Abstract
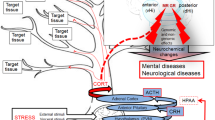
Focal brain injuries (in particular, stroke and traumatic brain injury) induce with high probability the development of delayed (months, years) cognitive and depressive disturbances which are frequently comorbid. The association of these complications with hippocampal alterations (in spite of the lack of a primary injury of this structure), as well as the lack of a clear dependence between the probability of depression and dementia development and primary damage severity and localization served as the basis for a new hypothesis on the distant hippocampal damage as a key link in the pathogenesis of cognitive and psychiatric disturbances. According to this hypothesis, the excess of corticosteroids secreted after a focal brain damage, in particular in patients with abnormal stress-response due to hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPAA) dysfunction, interacts with corticosteroid receptors in the hippocampus inducing signaling pathways which stimulate neuroinflammation and subsequent events including disturbances in neurogenesis and hippocampal neurodegeneration. In this article, the molecular and cellular mechanisms associated with the regulatory role of the HPAA and multiple functions of brain corticosteroid receptors in the hippocampus are analyzed. Functional and structural damage to the hippocampus, a brain region selectively vulnerable to external factors and responding to them by increased cytokine secretion, forms the basis for cognitive function disturbances and psychopathology development. This concept is confirmed by our own experimental data, results of other groups and by prospective clinical studies of post-stroke complications. Clinically relevant biochemical approaches to predict the risks and probability of post-stroke/post-trauma cognitive and depressive disturbances are suggested using the evaluation of biochemical markers of patients’ individual stress-response. Pathogenetically justified ways for preventing these consequences of focal brain damage are proposed by targeting key molecular mechanisms underlying hippocampal dysfunction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACTH:
-
adrenocorticotropic hormone
- Aβ:
-
amyloid β
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- BDNF:
-
brain derived neurotrophic factor
- CNS:
-
central nervous system
- CRH:
-
corticotropin-releasing hormone
- CS:
-
cortisosteroid
- GR:
-
glucocorticoid receptor
- HPAA:
-
hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis
- 11HSD:
-
11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
- IL:
-
interleukin
- MCI:
-
mild cognitive impairment
- MR:
-
mineralocorticoid receptor
- PSD:
-
poststroke depression
- TNF-α:
-
tumor necrosis factor-α
- TrkB:
-
tropomyosin receptor kinase B
References
McEwen, B. S. (1996) Gonadal and adrenal steroids regulate neurochemical and structural plasticity of the hippocampus via cellular mechanisms involving NMDA receptors, Cell. Mol. Neurobiol., 16, 103–116.
De Kloet, E. R., Han, F., and Meijer, O. C. (2008) From the stalk to down under about brain glucocorticoid receptors, stress and development, Neurochem. Res., 33, 637–642.
Uchoa, E. T., Aguilera, G., Herman, J. P., Fiedler, J. L., Deak, T., and de Sousa, M. B. (2014) Novel aspects of glucocorticoid actions, J. Neuroendocrinol., 26, 557–572.
Gulyaeva, N. V. (2019) Functional neurochemistry of the ventral and dorsal hippocampus: stress, depression, dementia and remote hippocampal damage, Neurochem. Res., 44, 1306–1322.
De Kloet, E. R. (2000) Stress in the brain, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 405, 187–198.
De Kloet, E. R., Vreugdenhil, E., Oitzl, M. S., and Joels, M. (1998) Brain corticosteroid receptor balance in health and disease, Endocr. Rev., 19, 269–301.
Meijer, O. C., Buurstede, J. C., and Schaaf, M. J. M. (2019) Corticosteroid receptors in the brain: transcriptional mechanisms for specificity and context-dependent effects, Cell. Mol. Neurobiol., 39, 539–549.
Joels, M. (2018) Corticosteroids and the brain, J. Endocrinol., 238, R121–R130.
Groeneweg, F. L., Karst, H., de Kloet, E. R., and Joels, M. (2011) Rapid non-genomic effects of corticosteroids and their role in the central stress response, J. Endocrinol., 209, 153–167.
