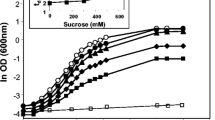
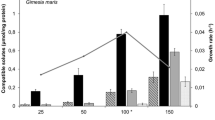
Abstract—
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy was used for investigation of the pool of compatible solutes accumulated in the cells of Glutamicibacter sp. strain SMB32 in response to abiotic environmental factors. The original habitat of the strain was anthropogenically salinated soil at the Verkhnekamsk deposit of potassium and magnesium salts (Perm krai, Russia). The strain grew within the temperature range from 5 to 35°C. At 5 and 32°C, the intracellular content of trehalose in the cells of Glutamicibacter sp. SMB32 was significantly higher than at 25°C. Glutamicibacter sp. SMB32 was able to grow both in the absence of NaCl and at its concentrations up to 11%. Glutamate predominated in the cells grown without NaCl. At high salinity (8% NaCl), predominant compounds in the studied strain cells were trehalose, proline, glutamine, and glutamate. Increasing salinity of the growth medium resulted in higher levels of intracellular proline. This is the first report of ability of a Glutamicibacter strain to synthesize mannitol; its accumulation was found to depend on the aeration mode. Thus, Glutamicibacter sp. strain SMB32 possesses high metabolic plasticity and is able to adapt to the action of unfavorable physicochemical factors.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Anan’ina, L.N., Kosheleva, I.A., and Plotnikova, E.G., Bacterial consortium as a model for studying the response of the microbial community of the Verkhnekamsk salt mining region to combined pollution, Teor. Prikl. Ekol., 2022, no. 2, pp. 116‒123.
Bernard, T., Jebbar, M., Rassouli, Y., Himdi-Kabbab, S., Hamelin, J., and Blanco, C., Ectoine accumulation and osmotic regulation in Brevibacterium linens, J. Gen. Microb-iol., 1993, vol. 139, pp. 129‒136.
Brill, J., Hoffmann, T., Bleisteiner, M., and Bremer, E., Osmotically controlled synthesis of the compatible solute proline is critical for cellular defense of Bacillus subtilis against high osmolarity, J. Bacteriol., 2011, vol. 193, pp. 5335‒5346.
Busse, H.-J., Review of the taxonomy of the genus Arthrobacter, emendation of the genus Arthrobacter sensu lato, proposal to reclassify selected species of the genus Arthrobacter in the novel genera Glutamicibacter gen. nov., Paeniglutamicibacter gen. nov., Pseudoglutamicibacter gen. nov., Paenarthrobacter gen. nov. and Pseudarthrobacter gen. nov., and emended description of Arthrobacter roseus, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2016, vol. 66, pp. 9‒37.
Busse, H.-J., Wieser, M., and Buczolits, S., Genus Arthrobacter, in Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria, Wiley, 2012, pp. 1–71. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118960608.gbm00118
Cavicchioli, R., On the concept of a psychrophile, ISME J., 2016, vol. 10, pp. 793–795.
Chen, X.-M., Jiang, Y., Li, Y.-T., Zhang, H.-H., Li, J., Chen, X., Zhao, Q., Zhao, J., Si, J., Lin, Z.-W., Zhang, H., Dyson, P., and An, L.-Z., Regulation of expression of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase during cold shock in Arthrobacter strain A3, Extremophiles, 2011, vol. 15, pp. 499–508.
Dmitrieva, O.A., Fedotova, M.V., and Buchner, R., Evidence for cooperative Na+ and Cl− binding by strongly hydrated L-proline, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017, vol. 19, pp. 20 474‒20 483.
Feng, W.-W., Wang, T.-T., Bai, J.-L., Ding, P., Xing, K., Jiang, J.-H., Peng, X., and Qin, S., Glutamicibacter halophytocola sp. nov., an endophytic actinomycete isolated from the roots of a coastal halophyte, Limonium sinense, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2017, vol. 67, pp. 1120–1125.
