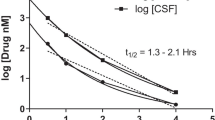
Abstract
Neurologic decline associated with penetration of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) into the central nervous system is thought to be due, in large part, to inflammation and local secretion of neurotoxic substances. To examine the cellular processes that mediate neurotoxicity in vivo, the authors evaluated the ability of neurons to maintain intracellular calcium homeostasis in the presence of toxic cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) (CSFtox) collected from a subset of HIV-infected individuals. Exposure of rat neural cultures to CSFtox resulted in a gradual increase in intracellular calcium in neurons (+63%), microglia (+251%), and astrocytes (+52%). Pretreatment of neural cultures with CSFtox resulted in an exaggerated calcium response to a brief pulse of glutamate and a >90% suppression of the rate of recovery of intracellular calcium. Attempts to model the deficit using inhibitors of calcium transport across endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrial, or plasma membrane indicated that blockade of the plasma membrane sodium/calcium exchanger was best able to reproduce the deficits seen during exposure to CSFtox. Because the inability of cells to maintain calcium homeostasis would lead to exaggerated responses from a wide variety of stimuli, therapeutics designed to facilitate calcium transport from the cell may provide more comprehensive and effective intervention than strategies targeted to specific receptor pathways.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson DC, McArthur JC, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (1999). Rate and severity of HIV-associated dementia (HAD): correlations with Gp41 and iNOS. Mol Med 5: 98–109.
Bernton EW, Bryant HU, Decoster MA, Orenstein JM, Ribas JL, Meltzer MS, Gendelman HE (1992). No direct neuronotoxicity by HIV-1 virions or culture fluids from HIV-1-infected T cells or monocytes. Aids Res Hum Retroviruses 8: 495–503.
Bragg D, Hudson L, Liang Y, Tompkins M, Fernandes A, Meeker R (2002a). Choroid plexus macrophages proliferate and release toxic factors in response to feline immunodeficiency virus. J NeuroVirol 8: 225–239.
Bragg DC, Boles JC, Meeker RB (2002b). Destabilization of neuronal calcium homeostasis by factors secreted from choroid plexus macrophage cultures in response to feline immunodeficiency virus. Neurobiol Dis 9: 173–186.
Bragg DC, Meeker RB, Duff BA, English RV, Tompkins MB (1999). Neurotoxicity of FIV and FIV envelope protein in feline cortical cultures. Brain Res 816: 431–437.
Brenneman DE, Westbrook GL, Fitzgerald SP, Ennist DL, Elkins KL, Ruff MR, Pert CB (1988). Neuronal cell killing by the envelope protein of HIV and its prevention by vasoactive intestinal peptide. Nature 335: 639–642.
Carafoli E, Stauffer T (1994). The plasma membrane calcium pump: functional domains, regulation of the activity, and tissue specificity of isoform expression. J Neurobiol 25: 312–324.
Caride AJ, Filoteo AG, Penheiter AR, Paszty K, Enyedi A, Penniston JT (2001). Delayed activation of the plasma membrane calcium pump by a sudden increase in Ca2+: fast pumps reside in fast cells. Cell Calcium 30: 49–57.
Castilho RF, Ward MW, Nicholls DG (1999). Oxidative stress, mitochondrial function, acute glutamate excitotoxicity in cultured cerebellar granule cells. J Neurochem 72: 1394–1401.
Chard PS, Bleakman D, Christakos S, Fullmer CS, Miller RJ (1993). Calcium buffering properties of calbindin D28k and parvalbumin in rat sensory neurones. J Physiol 472: 341–357.
Cheng J, Nath A, Knudsen B, Hochman S, Geiger JD, Ma M, Magnuson DS (1998). Neuronal excitatory properties of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat protein. Neuroscience 82: 97–106.
Colegrove SL, Albrecht MA, Friel DD (2000). Quantitative analysis of mitochondrial ca2+ uptake and release pathways in sympathetic neurons. Reconstruction of the recovery after depolarization-evoked [ca2+]i elevations. J Gen Physiol 115: 371–388.
Conant K, Garzino-Demo A, Nath A, McArthur JC, Halliday W, Power C, Gallo RC, Major EO (1998). Induction of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in HIV-1 Tat-stimulated astrocytes and elevation in AIDS dementia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 3117–3121.
Diop AG, Lesort M, Esclaire F, Sindou P, Couratier P, Hugon J (1994). Tetrodotoxin blocks HIV coat protein (gp120) toxicity in primary neuronal cultures. Neurosci Lett 165: 187–190.
D’Orlando C, Celio MR, Schwaller B (2002). Calretinin and calbindin D-28k, but not parvalbumin, protect against glutamate-induced delayed excitotoxicity in transfected N18-RE 105 neuroblastoma-retina hybrid cells. Brain Res 945: 181–190.
Dreyer E, Kaiser P, Offerman J, Lipton S (1990). HIV-1 coat protein neurotoxicity prevented by calcium channel antagonists. Science 248: 364–367.
Duchen MR (2000). Mitochondria and calcium: from cell signalling to cell death. J Physiol 529(Pt 1): 57–68.
Gelbard HA, Nottet HS, Swindells S, Jett M, Dzenko KA, Genis P, White R, Wang L, Choi Y-B, Zhang D, Lipton SA, Tourtellotte WW, Epstein LG, Gendelman HE (1994). Platelet-activating factor: a candidate human immunodeficiency virus type 1-induced neurotoxin. J Virol 68: 4628–4635.