Nishi, M., and Kawata, M. (2006) Brain corticosteroid receptor dynamics and trafficking: implications from live cell imaging, Neuroscientist, 12, 119–133.
De Kloet, E. R., Oitzl, M. S., and Schobitz, B. (1994) Cytokines and the brain corticosteroid receptor balance: relevance to pathophysiology of neuroendocrine-immune communication, Psychoneuroendocrinology, 19, 121–134.
De Kloet, E. R., Meijer, O. C., de Nicola, A. F., de Rijk, R. H., and Joels, M. (2018) Importance of the brain corticosteroid receptor balance in metaplasticity, cognitive performance and neuro-inflammation, Front. Neuroendocrinol., 49, 124–145.
Murakami, G., Hojo, Y., Kato, A., Komatsuzaki, Y., Horie, S., Soma, M., Kim, J., and Kawato, S. (2018) Rapid nongenomic modulation by neurosteroids of dendritic spines in the hippocampus: androgen, oestrogen and corticosteroid, J. Neuroendocrinol., 30, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/jne.12561.
Giordano, R., Pellegrino, M., Picu, A., Bonelli, L., Balbo, M., Berardelli, R., Lanfranco, F., Ghigo, E., and Arvat, E. (2006) Neuroregulation of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis in humans: effects of GABA-, miner-alocorticoid-, and GH-secretagogue-receptor modulation, Sci. World J., 6, 1–11.
Joels, M., and de Kloet, E. R. (2017) 30 years of the min-eralocorticoid receptor: the brain mineralocorticoid receptor: a saga in three episodes, J. Endocrinol., 234, T49–T66.
Le Menuet, D., and Lombes, M. (2014) The neuronal min-eralocorticoid receptor: from cell survival to neurogenesis, Steroids, 91, 11–19.
Odermatt, A., and Kratschmar, D. V. (2012) Tissue-specific modulation of mineralocorticoid receptor function by 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases: an overview, Mol. Cell. Endocrinol., 350, 168–186.
Kellendonk, C., Gass, P., Kretz, O., Schutz, G., and Tronche, F. (2002) Corticosteroid receptors in the brain: gene targeting studies, Brain Res. Bull., 57, 73–83.
Saaltink, D. J., and Vreugdenhil, E. (2014) Stress, glucocorticoid receptors, and adult neurogenesis: a balance between excitation and inhibition? Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 71, 2499–2515.
Vitellius, G., Trabado, S., Bouligand, J., Delemer, B., and Lombes, M. (2018) Pathophysiology of glucocorticoid signaling, Ann. Endocrinol. (Paris), 79, 98–106.
Van Weert, L. T. C. M., Buurstede, J. C., Sips, H. C. M., Mol, I. M., Puri, T., Damsteegt, R., Roozendaal, B., Sarabdjitsingh, R. A., and Meijer, O. C. (2019) Mechanistic insights in NeuroD potentiation of mineralocorticoid receptor signaling, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 20, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071575.
Joels, M., and Karst, H. (2012) Corticosteroid effects on calcium signaling in limbic neurons, Cell. Calcium, 51, 277–283.
Lapp, H. E., Bartlett, A. A., and Hunter, R. G. (2019) Stress and glucocorticoid receptor regulation of mitochondrial gene expression, J. Mol. Endocrinol., 62, R121–R128.
Reul, J. M. (2014) Making memories of stressful events: a journey along epigenetic, gene transcription, and signaling pathways, Front. Psychiatry, 5, 5.
Mifsud, K. R., Gutierrez-Mecinas, M., Trollope, A. F., Collins, A., Saunderson, E. A., and Reul, J. M. (2011) Epigenetic mechanisms in stress and adaptation, Brain Behav. Immun., 25, 1305–1315.
Bennett, M. R., and Lagopoulos, J. (2014) Stress and trauma: BDNF control of dendritic-spine formation and regression, Prog. Neurobiol., 112, 80–99.
