Abstract
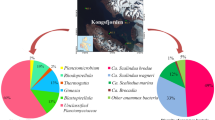
The genes encoding the key metabolic reactions are often used as functional markers for phylogenetic analysis and microbial ecology studies. The composition and structure of the genes encoding ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase (RuBisCO) of various photoautotrophic bacteria, representatives of the order Chromatiales, including collection strains and the strains isolated from saline and soda lakes, were studied in detail. The green-like form I RuBisCO was detected in the majority of the studied strains. In some strains, the genes encoding both form I and form II RuBisCO were present, which has not been previously known for the representatives of this group of bacteria. Moreover, RuBisCO genes were used as functional markers to investigate the autotrophic microbial community inhabiting the upper horizons of bottom sediments of two saline soda lakes and two hypersaline neutral lakes of the Kulunda Steppe. In general, the diversity of autotrophic bacteria in the studied sediment horizons was low. In soda lakes, haloalkaliphilic cyanobacteria and sulfuroxidizing bacteria (SOB) of the genus Halorhodospira were predominant. In saline lakes, halophilic chemoautotrophic SOB Halothiobacillus and Thioalkalivibrio were found, as well as photoautotrophic bacteria of the genus Ectothiorhodosinus and cyanobacteria. Many phylotypes remained unidentified, which indicates the presence of groups of microorganisms with an unknown type of metabolism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sorokin, D.Y., Tourova, T.P., Lysenko, A.M., and Muyzer, G., Diversity of Culturable Halophilic Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria in Hypersaline Habitats, Microbiology (UK), 2006, vol. 152, pp. 3013–3023.
Sorokin, D.Y., Tourova, T.P., Galinski, E.A., Muyzer, G., and Kuenen, J.G., Thiohalorhabdus denitrificans gen. nov., sp. nov., an Extremely Halophilic, Sulfur-Oxidizing, Deep Lineage Gammaproteobacterium from Hypersaline Habitats, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2008, vol. 58, pp. 2890–2897.
Sorokin, D.Y., Tourova, T.P., Muyzer, G., and Kuenen, G.J., Thiohalospira halophila gen. nov., sp. nov. and Thiohalospira alkaliphila sp. nov., Novel Obligately Chemolithoautotrophic, Halophilic, Sulfur-Oxidizing Gammaproteobacteria from Hypersaline Habitats, Int.J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2008, vol. 58, pp. 1685–1692.
Sorokin, D.Y. and Kuenen, J.G., Chemolithotrophic Haloalkaliphiles from Soda Lakes, FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 2005, vol. 52, pp. 287–295.
Gorlenko, V.M., Anoxygenic Phototrophic Bacteria from Soda Lakes, Trudy Instituta mikrobiologii im. S.N.Vinogradskogo. Vyp. XIV. Alkalofil’nye mikrobnye soobshchestva (Proc. Winogradsky Inst. Microbiol., vol. 15. Alkaliphilic Microbial Communities), 2007, Moscow: Nauka, pp. 225–257.
Humayoun, S.B., Bano, N., and Hollibaugh, J.T., Depth Distribution of Microbial Diversity in Mono Lake, a Meromictic Soda Lake in California, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2003, vol. 69, pp. 1030–1042.
Mesbah, N., Abou-El-Ela S., and Wiegel J., Novel and Unexpected Prokaryotic Diversity in Water and Sediments of the Alkaline, Hypersaline Lakes of the Wadi an Natrun, Microb. Ecol., 2007, vol. 54, pp. 598–617.
Giri, B.J., Bano, N., and Hollibaugh, J.T., Distribution of RuBisCO Genotypes along a Redox Gradient in Mono Lake, California, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2004, vol. 70, pp. 3443–3448.
Kovaleva, O.L., Tourova, T.P., Muyzer, G., Kolganova, T.V., and Sorokin, D.Yu., Diversity of RuBisCO and ATP Citrate Lyase Genes in Soda Lake Sediments, FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 2011, vol. 75, pp. 37–47.
Tourova, T.P., Kovaleva, O.L., Sorokin, D.Yu., and Muyzer, G., Ribulose-1.5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase Genes as a Functional Marker for Chemolithoautotrophic Halophilic Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria in Hypersaline Habitats, Microbiology (UK), 2010, vol. 156, pp. 2016–2025.
Spiridonova, E.M., Berg, I.A., Kolganova, T.V., Ivanovskii, R.N., Kuznetsov, B.B, and Turova, T.P., An Oligonucleotide Primer System for Amplification of the Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase Genes of Bacteria of Various Taxonomic Groups, Mikrobiologiya, 2004, vol. 73, no. 3, pp. 377–387 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 73, no. 3, pp. 316–325].
Elsaied, H.E., Kimura, H., and Naganuma, T., Composition of Archaeal, Bacterial, and Eukaryal RuBisCO Genotypes in Three Western Pacific Arc Hydrothermal Vent Systems, Extremophiles, 2007, vol. 11, pp. 191–202.
Alfreider, A., Vogt, C., Hoffmann, D., and Babel, W.I., Diversity of Ribulose-1.5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase Large-Subunit Genes from Groundwater and Aquifer Microorganisms, Microb. Ecol., 2003, vol. 45 P, pp. 317–328.
Stackebrandt, E. and Ebers, J., Taxonomic Parameters Revisited: Tarnished Gold Standards, Microbiology Today, 2006, vol. Nov, pp. 152–155.