Friesen, S., Fedotova, M.V., Kruchinin, S.E., and Buchner, R., Hydration and dynamics of l-glutamate ion in aqueous solution, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021, vol. 23, pp. 1590‒1600.
Galinski, E.A., Compatible solutes of halophilic eubacteria: molecular principles, water-solute interaction, stress protection, Experientia, 1993, vol. 49, pp. 487–496.
Gerhardt, P., Manual of Methods for General Bacteriology, Washington, DC: Amer. Soc. Microbiol., 1981.
Hasegawa, S., Uematsu, K., Natsuma, Y., Suda, M., Hiraga, K., Jojima, T., Inui, M., and Yukawa, H., Improvement of the redox balance increases L-valine production by Corynebacterium glutamicum under oxygen deprivation conditions, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2012, vol. 78, p. 865e875.
Hoch, J.C., Baskaran, K., Burr, H., Chin, J., Eghbalnia, H.R., Fujiwara, T., Gryk, M.R., Iwata, T., Kojima, C., Kurisu, G., Maziuk, D., Miyanoiri, Y., Wedell, J.R., Wilburn, C., Yao, H., and Yokochi, M., Biological magnetic resonance data bank, Nucleic Acids Res., 2023, vol. 51, D1, pp. D368–D376.
Jeong, J.-A., Park, S.W., Yoon, D., Kim, S., Kang, H.-Y., and Oh, J.-I., Roles of alanine dehydrogenase and induction of its gene in Mycobacterium smegmatis under respiration-inhibitory conditions, J. Bacteriol., 2018, vol. 200, p. e00152-18.
Kalabin, G.A., Kanitkaya, L.V., and Kushnarev, D.F., Kolichestvennaya spektroskopiya YaMR prirodnogo organicheskogo syr’ya i produktov ego pererabotki (Quantitative NMR Spectroscopy of Natural Orgaic Materials and Products of their Transformation), Moscow: Khimiya, 2000.
Komarova, T.I., Koronelli, T.V., and Timokhina, E.A., The role of low-molecular-weight nitrogen compounds in the osmotolerance of Rhodococcus erythropolis and Arthrobacter globiformis, Microbiology (Moscow), 2002, vol. 71, pp. 139–142.
Kumar, N. and Roy, J.I., Effect of trehalose on protein structure, Protein Sci., 2009, vol. 18, pp. 24–36.
Matveeva, N.I., Voronina, N.A., Borzenkov, I.A., Plakunov, V.K., and Belyaev, S.S., Composition and content of osmoprotectants in oil-oxidizing bacteria grown under different cultivation conditions, Microbiology (Moscow), 1997, vol. 66, pp. 32‒37.
Nagata, S., Adachi, K., and Sano, H., NMR analyses of compatible solutes in a halotolerant Brevibacterium sp., Microbiology (SGM), 1996, vol. 142, pp. 3355–3362.
Narváez-Reinaldo, J.J., Barba, I., González-López, J., Tunnacliffe, A., and Manzanera, M., Rapid method for isolation of desiccation-tolerant strains and xeroprotectants, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 76, pp. 5254–5262.
Nazarov, A.V., Anan’ina, L.N., Gorbunov, A.A., and Pyankova, A.A., Bacteria producing ectoine in the rhizosphere of plants growing on technogenic saline soil, Euras. Soil Sci., 2022, vol. 55. № 8, pp. 1074‒1081.
Nishu, S.D., Hyun, H.R., and Lee, T.K., Complete genome sequence of drought tolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium Glutamicibacter halophytocola DR408, Korean J. Microbiol., 2019, vol. 55, pp. 300‒302.
Qin, S., Feng, W.-W., Zhang, Y.-J., Wang, T.-T., Xiong, Y.-W., and Xing, K., Diversity of bacterial microbiota of coastal halophyte Limonium sinense and amelioration of salinity stress damage by symbiotic plant growth-promoting actinobacterium Glutamicibacter halophytocola KLBMP 5180, A-ppl. Environ. Microbiol., 2018, vol. 84, p. e01533–18.