Gulyaeva, N. V. (2017) Interplay between brain BDNF and glutamatergic systems: a brief state of the evidence and association with the pathogenesis of depression, Biochemistry (Moscow), 82, 301–307.
Leal, G., Bramham, C. R., and Duarte, C. B. (2017) BDNF and hippocampal synaptic plasticity, Vitam. Horm., 104, 153–195.
Suri, D., and Vaidya, V. A. (2013) Glucocorticoid regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor: relevance to hippocampal structural and functional plasticity, Neuroscience, 239, 196–213.
Linz, R., Puhlmann, L. M. C., Apostolakou, F., Mantzou, E., Papassotiriou, I., Chrousos, G. P., Engert, V., and Singer, T. (2019) Acute psychosocial stress increases serum BDNF levels: an antagonistic relation to cortisol but no group differences after mental training, Neuropsychopharmacology, 44, 1797–1804, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-019-0391-y.
Daskalakis, N. P., De Kloet, E. R., Yehuda, R., Malaspina, D., and Kranz, T. M. (2015) Early life stress effects on glucocorticoid—BDNF interplay in the hippocampus, Front. Mol. Neurosci., 8, 68.
Finsterwald, C., and Alberini, C. M. (2014) Stress and glucocorticoid receptor-dependent mechanisms in long-term memory: from adaptive responses to psychopathologies, Neurobiol. Learn. Mem., 112, 17–29.
Sapolsky, R. M. (1990) Glucocorticoids, hippocampal damage and the glutamatergic synapse, Prog. Brain Res., 86, 13–23.
Popoli, M., Yan, Z., McEwen, B. S., and Sanacora, G. (2011) The stressed synapse: the impact of stress and glucocorticoids on glutamate transmission, Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 13, 22–37.
Chaouloff, F., and Groc, L. (2011) Temporal modulation of hippocampal excitatory transmission by corticosteroids and stress, Front. Neuroendocrinol., 32, 25–42.
Goujon, E., Lay E. S., Parnet, P., and Dantzer, R. (1997) Regulation of cytokine gene expression in the central nervous system by glucocorticoids: mechanisms and functional consequences, Psychoneuroendocrinology, 22(Suppl. 1), S75–S80.
Duque Ede, A., and Munhoz, C. D. (2016) The proinflammatory effects of glucocorticoids in the brain, Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne), 7, 78.
Pariante, C. M. (2017) Why are depressed patients inflamed? A reflection on 20 years of research on depression, glucocorticoid resistance and inflammation, Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol., 27, 554–559.
Walker, F. R., Nilsson, M., and Jones, K. (2013) Acute and chronic stress-induced disturbances of microglial plasticity, phenotype and function, Curr. Drug Targets, 14, 1262–1276.
Gadek-Michalska, A., Tadeusz, J., Rachwalska, P., and Bugajski, J. (2013) Cytokines, prostaglandins and nitric oxide in the regulation of stress-response systems, Pharmacol. Rep., 65, 1655–1662.
Johnson, J. D., Barnard, D. F., Kulp, A. C., and Mehta, D. M. (2019) Neuroendocrine regulation of brain cytokines after psychological stress, J. Endocr. Soc., 3, 1302–1320.
Deak, T., Quinn, M., Cidlowski, J. A., Victoria, N. C., Murphy, A. Z., and Sheridan, J. F. (2015). Neuroimmune mechanisms of stress: sex differences, developmental plasticity, and implications for pharmacotherapy of stress-related disease, Stress, 18, 367–380.
Bekhbat, M., Rowson, S. A., and Neigh, G. N. (2017) Checks and balances: the glucocorticoid receptor and NFkB in good times and bad, Front. Neuroendocrinol., 46, 15–31.
De Kloet, E. R., and Joels, M. (2017) Brain mineralocorticoid receptor function in control of salt balance and stress-adaptation, Physiol. Behav., 178, 13–20.
Brocca, M. E., Pietranera, L., de Kloet, E. R., and De Nicola, A. F. (2019) Mineralocorticoid receptors, neuroinflammation and hypertensive encephalopathy, Cell. Mol. Neurobiol., 39, 483–492.
