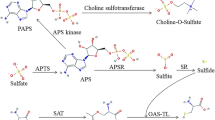
Abstract
Cyanobacteria sense the environmental phosphate level and respond accordingly with the help of a two component regulatory system SphS-SphR orthologous to PhoR-PhoB of E. coli, where SphS act as a sensor kinase and SphR as a response regulator. Under phosphate limiting condition SphS-SphR regulates the expression of many genes including genes which do not have the direct role in metabolism and transport of phosphate. Thus there is some crosstalk mechanism which connects this regulatory system to the other metabolic processes. Different types of enzymes and transporters are expressed by cyanobacteria under phosphate limitation to release and transport the phosphate from different organic compounds present in the environment. Genes encoding these enzymes and transporters contain Pho boxes in their promoter region where SphR binds and regulate their expression under phosphate limitation. The machinery and mechanism of regulation is not uniform in cyanobacteria as it varies in different groups according to their evolutionary adaptations. This review article is summarizing the reports on machinery and mechanism of organophosphate metabolism in cyanobacteria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Henson, B.J., Hesselbrock, S.M., Watson, L.E., and Barnum, S.R., Molecular phylogeny of the heterocystous cyanobacteria (subsections IV and V) based on nif D, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2004, vol. 54, pp. 493–497.
Singh, P., Singh, S.S., Elster, J., and Mishra, A.K., Molecular phylogeny, population genetics, and evolution of heterocystous cyanobacteria using nif H gene sequences, Protoplasma, 2013, vol. 250, pp. 751–764.
Fay, P., Oxygen relations of nitrogen fixation in cyanobacteria, Microbiol. Rev., 1992, vol. 56 pp. 340–373.
Singh, S.K., Singh, S.S., Pandey, V.D., and Mishra, A.K., Factors modulating alkaline phosphatase activity in the diazotrophic rice-field cyanobacterium, Anabaena oryzae, World J. Microb. Biotechnol., 2006, vol. 22, pp. 927–935.
Hedley, M.J., Mortvedt, J.J., Bolan, N.S., and Syers, J.K., Phosphorus fertility management in agroecosystems, in Phosphorus in the Global Environment, Tiessen, H., Ed., 1995, pp. 59–92.
Fardeau, J.C., Dynamics of phosphate in soil. An isotopic outlook, Fert. Res., 1996, vol. 45, pp. 91–100.
Mengel, K., Agronomic measures for better utilization of soil and fertilizer phosphates Eur. J. Agron., 1997, vol. 7, pp. 221–233.
Schweitzer, B. and Simon, M., Growth limitation of planktonic bacteria in a large mesotrophic lake, Microb. Ecol., 1995, vol. 30, pp. 89–104.
Tyrrell, T., The relative influences of nitrogen and phosphorus on oceanic primary production, Nature, 1999, vol. 400, pp. 525–531.
Karl, D.M. and Tien, G., Temporal variability in dissolved phosphorus concentrations in the subtropical North Pacific Ocean, Mar. Chem., 1997, vol. 56, pp. 77–96.
Wu, J.-F., Sunda, W., Boyle, E.A., and Karl, D.M., Phosphate depletion in the western North Atlantic Ocean, Science, 2000, vol. 289, pp. 759–762.
Mills, M.M., Ridame, C., Davey, M., Roche, J.L., and Geider R.J., Iron and phosphorus colimit nitrogen fixation in the eastern tropical North Atlantic, Nature, 2004, vol. 429, pp. 292–294.
Ammerman, J.W., Hood, R.R., Case, D.A., and Cotner, J.B., Phosphorus deficiency in the Atlantic: an emerging paradigm in oceanography, EOS, 2003, vol. 84, pp. 165–170.
Mather, R.L., Reynolds, S.E., Wolff, G.A., Williams, R.G., TorresValdes, S., Woodward, E.M.S., Landolfi, A., Pan, X., Sanders, R., and Achterberg, E.P., Phosphorus cycling in the North and South Atlantic Ocean subtropical gyres, Nat. Geosci., 2008, vol. 1 pp. 439–443.
Lomas, M.W., Burke, A.L., Lomas, D.A., Bell, D.W., Shen, C., Dyhrman, S.T., and Ammerman, J.W., Sargasso Sea phosphorus biogeochemistry: an important role for dissolved organic phosphorus (DOP), Biogeosciences, 2010, vol. 7, pp. 695–710.