Raymond, R.L., Microbial oxidation of n-paraffinic hydrocarbons, Develop. Ind. Microbiol., 1961, vol. 2, pp. 23–32.
Santos, R.G., Hurtado, R., Gomes, L.G.R., Profeta, R., Rificie, C., Attilif, A.R., Spier, S.J., Mazzullo, G., Morais-Rodrigues, F., Gomide, A.C.P., Brenig, B., Gala-Garciaa, A., Cuteri, V., de Paula Castro, T.L., Ghosh, P., et al., Complete genome analysis of Glutamicibacter creatinolyticus from mare abscess and comparative genomics provide insight of diversity and adaptation for Glutamicibacter, Gene, 2020, vol. 741, p. 144566.
Singh, R.N., Gaba, S., Yadav, A.N., Gaur, P., Gulati, S., Kaushik, R., and Saxena, A.K., First high quality draft genome sequence of a plant growth promoting and cold active enzyme producing psychrotrophic Arthrobacter agilis strain L77, Stand. Genomic Sci., 2016, vol. 11, p. 54.
Tritsch, G.L. and Moore, G.E., Spontaneous decomposition of glutamine in cell culture media, Exp. Cell Res., 1962, vol. 28, pp. 360‒364.
Vasilets, E.A., Conditions of soil freezing in the Perm krai, Geograficheskoe izuchenie territorial’nykh sistem (Geographic Study of Territorial Systems) (Proc. 15th All-Russian Sci.-Pract. Conf. Stud., Aspir. Young Scientists), Safaryan, A.A., Ed., Perm: Perm Gos. Univ., 2021, pp. 153–157.
Wang, H.-F., Li, L., Zhang, Y.-G., and Hozzein, W.N., Arthrobacter endophyticus sp. nov., an endophytic actinobacterium isolated from root of Salsola affinis, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2015, vol. 65, pp. 2154–2160.
Wise, W.S., The measurement of the aeration of culture media, J. Gen. Microbiol., 1951, vol. 5, pp. 167‒177.
Yamazaki, T., Eyama, S., and Takatsu, A., Concentration measurement of amino acid in aqueous solution by quantitative 1H NMR spectroscopy with iInternal standard method, Anal. Sci., 2017, vol. 33, pp. 369‒373.
Yasid, N.A., Rolfe, M.D., Green, J., and Williamson, M.P., Homeostasis of metabolites in Escherichia coli on transition from anaerobic to aerobic conditions and the transient secretion of pyruvate, Royal Soc. Open Sci., 2016, vol. 3, p. rsos.160187.
Yastrebova, O.V., Malysheva, A.A., and Plotnikova, E.G., Halotolerant terephthalic acid-degrading bacteria of the genus Glutamicibacter, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2022, vol. 58, pp. 590–597.
Zevenhuizen, L.P., Levels of trehalose and glycogen in Arthrobacter globiformis under conditions of nutrient starvation and osmotic stress, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 1992, vol. 61, pp. 61‒68.
Zhou, Y., Han, L.-R., He, H.-W., Sang, B., Yu, D.-L., Feng, J.-T., and Zhang, X., Effects of agitation, aeration and temperature on production of a novel glycoprotein GP-1 by Streptomyces kanasenisi ZX01 and scale-up based on volumetric oxygen transfer coefficient, Molecules, 2018, vol. 23, p. 125.
Funding
This study was carried out within the framework of the State Assignment АААА-А19-119112290008-4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by E. Babchenko
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anan’ina, L.N., Gorbunov, A.A., Shestakova, E.A. et al. Compatible Solutes Accumulated by Glutamicibacter sp. Strain SMB32 in Response to Abiotic Environmental Factors. Microbiology 92, 650–657 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261723601677
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261723601677