Abstract
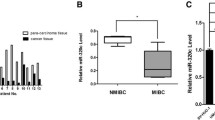
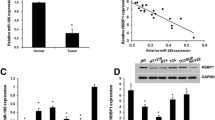
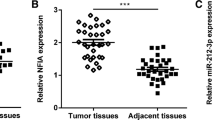
In our study we examined the role of microRNA-294 (miR-294) in bladder cancer and related mechanisms. Realtime polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was performed to determine the expression level of miR-294. Western blot was used to determine the expression of NRAS, mainly factors in the PI3K/AKT and JAK/STAT pathways. Cell counting kit8 assay, clonogenic assay, wound-healing assay, transwell and flow cytometry were used to explore, respectively, cell proliferation, survival, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of bladder cancer cell line T24. The expressions of miR-294 in bladder cancer cells including J82, HT1376, T24, and SW780 were significantly increased compared to those in human bladder epithelium cells (both HCV29 and SV-HUC-1). The proliferation rate, surviving fraction, migration, and invasion of T24 cells in miR-294 mimetic transfected group were significantly increased, while they were significantly decreased by miR294 inhibitor transfection. Moreover, miR-294 suppression could increase the apoptotic rate of T24 cells. In addition, drug resistance of T24 cells to cisplatin was increased in miR-294 mimetic-treated group, while it was decreased by miR-294 inhibitor compared to empty control. Overexpression of miR-294 could upregulate NRAS expression in T24 cells and activate PI3K/AKT and JAK/STAT pathways. We found that miR-294 expression was positively related with proliferation and motility of T24 cells. Moreover, miR-294 suppression could promote the sensitivity of T24 cells to cisplatin. We also found miR-294 could upregulate NRAS and activate the PI3K/AKT and JAK/STAT pathways in T24 cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal, A., Siegel, R., Ward, E., Hao, Y., Xu, J., and Thun, M. J. (2009) Cancer statistics, 2009 CA, Cancer J. Clin., 59, 225–249.
Cheung, G., Sahai, A., Billia, M., Dasgupta, P., and Khan, M. S. (2013) Recent advances in the diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer, BMC Med., 11, 1–8.
Martyn-Hemphill, C., Mak, D., Khan, M. S., Challacombe, B. J., and Bishop, C. V. (2013) Recent advances in diagnosis and treatment of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder, Int. J. Surg., 11, 749–752.
Moyer, V. A. (2011) Screening for bladder cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommendation statement, Ann. Int. Med., 155, 246–251.
Yafi, F. A., Aprikian, A. G., and Chin, J. L. (2011) Contemporary outcomes of 2287 patients with bladder cancer who were treated with radical cystectomy: a Canadian multicentre experience, BJU Int., 108, 539–545.
Dalbagni, G., Vora, K., Kaag, M., Cronin, A., Bochner, B., Donat, S. M., and Herr, H. W. (2009) Clinical outcome in a contemporary series of restaged patients with clinical T1 bladder cancer, Eur. Urol., 56, 903–910.
Richards, K. A., Smith, N. D., and Steinberg, G. D. (2014) The importance of transurethral resection of bladder tumor in the management of nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer: a systematic review of novel technologies, J. Urol., 191, 1655–1664.
Herr, H. W., and Donat, S. M. (2008) Quality control in transurethral resection of bladder tumours, BJU Int., 102, 1242–1246.
Filipowicz, W., Bhattacharyya, S. N., and Sonenberg, N. (2008) Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat. Rev. Genet., 9, 102–114.
Lagos-Quintana, M., Rauhut, R., Lendeckel, W., and Tuschl, T. (2001) Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs, Science, 294, 853–858.
Lawrie, C. H. (2013) MicroRNAs as Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors. MicroRNAs in Medicine, Wiley, Hoboken, NJ, pp. 223–243.
Feng, Y., Liu, J., Kang, Y., He, Y., Liang, B., Yang, P., and Yu, Z. (2014) miR-19a acts as an oncogenic microRNA and is up-regulated in bladder cancer, J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res., 33, 1–10.
Gan, Y., Yao, W., Wei, X., Li, H., Hua, X., and Lang, B. (2014) MicroRNA-34a functions as an anti-metastatic microRNA and suppresses angiogenesis in bladder cancer by directly targeting CD44, J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res., 33, 1–13.