Rodríguez, H. and Fraga, R., Phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion, Biotechnol. Adv., 1999, vol. 17, pp. 319–339.
Clark, L.L., Ingall, E.D., and Benner, R., Marine phosphorus is selectively remineralized, Nature, 1998, vol. 393, pp. 426–428.
Kolowith, L.C., Ingall, E.D., and Benner, R., Composition and cycling of marine organic phosphorus, Limnol. Oceanogr., 2001, vol. 46, pp. 309–320.
Makino, K., Shinagawa, H., Amemura, M., Kawamoto, T., Yamada, M., and Nakata, A., Signal transduction in the phosphate regulon of Escherichia coli involves phosphotransfer between PhoR and PhoB proteins, J. Mol. Biol., 1989, vol. 210, pp. 551–559.
Suzuki, S., Ferjani, A., Suzuki, I., and Murata, N., The SphS–SphR two component system is the exclusive sensor for the induction of gene expression in response to phosphate limitation in Synechocystis, J. Biol. Chem., 2004, vol. 279, pp. 13234–13240.
Makino, K., Shinagawa, H., Amemura, M., and Nakata, A., Nucleotide sequence of the phoR gene, a regulatory gene for the phosphate regulon of Escherichia coli, J. Mol. Biol., 1986, vol. 192, pp. 549–556.
Shinagawa, H., Makino, K., Yamada, M., Amemura, M., Sato, T., and Nakata, A., Signal transduction in thephosphate regulon of Escherichia coli: dual function of PhoR as a protein kinase and protein phosphatase, in Phosphate in Microorganisms: Cellular and Molecular Biology, TorrianiGorini, A., et al., Eds., Washington: Am. Soc. Microbiol., 1994, pp. 285–289.
Makino, K., Amemura, M., Kim, S.K., Nakata, A., and Shinagawa, H., Mechanism of transcriptional activation of the phosphate regulon in Escherichia coli, in Phosphate in Microorganisms: Cellular and Molecular Biology, Torriani-Gorini, A., et al., Eds., Washington: Am. Soc. Microbiol., 1994, pp. 5–12.
Vershinina, O.A. and Znamenskaya, L.V., The Pho regulons of bacteria, Microbiology (Moscow), 2002, vol. 71, pp. 497–511.
Su, Z., Olman, V., and Xu, Y., Computational prediction of Pho regulons in cyanobacteria, BMC Genomics, 2007, vol. 8, pp. 156–167.
Aiba, H., Nagaya, M., and Mizuno T., Sensor and regulator proteins from the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC7942 that belong to the bacterial signal transduction protein families: implication in the adaptive response to phosphate limitation, Mol. Microbiol., 1993, vol. 8, pp. 81–91.
Hirani, T.A., Suzuki, I., Murata, N., Hayashi, H., and Eaton-Rye, J.J., Characterization of a two-component signal transduction system involved in the induction of alkaline phosphatase under phosphatelimiting conditions in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, Plant Mol. Biol., 2001, vol. 45, pp. 133–144.
Stock A.M., Robinson, V.L., and Goudreau, P.N., Two-component signal transduction, Annu. Rev. Biochem., 2000, Vol. 69 pp. 183–215.
Mascher, T., Helmann, J.D., and Unden, G., Stimulus perception in bacterial signaltransducing histidine kinases, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 2006, vol. 70 (4): 910–938.
Burut-Archanai, S., Incharoensakdi, A., and Eaton-Rye, J.J. The extended N-terminal region of SphS is required for detection of external phosphate levels in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2009, vol. 378, pp. 383–388.
Toll-Riera, M., Rado-Trilla, N., Martys, F., and Alba, M.M., Role of low-complexity sequences in the formation of novel protein coding sequences, Mol. Biol. Evol., 2012, vol. 29, pp. 883–886.
Kimura, S., Makino, K., Shinagawa, H., Amemura, M., and Nakata, A., Regulation of the phosphate regulon of Escherichia coli: characterization of the promoter of the pstS gene, Mol. Gen. Genet., 1989, vol. 215, pp. 374–380.