Frank, M. G., Weber, M. D., Watkins, L. R., and Maier, S. F. (2015) Stress sounds the alarmin: the role of the danger-associated molecular pattern HMGB1 in stress-induced neuroinflammatory priming, Brain Behav. Immun., 48, 1–7.
Pearson-Leary, J., Osborne, D. M., and McNay, E. C. (2016) Role of glia in stress-induced enhancement and impairment of memory, Front. Integr. Neurosci., 9, 63.
Van Olst, L., Bielefeld, P., Fitzsimons, C. P., de Vries, H. E., and Schouten, M. (2018) Glucocorticoid-mediated modulation of morphological changes associated with aging in microglia, Aging Cell, 17, e12790.
McEwen, B. S. (1997) Possible mechanisms for atrophy of the human hippocampus, Mol. Psychiatry, 2, 255–262.
Vyas, S., Rodrigues, A. J., Silva, J. M., Tronche, F., Almeida, O. F., Sousa, N., and Sotiropoulos, I. (2016) Chronic stress and glucocorticoids: from neuronal plasticity to neurodegeneration, Neural Plast., 2016, 6391686.
Libro, R., Bramanti, P., and Mazzon, E. (2017) Endogenous glucocorticoids: role in the etiopathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease, Neuro Endocrinol. Lett., 38, 1–12.
Vyas, S., and Maatouk, L. (2013) Contribution of glucocorticoids and glucocorticoid receptors to the regulation of neurodegenerative processes, CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets, 12, 1175–1193.
Ouanes, S., and Popp, J. (2019) High cortisol and the risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease: a review of the literature, Front. Aging Neurosci., 11, 43.
Paul, S., Jeon, W. K., Bizon, J. L., and Han, J. S. (2015) Interaction of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons with the glucocorticoid system in stress regulation and cognitive impairment, Front. Aging Neurosci., 7, 43.
Kootar, S., Frandemiche, M. L., Dhib, G., Mouska, X., Lorivel, T., Poupon-Silvestre, G., Hunt, H., Tronche, F., Bethus, I., Barik, J., and Marie, H. (2018) Identification of an acute functional cross-talk between amyloid-β and glucocorticoid receptors at hippocampal excitatory synapses, Neurobiol. Dis., 118, 117–128.
Bisht, K., Sharma, K., and Tremblay, M. E. (2018) Chronic stress as a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease: roles of microglia-mediated synaptic remodeling, inflammation, and oxidative stress, Neurobiol. Stress, 9, 9–21.
Pomara, N., Greenberg, W. M., Branford, M. D., and Doraiswamy, P. M. (2003) Therapeutic implications of HPA axis abnormalities in Alzheimer’s disease: review and update, Psychopharmacol. Bull., 37, 120–134.
Numakawa, T., Odaka, H., and Adachi, N. (2017) Actions of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and glucocorticoid stress in neurogenesis, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 18, E2312, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112312.
Fitzsimons, C. P., Herbert, J., Schouten, M., Meijer, O. C., Lucassen, P. J., and Lightman, S. (2016) Circadian and ultradian glucocorticoid rhythmicity: implications for the effects of glucocorticoids on neural stem cells and adult hippocampal neurogenesis, Front. Neuroendocrinol., 41, 44–58.
Lucassen, P. J., Oomen, C. A., Naninck, E. F., Fitzsimons, C. P., van Dam, A. M., Czeh, B., and Korosi, A. (2015) Regulation of adult neurogenesis and plasticity by (early) stress, glucocorticoids, and inflammation, Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol., 7, a021303.
Schoenfeld, T. J., and Gould, E. (2012). Stress, stress hormones, and adult neurogenesis, Exp. Neurol., 233, 12–21.
Lupien, S. J., and Lepage, M. (2001) Stress, memory, and the hippocampus: can’t live with it, can’t live without it, Behav. Brain Res., 127, 137–158.
