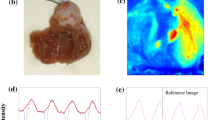
Abstract
Optical imaging of cardiac electrical activity using a voltage-sensitive dye provides high spatial resolution maps of action potential propagation and repolarization. Charge-coupled-device (CCD) camera-based imaging systems, however, are limited by their low signal-to-noise ratio. We have developed an image processing method to enhance the quality of optical signals recorded using a CCD camera. The method is based on the observation that within a small neighborhood of adjacent pixels, the morphology of the optical action potential varies little except for a phase shift in time resulting from the propagation of the wavefront. The method uses a phase-correlation technique to first correct for this time shift before spatially filtering with a 5 × 5 Gaussian convolution kernel (Σ =1.179). A length 5 median filter is then applied to further reduce noise by filtering in the temporal domain. The image-processing scheme allows for more accurate extraction of maps of electrical activation, repolarization, and action potential duration. © 2001 Biomedical Engineering Society.
PAC01: 8780Tq, 8719Hh, 8719Nn, 8757Ce
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Baxter, W. T., J. M. Davidenko., L. M. Loew., J. P. Wuskell., and J. Jalife. Technical features of a CCD video camera system to record cardiac fluorescence data. Ann. Biomed. Eng.25.:713–725., 1997.
De Castro, E., and C. Morandi. Registration of translated and rotated images using finite Fourier transforms. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell.PAMI-9.:700–703., 1987.
Efimov, I. R., G. J. Fahy., Y. Cheng., D. R. Van Wagoner., P. J. Tchou., and T. N. Mazgalev. High-resolution fluorescent imaging does not reveal a distinct atrioventricular nodal anterior input channel (fast pathway) in the rabbit heart during sinus rhythm. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophys.8.:295–306., 1997.
Efimov, I. R., D. T. Huang., J. M. Rendt., and G. Salama. Optical mapping of repolarization and refractoriness from intact hearts. Circulation.90.:1469–1480., 1994.
Girouard, S. D., K. R. Laurita., and D. S. Rosenbaum. Unique properties of cardiac action potentials recorded with voltage-sensitive dyes. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophys.7.:1024–1038., 1996.
Girouard, S. D., J. M. Pastore., K. R. Laurita., K. W. Gregory., and D. S. Rosenbaum. Optical mapping in a new guinea pig model of ventricular tachycardia reveals mechanisms for multiple wavelengths in a single reentrant circuit. Circulation.93.:603–613., 1996.
Gray, R. A., J. Jalife., A. Panfilov., W. T. Baxter., C. Cabo., J. M. Davidenko., and A. M. Pertsov. Nonstationary vortexlike reentrant activity as a mechanism of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia in the isolated rabbit heart. Circulation.91.:2454–2469., 1995.
Gray, R. A., A. M. Pertsov., and J. Jalife. Incomplete reentry and epicardial breakthrough patterns during atrial fibrillation in the sheep heart. Circulation.94.:2649–2661., 1996.
Knapp, C. H., and G. C. Carter. The generalized correlation method for estimation of time delay. IEEE Trans. Acoust., Speech, Signal Process.24.:320–327., 1976.
Knisley, S. B..Transmembrane voltage changes during unipolar stimulation of rabbit ventricle. Circ. Res.77.:1229–1239., 1995.
Kuglin, C. D., and D. C. Hines. The phase correlation image alignment method. Proceedings of the 1975 International Conference on Cybernetics and Society. San Francisco, CA: IEEE, 1975, pp. 163–165.
Loew, L. M..Potentiometric dyes: Imaging electrical activity of cell membranes. Pure Appl. Chem.68.:1405–1409., 1996.
Ni, Q., R. S. MacLeod., R. L. Lux., and B. Taccardi. A novel interpolation method for electric potential fields in the heart during excitation. Ann. Biomed. Eng.26.:597–607., 1998.
Pertsov, A. M., J. M. Davidenko., R. Salomonsz., W. T. Baxter., and J. Jalife. Spiral waves of excitation underlie reentrant activity in isolated cardiac muscle. Circ. Res.72.:631–650., 1993.
Reiter, M. J., M. Landers., Z. Zetelaki., C. J. H. Kirchhof., and M. A. Allessie. Electrophysiological effects of acute dilation in the isolated rabbit heart: Cycle length-dependent effects on ventricular refractoriness and conduction velocity. Circulation.96.:4050–4056., 1997.
Rogers, J. M., and A. D. McCulloch. Nonuniform muscle fiber orientation causes spiral wave drift in a finite element model of cardiac action potential propagation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol.5.:496–509., 1994.
Rohr, S., and B. M. Salzberg. Multiple site optical recording of transmembrane voltage (MSORTV) in patterned growth heart cell cultures: Assessing electrical behavior, with microsecond resolution, on a cellular and subcellular scale. Biophys. J.67.:1301–1315., 1994.
Sung, D., J. H. Omens., and A. D. McCulloch. Model-based analysis of optically mapped epicardial activation patterns and conduction velocity. Ann. Biomed. Eng.28.:1085–1092., 2000.
Windisch, H., H. Ahammer., P. Schaffer., W. Muller., and D. Platzer. Optical multisite monitoring of cell excitation phenomena in isolated cardiomyocytes. Pflugers Arch.430.:508–518., 1995.
Witkowski, F. X., L. J. Leon., R. B. Clark., M. L. Spano., W. L. Ditto., and W. R. Giles. A method for visualization of ventricular fibrillation: Design of a cooled fiberoptically coupled image intensified CCD data acquisition system incorporating wavelet shrinkage based adaptive filtering. Chaos.8.:94–102., 1998.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sung, D., Somayajula-Jagai, J., Cosman, P. et al. Phase Shifting Prior to Spatial Filtering Enhances Optical Recordings of Cardiac Action Potential Propagation. Annals of Biomedical Engineering 29, 854–861 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1114/1.1408927
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1114/1.1408927