Taylor, B.L. and Zhulin, I.B., PAS domains: internal sensors of oxygen, redox potential, and light, MMBR, 1999, vol. 63, pp. 479–506.
Hefti, M.H., Françoijs, K.J., de Vries, S.C., Dixon, R., and Vervoort, J., The PAS fold. A redefinition of the PAS domain based upon structural prediction, Eur. J. Biochem., 2004, vol. 271, pp. 1198–208.
Dutta, R., Qin, L., and Inouye, M., Histidine kinases: diversity of domain organization, Mol. Microbiol., 1999, vol. 34, pp. 633–640.
Okamura, H., Hanaoka, S., Nagadoi, A., Makino, K., and Nishimura, Y., Structural comparison of the PhoB and OmpR DNA-binding/transactivation domains and the arrangement of PhoB molecules on the phosphate box, J. Mol. Biol., 2000, vol. 295, no. 5, pp. 1225–1230.
Juntarajumnong, W., Hirani, T.A. Simpson, J.M., Incharoensakdi, A., and Eaton-Rye, J.J., Phosphate sensing in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803: SphU and the SphS–SphR two-component regulatory system, Arch. Microbiol., 2007, vol. 188, pp. 389–402.
Pitt, F.D., Mazard, S., Humphreys, L., and Scanlan, D.J., Functional characterization of Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 pst1 and pst2 gene clusters reveals a novel strategy for phosphate uptake in a freshwater cyanobacterium, J. Bacteriol., 2010, vol. 192, pp. 3512–3523.
Nagaya, M., Aiba, H., and Mizuno, T., The sphR product, a two-component system response regulator protein, regulates phosphate assimilation in Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942 by binding to two sites upstream from the phoA promoter, J. Bacteriol., 1994, vol. 176, pp. 2210–2215.
Qi, Y., Kobayashi, Y., and Hulett, F.M., The pst operon of Bacillus subtilis has a phosphateregulated promoter and is involved in phosphatentransport but not in regulation of the Pho regulon, J. Bacteriol., 1997, vol. 179, pp. 2534–2539.
Tetu, S.G., Brahamsha, B., Johnson, D.A., Tai, V., Phillippy, K., Palenik, B., and Paulsen, I.T., Microarray analysis of phosphate regulation in the marine cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. WH8102, ISME J., 2009, vol. 3, pp. 835–849.
Ostrowski, M., Mazard, S., Tetu, S.G., Phillippy, K., Johnson, A., Palenik, B., Paulsen, I.T., and Scanlan, D.J., PtrA is required for coordinate regulation of gene expression during phosphate stress in a marine Synechococcus, The ISME J., 2010, vol. 4, pp. 908–921.
Dyhrman, S.T., Chappell, P.D., Haley, S.T., Moffett, J.W., Orchard, E.D., Waterbury, J., and Webb, E.A., Phosphonate utilization by the globally important marine diazotroph Trichodesmium, Nature, 2006, vol. 439, pp. 68–71.
Singh S.K. and Tiwari D.N., Control of alkaline phosphatase activity in Anabaena oryzae Fritsch, J. Plant Physiol., 2000, vol. 157, pp. 467–472.
Subramanian, G., Sekar, S., and Sampoornam, S., Biodegradation and utilization of organophosphorus pesticides by cyanobacteria, Int. Biodeter. Biodegr., 1994, vol. 33, pp. 2129–143.
Megharaj, M., Madhavi, D.R., Sreeinvasaulu, C., Umamaheswari, A., and Venkateswarlu, K., Biodegradation of methyl parathion by soil isolates of microalgae and cyanobacteria, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 1994, vol. 53, pp. 292–297.
Rao, N.N. and Torriani, A., Molecular aspects of phosphate transport in Escherichia coli, Mol. Microbiol., 1990, vol. 4, pp. 1083–1090.
Higgins, C.F., ABC transporters: physiology, structure and mechanism?an overview, Res. Microbiol., 2001, vol. 152, pp. 205–210.
Ray, J.M., Bhaya, D., Block, M.A., and Grossman, A.R., Isolation, transcription, and inactivation of the gene for an atypical alkaline phosphatase of Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942, J. Bacteriol., 1991, vol. 173, pp. 4297–4309.