Watson, G.M.F. and Tabita, F.R., Microbial Ribulose 1.5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase: a Molecule for Phylogenetic and Enzymological Investigation, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 1997, vol. 146, pp. 13–22.
Tourova, T.P., Spiridonova, E.M., Berg, I.A., Slobodova, N.V., Boulygina, E.S., and Sorokin, D.Y., Phylogeny and Evolution of the Family Ectothiorhodospiraceae Based on Comparison of 16S rRNA, cbbL and nifH Gene Sequences, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2007, vol. 57, pp. 2387–2398.
Viale, A.M., Kobayashi, H., and Akazawa, T., Expressed Genes for Plant-Type Ribulose-1.5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase in the Photosyntetic Bacterium Chromatium vinosum, Which Possesses Two Complete Sets of the Genes, J. Bacteriol., 1989, vol. 5, pp. 2391–2400.
Turova, T.P., Keppen, O.I, Kovaleva, O.L, Slobodova, N.V, Berg, I.A, and Ivanovskii, R.N., Phylogenetic Characterization of the Purple Sulfur Bacterium Thiocapsa sp. BBS by Analysis of the 16S rRNA, cbbL, and nifH Genes and Its Description as Thiocapsa bogorovii sp. nov., a New Species, Mikrobiologiya, 2009, vol. 78, no. 3, pp. 1–12 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 78, no. 3, pp. 339–349].
Kobayashi, H., Viale, A.M., Takabe, T., Akazawa, T., Wada, K., Shinozaki, K., Kobayashi, K., and Sugiura, M., Sequence and Expression of Genes Encoding the Large and Small Subunits of Ribulose 1.5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase from Chromatium vinosum, Gene, 1991, vol. 97, pp. 55–62.
Turova, T.P., Spiridonova, E.M., Berg, I.A., Kuznetsov, B.B., and Sorokin, D.Yu., Phylogeny of Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase Genes in Haloalkaliphilic Obligately Autotrophic Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria of the Genus Thioalkalivibrio, Mikrobiologiya, 2005, vol. 74, no. 3, pp. 378–386 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 74, no. 3, pp. 321–328].
Bryantseva, I.A., Turova, T.P., Kovaleva, O.L., Kostrikina, N.A., Gorlenko, V.M., Ectothiorhodospira magna sp. nov., a New Large Alkaliphilic Purple Sulfur Bacterium, Mikrobiologiya, 2010, vol. 79, no. 6, pp. 782–792 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 79, no. 6, pp. 780–790].
Sorokin, D.Y. and Tourova, T.P., Spiridonova, E. M., Rainey, F. A., and Muyzer, G., Thioclava pacifica gen. nov., sp. nov., a Novel Facultatively Autotrophic, Marine, Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacterium from a Near-Shore Sulfidic Hydrothermal Area, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 55, pp. 1069–1075.
Sorokin, D.Y., Tourova, T.P., Braker, G., and Muyzer, G., Thiohalomonas denitrificans gen. nov., sp. nov. and Thiohalomonas nitratireducens sp. nov., Novel Obligately Chemolithoautotrophic, Moderately Halophilic, Thiodenitrifying Gammaproteobacteria from Hypersaline Habitats, Int.J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2007, vol. 57, pp. 1582–1589.
Kompantseva, E.I., Komova, A.V., and Sorokin, D.Yu., Communities of Anoxygenic Phototrophic Bacteria in the Saline Soda Lakes of the Kulunda Steppe (Altai Krai), Mikrobiologiya, 2010, vol. 79, no. 1, pp. 96–102 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 79, no. 1, pp. 89–95].
Sorokin, D.Y., Tourova, T.P., Bezsoudnova, E.Y., Pol, A., and Muyzer, G., Denitrifcation in a Binary Culture and Thiocyanate Metabolism in Thiohalophilus thiocyanatoxidans gen. nov. sp. nov. — a Moderately Halophilic Chemolithoautotrophic Sulfur-Oxidizing Gammaproteobacterium from Hypersaline Lakes, Arch. Microbiol., 2007, vol. 187, pp. 441–450.
Gerasimenko, L.M., Alkaliphiloc Oxygenic Photosynthetic Organisms, in Trudy Instituta mikrobiologii im. S.N.Vinogradskogo. Vyp. XIV. Alkalofil’nye mikrobnye soobshchestva (Proc. Winogradsky Inst. Microbiol., vol. 15. Alkaliphilic Microbial Communities), 2007, Moscow: Nauka, pp. 88–158.
Gorlenko, V.M., Namsaraev, B.B., Kulyrova, A.V., Zavarzina, D.G., and Zhilina, T.N., The Activity of Sulfate-reducing Bacteria in Bottom Sediments of Soda Lakes of the Southeastern Transbaikal Region, Mikrobiologiya, 1999, vol. 68, no. 5, pp. 664–670 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 68, no. 5, pp. 580–585].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © T.P. Tourova, O.L. Kovaleva, B.K. Bumazhkin, E.O. Patutina, B.B. Kuznetsov, I.A. Bryantseva, V.M. Gorlenko, D.Yu. Sorokin, 2011, published in Mikrobiologiya, 2011, Vol. 80, No. 6, pp. 803–817.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tourova, T.P., Kovaleva, O.L., Bumazhkin, B.K. et al. Application of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase genes as molecular markers for assessment of the diversity of autotrophic microbial communities inhabiting the upper sediment horizons of the saline and soda lakes of the Kulunda Steppe. Microbiology 80, 812–825 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261711060221
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261711060221