Dyrskjot, L., Ostenfeld, M. S., Bramsen, J. B., Silahtaroglu, A. N., Lamy, P., Ramanathan, R., Fristrup, N., Jensen, J. L., Andersen, C. L., Zieger, K., Kauppinen, S., Ulhoi, B. P., Kjems, J., Borre, M., and Orntoft, T. F. (2009) Genomic profiling of microRNAs in bladder cancer: miR-129 is associated with poor outcome and promotes cell death in vitro, Cancer Res., 69, 4851–4860.
Ichimi, T., Enokida, H., Okuno, Y., Kunimoto, R., Chiyomaru, T., Kawamoto, K., Kawahara, K., Toki, K., Kawakami, K., Nishiyama, K., Tsujimoto, G., Nakagawa, M., and Seki, N. (2009) Identification of novel microRNA targets based on microRNA signatures in bladder cancer, Int. J. Cancer, 125, 345–352.
Chen, C., Ridzon, D., Lee, C. T., Blake, J., Sun, Y., and Strauss, W. M. (2007) Defining embryonic stem cell identity using differentiation-related microRNAs and their potential targets, Mammal. Genome (Official J. Int. Mammal. Genome Soc.), 18, 316–327.
Houbaviy, H. B., Dennis, L., Jaenisch, R., and Sharp, P. A. (2005) Characterization of a highly variable eutherian microRNA gene, RNA (A Publ. RNA Soc.), 11, 1245–1257.
Wang, Y., Baskerville, S., Shenoy, A., Babiarz, J. E., Baehner, L., and Blelloch, R. (2008) Embryonic stem cellspecific microRNAs regulate the G1–S transition and promote rapid proliferation, Nat. Genet., 40, 1478–1483.
Parkin, D. M., Bray, F., Ferlay, J., and Pisani, P. (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002, Cancer J. Clin., 55, 74–108.
Nobori, T. (1994) Deletions of the cyclin-dependent kinase-4 inhibitor gene in multiple human cancers, Nature, 368, 753–756.
Tricoli, J. V., and Jacobson, J. W. (2007) MicroRNA: potential for cancer detection, diagnosis, and prognosis, Cancer Res., 67, 4553–4555.
Hammond, S. M. (2007) MicroRNAs as tumor suppressors, Nat. Genet., 39, 582–583.
Lee, B. R., Feinbaum, R., and Ambros, V. (2012) The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14, Cell, 75, 843–854.
Kamb, A. (1994) A cell regulator potentially involved in genesis of many tumor types, Science, 264, 436–440.
Androulakakis, P. A., Davaris, P., Karayannis, A., Michael, V., and Aghioutantis, C. (1992) Urothelial tumors of the bladder, Child Nephrol. Urol., 12, 32–34.
Han, Y., Chen, J., Zhao, X., Liang, C., Wang, Y., Sun, L., Jiang, Z., Zhang, Z., Yang, R., and Chen, J. (2011) MicroRNA expression signatures of bladder cancer revealed by deep sequencing, PLoS One, 6, e18286.
Lin, T., Dong, W., Huang, J., Pan, Q., Fan, X., Zhang, C., and Huang, L. (2009) MicroRNA-143 as a tumor suppressor for bladder cancer, J. Urol., 181, 1372–1380.
Noguchi, S., Yasui, Y., Iwasaki, J., Kumazaki, M., Yamada, N., Naito, S., and Akao, Y. (2012) Replacement treatment with microRNA-143 and -145 induces synergistic inhibition of the growth of human bladder cancer cells by regulating PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways, Cancer Lett., 328, 353–361.
Uchino, K., Takeshita, F., Takahashi, R. U., Kosaka, N., Fujiwara, K., Naruoka, H., Sonoke, S., Yano, J., Sasaki, H., Nozawa, S., et al. (2013) Therapeutic effects of microRNA582–5p and -3p on the inhibition of bladder cancer progression, Mol. Ther. (J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther.), 21, 610–619.
Xu, X., Chen, H., Lin, Y., Hu, Z., Mao, Y., Wu, J., Xu, X., Zhu, Y., Li, S., and Zheng, X. (2013) MicroRNA-409–3p inhibits migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells via targeting c-Met, Mol. Cells, 36, 62–68.
Majid, S., Dar, A. A., Saini, S., Deng, G., Chang, I., Greene, K., Tanaka, Y., Dahiya, R., and Yamamura, S. (2013) MicroRNA-23b functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating Zeb1 in bladder cancer, PLoS One, 8, e67686.