Herman, J. P., Ostrander, M. M., Mueller, N. K., and Figueiredo, H. (2005) Limbic system mechanisms of stress regulation: hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis, Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry, 29, 1201–1213.
Joels, M., Pasricha, N., and Karst, H. (2013) The interplay between rapid and slow corticosteroid actions in brain, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 719, 44–52.
Zunszain, P. A., Anacker, C., Cattaneo, A., Carvalho, L. A., and Pariante, C. M. (2011) Glucocorticoids, cytokines and brain abnormalities in depression, Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry, 35, 722–729.
Leonard, B. (2000) Stress, depression and the activation of the immune system, World J. Biol. Psychiatry, 1, 17–25.
Oglodek, E., Szota, A., Just, M., Mos, D., and Araszkiewicz, A. (2014) The role of the neuroendocrine and immune systems in the pathogenesis of depression, Pharmacol. Rep., 66, 776–781.
Silverman, M. N., and Sternberg, E. M. (2012) Glucocorticoid regulation of inflammation and its functional correlates: from HPA axis to glucocorticoid receptor dysfunction, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 1261, 55–63.
Leonard, B. E. (2018) Inflammation and depression: a causal or coincidental link to the pathophysiology? Acta Neuropsychiatr., 30, 1–16.
Makhija, K., and Karunakaran, S. (2013) The role of inflammatory cytokines on the etiopathogenesis of depression, Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry, 47, 828–839.
Bauer, M. E., and Teixeira, A. L. (2019) Inflammation in psychiatric disorders: what comes first? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 437, 57–67.
Maes, M., Yirmyia, R., Noraberg, J., Brene, S., Hibbeln, J., Perini, G., Kubera, M., Bob, P., Lerer, B., and Maj, M. (2009) The inflammatory and neurodegenerative (I&ND) hypothesis of depression: leads for future research and new drug developments in depression, Metab. Brain Dis., 24, 27–53.
Kim, Y. K., Na, K. S., Myint, A. M., and Leonard, B. E. (2016) The role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in neuroinflammation, neurogenesis and the neuroendocrine system in major depression, Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry, 64, 277–284.
Barnard, D. F., Gabella, K. M., Kulp, A. C., Parker, A. D., Dugan, P. B., and Johnson, J. D. (2019) Sex differences in the regulation of brain IL-1β in response to chronic stress, Psychoneuroendocrinology, 103, 203–211.
Cattaneo, A., and Riva, M. A. (2016) Stress-induced mechanisms in mental illness: a role for glucocorticoid signaling, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol., 160, 169–174.
Zimmermann, C. A., Arloth, J., Santarelli, S., Loschner, A., Webe, P., Schmidt, M. V., Spengler, D., and Binder, E. B. (2019) Stress dynamically regulates co-expression networks of glucocorticoid receptor-dependent MDD and SCZ risk genes, Transl. Psychiatry, 9, 41, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-019-0373-1.
Gray, J. D., Kogan, J. F., Marrocco, J., and McEwen, B. S. (2017) Genomic and epigenomic mechanisms of glucocorticoids in the brain, Nat. Rev. Endocrinol., 13, 661–673.
Sousa, N., and Almeida, O. F. (2002) Corticosteroids: sculptors of the hippocampal formation, Rev. Neurosci., 13, 59–84.
Chen, J., Wang, Z. Z., Zhang, S., Chu, S. F., Mou, Z., and Chen, N. H. (2019) The effects of glucocorticoids on depressive and anxiety-like behaviors, mineralocorticoid receptor-dependent cell proliferation regulates anxiety-like behaviors, Behav. Brain Res., 362, 288–298.
Li, Y., Qin, J., Yan, J., Zhang, N., Xu, Y., Zhu, Y., Sheng, L., Zhu, X., and Ju, S. (2018) Differences of physical vs. psychological stress: evidences from glucocorticoid receptor expression, hippocampal subfields injury, and behavioral abnormalities, Brain Imaging Behav., doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9956-3 [Epub ahead of print].
