenko I., et al. 2010. New genetic loci implicated in fasting glucose homeostasis and their impact on type 2 diabetes risk. Nat. Genet. 42, 105–116.
Suhre K., Shin S.Y., Petersen A.K., et al. 2011. Human metabolic individuality in biomedical and pharmaceutical research. Nature. 477, 54–60.
Teslovich T.M., Musunuru K., Smith A.V., et al. 2010. Biological, clinical and population relevance of 95 loci for blood lipids. Nature. 466, 707–713.
Pautsch A., Stadler N., Löhle A., Rist W., Berg A., Glocker L., Nar H., Reinert D., Lenter M., Heckel A., Schnapp G., Kauschke S.G. 2013. Crystal structure of glucokinase regulatory protein. Biochemistry. 52, 3523–3531.
Choi J.M., Seo M.-H., Kyeong H.-H., Kim E., Kim H.S. 2013. Molecular basis for the role of regulatory protein as the allosteric switch for glucokinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110, 10171–10176.
Beck T., Miller B. 2013. Structural basis for regulation of human glucokinase by glucokinase regulatory protein. Biochemistry. 52, 6232–6239.
Chen K., Michelsen K., Kurzeja R.J.M., Han J., Vazir M., St Jean D.J.,Jr., Hale C., Wahl R.C. 2014. Discovery of small-molecule glucokinase regulatory protein modulators that restore glucokinase activity. J. Biomol. Screen. 19, 1014–1023.
Lloyd D.J., St. Jean D.J.,Jr., Kurzeja R.J., Wahl R.C., Michelsen K., Cupples R., Chen M., Wu J., Sivits G., Helmering J., Komorowski R., Ashton K.S., Pennington L.D., Fotsch C., Vazir M., Chen K., Chmait S., Zhang J., Liu L., Norman M.H., Andrews K.L., Bartberger M.D., Van G., Galbreath E.J., Vonderfecht S.L., Wang M., Jordan S.R., Véniant M.M., Hale C. 2013. Antidiabetic effects of glucokinase regulatory protein small-molecule disruptors. Nature. 504, 437–440.
Ashton K.S., Andrews K.L., Bryan M.C., Chen J., Chen K., Chen M., Chmait S., Croghan M., Cupples R., Fotsch C., Helmering J., Jordan S.R., Kurzeja R.J., Michelsen K., Pennington L.D., Poon S.F., Sivits G,. Van G., Vonderfecht S.L., Wahl R.C., Zhang J., Lloyd D.J., Hale C., St. Jean D.J.,Jr. 2014. Small molecular disruptors of the glucokinase-glucokinase regulatory protein interaction: Discovery of a novel tool compound for in vivo proof-of-concept. J. Med. Chem. 57, 309–324.
St. Jean D.J., Jr., Ashton K.S., Bartberger M.D., Chen J., Chmait S., Cupples R., Galbreath E., Helmering J., Hong F.T., Jordan S.R., Liu L., Kunz R.K., Michelsen K., Nishimura N., Pennington L.D., Poon S.F., Reid D., Sivits G., Stec M.M., Tadesse S., Tamayo N., Van G., Yang K.C., Zhang J., Norman M.H., Fotsch C., Lloyd D.J., Hale C. 2014. Small molecular disruptors of the glucokinase-glucokinase regulatory protein interaction: Leveraging structure-based drug design to identify analogues with improved pharmacokinetic profiles. J. Med. Chem. 57, 325–338.
Nishimura N., Norman M.H., Liu L., Yang K.C., Ashton K.S., Bartberger M.D., Chmait S., Chen J., Cupples R., Fotsch C., Helmering J., Jordan S.R., Kunz R.K., Pennington L.D., Poon S.F., Siegmund A., Sivits G., Lloyd D.J., Hale C., St. Jean D.J.,Jr. 2014. Small molecular disruptors of the glucokinase-glucokinase regulatory protein interaction: Structure–activity relationships within the aryl carbinol region of the N-arylsulfonamido-N'-arylpiperazine series. J. Med. Chem. 57, 3094–3116.
Hong F.-T., Norman M.H., Ashton K.S., Bartberger M.D., Chen J., Chmait S., Cupples R., Fotsch C., Jordan S.R., Lloyd D.J., Sivits G., Tadesse S., Hale C., St Jean D.J., Jr. 2014. Small molecular disruptors of the glucokinaseglucokinase regulatory protein interaction: Exploration of a novel binding pocket. J. Med. Chem. 5, 5949–5964.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © P.M. Rubtsov, E.L. Igudin, A.N. Tiulpakov, 2015, published in Molekulyarnaya Biologiya, 2015, Vol. 49, No. 4, pp. 555–560.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rubtsov, P.M., Igudin, E.L. & Tiulpakov, A.N. Glucokinase and glucokinase regulatory proteins as molecular targets for novel antidiabetic drugs. Mol Biol 49, 494–499 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893315040147
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893315040147