Mao, X. P., Zhang, L. S., Huang, B., Zhou, S. Y., Liao, J., Chen, L. W., Qiu, S. P., and Chen, J. X. (2015) Mir-135a enhances cellular proliferation through post-transcriptionally regulating PHLPP2 and FOXO1 in human bladder cancer, J. Transl. Med., 13, 1–13.
Jakob, J. A., Bassett, R. L., Jr., Ng, C. S., Curry, J. L., Joseph, R. W., Alvarado, G. C., Rohlfs, M. L., Richard, J., Gershenwald, J. E., Kim, K. B., Lazar, A. J., Hwu, P., and Davies, M. A. (2012) NRAS mutation status is an independent prognostic factor in metastatic melanoma, Cancer, 118, 4014–4023.
Kotoula, V., Sozopoulos, E., Litsiou, H., Fanourakis, G., Koletsa, T., Voutsinas, G., Tseleni-Balafouta, S., Mitsiades, C. S., Wellmann, A., and Mitsiades, N. (2009) Mutational analysis of the BRAF, RAS and EGFR genes in human adrenocortical carcinomas, Endocrine Rel. Cancer, 16, 565–572.
Vaughn, C. P., Zobell, S. D., Furtado, L. V., Baker, C. L., and Samowitz, W. S. (2011) Frequency of KRAS, BRAF, and NRAS mutations in colorectal cancer, Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 50, 307–312.
Mulligan, G., Lichter, D. I., Bacco, A. D., Blakemore, S. J., Berger, A., Koenig, E., Bernard, H., Trepicchio, W., Li, B., and Neuwirth, R. (2014) Mutation of NRAS but not KRAS significantly reduces myeloma sensitivity to singleagent bortezomib therapy, Blood, 123, 632–639.
Irahara, N., Baba, Y. K., Shima, K., Yan, L., Dias, S. D., Iafrate, A. J., Fuchs, C. S., Haigis, K. M., and Ogino, S. (2010) NRAS mutations are rare in colorectal cancer, Diagn. Mol. Pathol. (Am. J. Surg. Pathol.), Part B, 19, 157–163.
Fry, M. J. (2000) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase signalling in breast cancer: how big a role might it play? Breast Cancer Res., 3, 304–312.
Martinez, L., Anel, A., Sierra, J., Pineiro, A., Naval, J., and Alava, M. (2000) Tyrosine phosphorylation of the p85 subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase correlates with high proliferation rates in sublines derived from the Jurkat leukemia, Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol., 32, 435–445.
Krasilnikov, M., Adler, V., Fuchs, S. Y., Zheng, D., Haimovitz-Friedman, A., Herlyn, M., and Ronai, Z. E. (1999) Contribution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to radiation resistance in human melanoma cells, Mol. Carcinogen., 24, 64–69.
Lin, X., Bohle, A., Dohrmann, P., Leuschner, I., Schulz, A., Kremer, B., and Fandrich, F. (2001) Overexpression of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in human lung cancer, Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg., 386, 293–301.
Kaminska, B., and Swiatek-Machado, K. (2014) Targeting signaling pathways with small molecules to treat autoimmune disorders, Exp. Rev. Clin. Immunol., 4, 93–112.
Jackson, M., Howle, S. E. M., Weller, R. J., Sabin, E., Hunter, J. A. A., and Mckenzie, R. C. (1999) Psoriatic keratinocytes show reduced IRF-1 and STAT-1a activation in response to κ-IFN, FASEB, 13, 495–502.
Yamazaki, F., Aragane, Y., Maeda, A., Matsushita, K., Ueno, K., Yudate, T., Kawada, A., and Tezuka, T. (2002) Overactivation of IL-4-induced activator protein-1 in atopic dermatitis, J. Dermatol. Sci., 28, 227–233.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Published in Russian in Biokhimiya, 2017, Vol. 82, No. 4, pp. 644-654.
Originally published in Biochemistry (Moscow) On-Line Papers in Press, as Manuscript BM16-330, December 26, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Shan, Z., Liu, C. et al. MicroRNA-294 promotes cellular proliferation and motility through the PI3K/AKT and JAK/STAT pathways by upregulation of NRAS in bladder cancer. Biochemistry Moscow 82, 474–482 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917040095
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917040095