Leonard, B. E. (2007) Inflammation, depression and dementia: are they connected? Neurochem. Res., 32, 1749–1756.
Herbert, J., and Lucassen, P. J. (2016) Depression as a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease: genes, steroids, cytokines and neurogenesis — what do we need to know? Front. Neuroendocrinol., 41, 153–171.
Kino, T. (2015) Stress, glucocorticoid hormones, and hippocampal neural progenitor cells: implications to mood disorders, Front. Physiol., 6, 230.
Levada, O. A., and Troyan, A. S. (2018) Poststroke depression biomarkers: a narrative review, Front. Neurol., 16, 577.
Ben Assayag, E., Korczyn, A. D., Giladi, N., Goldbourt, U., Berliner, A. S., Shenhar-Tsarfaty, S., Kliper, E., Hallevi, H., Shopin, L., Hendler, T., Baashat, D. B., Aizenstein, O., Soreq, H., Katz, N., Solomon, Z., Mike, A., Usher, S., Hausdorff, J. M., Auriel, E., Shapira, I., and Bornstein, N. M. (2012) Predictors for poststroke outcomes: the Tel Aviv Brain Acute Stroke Cohort (TABASCO) study protocol, Int. J. Stroke, 7, 341–347.
Molad, J., Hallevi, H., Korczyn, A. D., Kliper, E., Auriel, E., Bornstein, N. M., and Ben Assayag, E. (2019) Vascular and neurodegenerative markers for the prediction of post-stroke cognitive impairment: results from the TABASCO study, J. Alzheimer’s Dis., 70, 889–898, doi: https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-190339.
Molad, J., Ben-Assayag, E., Korczyn, A. D., Kliper, E., Bornstein, N. M., Hallevi, H., and Auriel, E. (2018) Clinical and radiological determinants of transient symptoms associated with infarction (TSI), J. Neurol. Sci., 390, 195–199.
Kliper, E., Ben Assayag, E., Tarrasch, R., Artzi, M., Korczyn, A. D., Shenhar-Tsarfaty, S., Aizenstein, O., Hallevi, H., Mike, A., Shopin, L., Bornstein, N. M., and Ben Bashat, D. (2014) Cognitive state following stroke: the predominant role of preexisting white matter lesions, PLoS One, 9, e105461.
Ben Assayag, E., Tene, O., Korczyn, A. D., Shopin, L., Auriel, E., Molad, J., Hallevi, H., Kirschbaum, C., Bornstein, N. M., Shenhar-Tsarfaty, S., Kliper, E., and Stalder, T. (2017) High hair cortisol concentrations predict worse cognitive outcome after stroke: results from the TABASCO prospective cohort study, Psychoneuroendocrinology, 82, 133–139.
Tene, O., Hallevi, H., Korczyn, A. D., Shopin, L., Molad, J., Kirschbaum, C., Bornstein, N. M., Shenhar-Tsarfaty, S., Kliper, E., Auriel, E., Usher, S., Stalder, T., and Ben Assayag, E. (2018) The price of stress: high bedtime salivary cortisol levels are associated with brain atrophy and cognitive decline in stroke survivors. Results from the TABASCO prospective cohort study, J. Alzheimer’s Dis., 65, 1365–1375.
Tene, O., Shenhar-Tsarfaty, S., Korczyn, A. D., Kliper, E., Hallevi, H., Shopin, L., Auriel, E., Mike, A., Bornstein, N. M., and Assayag, E. B. (2016) Depressive symptoms following stroke and transient ischemic attack: is it time for a more intensive treatment approach? Results from the TABASCO cohort study, J. Clin. Psychiatry, 77, 673–680.
Kliper, E., Ben Assayag, E., Korczyn, A. D., Auriel, E., Shopin, L., Hallevi, H., Shenhar-Tsarfaty, S., Mike, A., Artzi, M., Klovatch, I., Bornstein, N. M., and Ben Bashat, D. (2016) Cognitive state following mild stroke: a matter of hippocampal mean diffusivity, Hippocampus, 26, 161–169.