Wagner, K., Masepoh, B., and Pistorius, E.K., The cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942 contains a second alkaline phosphatase encoded by phoV, Microbiology (UK), 1995, vol 141, pp. 3049–3058.
Zaheer, R., Morton, R., Proudfoot, M., Yakunin, A., and Finan, T.M., Genetic and biochemical properties of an alkaline phosphatase PhoX family protein found in many bacteria, Environ. Microbiol., 2009, vol. 11, pp. 1572–1587.
Eder, S., Shi, L., Jensen, K., Yamane, K., and Hulett, F.M., A Bacillus subtilis secreted phosphodiesterase / alkaline phosphatase is the product of a Pho regulon gene, phoD, Microbiology (UK), 1996, vol. 142, pp. 2041–2047.
Luo, H., Bennera, R., Long, R.A., and Hu, J., Subcellular localization of marine bacterial alkaline phosphatase, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2009, vol. 106, pp. 21219–21223.
Sebastian, M. and Ammerman, J.W., The alkaline phosphatase PhoX is more widely distributed in marine bacteria than the classical PhoA, The ISME J., 2009, vol. 3, pp. 563–572.
Angelini, S., Moreno, R., Gouffi, K., Santini, C., Yamagishi, A., Berenguer, J., and Wu, L., Export of Thermus thermophilus alkaline phosphatase via the twinarginine translocation pathway in Escherichia coli, FEBS Lett., 2001, vol. 506, pp. 103–107.
Kathuria, S. and Martiny, A.C., Prevalence of a calciumbased alkaline phosphatase associated with the marine cyanobacterium Prochlorococcus and other ocean bacteria, Env. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 13, pp. 74–83.
Kageyama, H., Tripathi, K,. Rai, A.K, Cha-um, S., Waditee-Sirisattha. R., and Takabe, T., An alkaline phosphatase/phosphodiesterase, PhoD, induced by salt stress and secreted out of the cells of Aphanothece halophytica, a halotolerant cyanobacterium, Appl Environ. Microbiol., 2011, vol. 77, pp. 5178–5183.
Singh, B.K., Organophosphorusdegrading bacteria: ecology and industrial applications, Nature Rev. Microbiol., 2009, vol.7, pp. 156–164.
Thengodkar, R.R.M. and Sivakami, S., Degradation of Chlorpyrifos by an alkaline phosphatase from the cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis, Biodegradation, 2010, vol. 21, pp. 637–644.
Villarreal-Chiu, J.F., Quinn, J.P., and McGrath, J.W., The genes and enzymes of phosphonate metabolism by bacteria, and their distribution in the marine environment, Front Microbiol., 2012, vol. 26, pp. 3:19.
Kononova, S.V. and Nesmeyanova M.A., Phosphonates and their degradation by microorganisms, Biochemistry (Moscow), 2002, vol. 67 pp. 184–195.
Nowack, B., Environmental chemistry of phosphonates, Water Res., 2003, vol. 37, pp. 2533–2546.
Gomez-Garcia, M.R., Davison, M., Blain-Hartnung, M., Grossman, A. R., and Bhaya, D., Alternative pathways for phosphonate metabolism in thermophilic cyanobacteria from microbial mats, The ISME J., 2011, vol. 5, pp. 141–149.
Ternan, N.G., McGrath, J.W., McMul-lan, G., and Quinn, J.P. Organophosphonates: occurrence, synthesis and biodegradation by microorganisms, World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 1998, vol.14, pp. 635–647.
Adams, M.M., Gomez-Garcia, M.R., Grossman, A.R., and Bhaya. D., Phosphorus deprivation responses and phosphonate utilization in a thermophilic Synechococcus sp. from microbial mats, J. Bacteriol., 2008, vol. 190, pp. 8171–8184.
Jiang, W., Metcalf, W.W., Lee, K., and Wanner, B.L., Molecular cloning, mapping, and regulation of Pho regulon genes for phosphonate breakdown by the phosphonatase pathway of Salmonella typhimurium LT2, J. Bacteriol., 1995, vol. 177, pp. 6411–6421.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tiwari, B., Singh, S., Kaushik, M.S. et al. Regulation of organophosphate metabolism in cyanobacteria. A review. Microbiology 84, 291–302 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261715030200
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261715030200