Herman, J. P., McKlveen, J. M., Ghosal, S., Kopp, B., Wulsin, A., Makinson, R., Scheimann, J., and Myers, B. (2016) Regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical stress response, Compr. Physiol., 6, 603–621.
Pochigaeva, K., Druzhkova, T., Yakovlev, A., Onufriev, M., Grishkina, M., Chepelev, A., Guekht, A., and Gulyaeva, N. (2017) Hair cortisol as a marker of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity in female patients with major depressive disorder, Metab. Brain Dis., 32, 577–583.
Druzhkova, T., Pochigaeva, K., Yakovlev, A., Kazimirova, E., Grishkina, M., Chepelev, A., Guekht, A., and Gulyaeva, N. (2019) Acute stress response to a cognitive task in patients with major depressive disorder: potential metabolic and proinflammatory biomarkers, Metab. Brain Dis., 34, 621–629.
Joels, M., Karst, H., and Sarabdjitsingh, R. A. (2018) The stressed brain of humans and rodents, Acta Physiol. (Oxf.), 223, e13066.
De Kloet, E. R., Otte, C., Kumsta, R., Kok, L., Hillegers, M. H., Hasselmann, H., Kliegel, D., and Joels, M. (2016) Stress and depression: a crucial role of the mineralocorticoid receptor, J. Neuroendocrinol., 28, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/jne.12379.
Martocchia, A., Curto, M., Toussan, L., Stefanelli, M., and Falaschi, P. (2011) Pharmacological strategies against glucocorticoid-mediated brain damage during chronic disorders, Recent Pat. CNS Drug Discov., 6, 196–204.
Muller, M., Holsboer, F., and Keck, M. E. (2002) Genetic modification of corticosteroid receptor signaling: novel insights into pathophysiology and treatment strategies of human affective disorders, Neuropeptides, 36, 117–131.
Sutanto, W., and de Kloet, E. R. (1991) Mineralocorticoid receptor ligands: biochemical, pharmacological, and clinical aspects, Med. Res. Rev., 11, 617–639.
Gomez-Sanchez, E. P. (2016) Third-generation mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists: why do we need a fourth? J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol., 67, 26–38.
Wang, W., Liu, L., Yang, X., Gao, H., Tang, Q. K., Yin, L. Y., Yin, X. Y., Hao, J. R., Geng, D. Q., and Gao, C. (2019) Ketamine improved depressive-like behaviors via hippocampal glucocorticoid receptor in chronic stress induced-susceptible mice, Behav. Brain Res., 364, 75–84.
Scheimann, J. R., Mahbod, P., Morano, R., Frantz, L., Packard, B., Campbell, K., and Herman, J. P. (2018) Deletion of glucocorticoid receptors in forebrain GABAergic neurons alters acute stress responding and passive avoidance behavior in female mice, Front. Behav. Neurosci., 12, 325.
Stepanichev, M., Onufriev, M., Aniol, V., Freiman, S., Brandstaetter, H., Winter, S., Lazareva, N., Guekht, A., and Gulyaeva, N. (2017) Effects of Cerebrolysin on nerve growth factor system in the aging rat brain, Restor. Neurol. Neurosci., 35, 571–581.
Joels, M. (2008) Functional actions of corticosteroids in the hippocampus, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 583, 312–321.
Gulyaeva, N. V. (2017) Molecular mechanisms of neuroplasticity: an expanding universe, Biochemistry (Moscow), 82, 237–242.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, grant no. 18-00-00125 (stress, depression), and the Russian Academy of Sciences Presidium Program “Fundamental bases of physiological adaptation technologies” (remote hippocampal damage).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Compliance with ethical norms
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by the author.
Published in Russian in Biokhimiya, 2019, Vol. 84, No. 11, pp. 1622–1648.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gulyaeva, N.V. Biochemical Mechanisms and Translational Relevance of Hippocampal Vulnerability to Distant Focal Brain Injury: The Price of Stress Response. Biochemistry Moscow 84, 1306–1328 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297919110087
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297919110087