Genis P, Jett M, Bernton EW (1992). Cytokines and arachidonic metabolites produced during human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected macrophage-astroglia interactions: implications for the neuropathogenesis of HIV disease. Exp Med 176: 1703–1718.
Giulian D, Vaca K, Noonan CA (1990). Secretion of neurotoxins by mononuclear phagocytes infected with HIV-1. Science 250: 1593–1596.
Giulian D, Yu J, Li X, Tom D, Li J, Wendt E, Lin S-N, Schwarcz R, Noonan C (1996). Study of receptormediated neurotoxins released by HIV-1-infected mononuclear phagocytes found in human brain. J Neurosci 16: 3139–3153.
Graziosi C, Gantt KR, Vaccarezza M, Demarest JF, Daucher M, Saag MS, Shaw GM, Quinn TC, Cohen OJ, Welbon CC, Pantaleo G, Fauci AS (1996). Kinetics of cytokine expression during primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 4386–4391.
Grimaldi LM, Martino GV, Franciotta DM, Brustia R, Castagna A, Pristera R, Lazzarin A (1991). Elevated alpha-tumor necrosis factor levels in spinal fluid from HIV-1 infected patients with central nervous system involvement. Ann Neurol 29: 21–25.
Gruol DL, Yu N, Parsons KL, Billaud JN, Elder JH, Phillips TR (1998). Neurotoxic effects of feline immunodeficiency virus, FIV-PPR. J NeuroVirol 4: 415–425.
Haughey NJ, Holden CP, Nath A, Geiger JD (1999). Involvement of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-regulated stores of intracellular calcium in calcium dysregulation and neuron cell death caused by HIV-1 protein tat. J Neurochem 73: 1363–1374.
Haughey NJ, Nath A, Mattson MP, Slevin JT, Geiger JD (2001). HIV-1 Tat through phosphorylation of NMDA receptors potentiates glutamate excitotoxicity. J Neurochem 78: 457–467.
Hesselgesser J, Taub D, Baskar P, Greenberg M, Hoxie J, Kolson DL, Horuk R (1998). Neuronal apoptosis induced by HIV-1 gp120 and the chemokine SDF-1 alpha is mediated by the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Curr Biol 8: 595–598.
Heyes MP, Brew BJ, Martin A, Price RW, Salazar AM, Sidtis JJ, Yergey JA, Mouradian MM, Sadler AE, Keilp J, Rubinow D, Markey SP (1991). Quinolinic acid in cerebrospinal fluid and serum in HIV-1 infection: relationship to clinical and neurological status. Ann Neurol 29: 202–209.
Holden CP, Haughey NJ, Nath A, Geiger JD (1999). Role of Na+/H+ exchangers, excitatory amino acid receptors and voltage-operated ca2+ channels in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120-mediated increases in intracellular ca2+ in human neurons and astrocytes. Neuroscience 91: 1369–1378.
Huschenbett J, Zaidi A, Michaelis ML (1998). Sensitivity of the synaptic membrane Na+/ca2+ exchanger and the expressed NCX1 isoform to reactive oxygen species. Biochim Biophys Acta 1374: 34–46.
Isaacs KR, Wolpoe ME, Jacobowitz DM (2000). Vulnerability to calcium-induced neurotoxicity in cultured neurons expressing calretinin. Exp Neurol 163: 311–323.
Jackson MB, Redman SJ (2003). Calcium dynamics, buffering, and buffer saturation in the boutons of dentate granule-cell axons in the hilus. J Neurosci 23: 1612–1621.
Kaul M, Garden GA, Lipton SA (2001). Pathways to neuronal injury and apoptosis in HIV-associated dementia. Nature 410: 988–994.
Kelder W, McArthur JC, Nance-Sproson T, McClernon D, Griffin DE (1998). Beta-chemokines MCP-1 and RANTES are selectively increased in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with human immunodeficiency virus-associated dementia. Ann Neurol 44: 831–835.
Khodorov B, Pinelis V, Golovina V, Fajuk D, Andreeva N, Uvarova T, Khaspekov L, Victorov I (1993). On the origin of a sustained increase in cytosolic ca2+ concentration after a toxic glutamate treatment of the nerve cell culture. FEBS Lett 324: 271–273.
Kiedrowski L, Costa E (1995). Glutamate-induced destabilization of intracellular calcium concentration homeostasis in cultured cerebellar granule cells: role of mitochondria in calcium buffering. Mol Pharmacol 47: 140–147.
Lipton S (1992). Requirement of macrophages in neuronal injury induced by HIV envelope protein gp120. NeuroReport 3: 913–915.
Lipton S (1993). Prospects for clinically tolerated NMDA antagonists: open-channel blockers and alternative redox states of nitric oxide. Trends Neurosci 16: 527–532.
Lipton S, Sucher N, Kaiser P, Dreyer E (1991). Synergistic effects of HIV coat protein and NMDA receptor-mediated neurotoxicity. Neuron 7: 111–118.
Lu J, Tong XY, Wang XL (2002). Altered gene expression of Na+/ca2+ exchanger isoforms NCX1, NCX2 and NCX3 in chronic ischemic rat brain. Neurosci Lett 332: 21–24.
Magnuson D, Knudsen B, Geiger J, Brownstone R, Nath A (1995). Human immunodeficiecy virus type 1 Tat activates non-N-methyl-d-aspartate excitatory amino acid receptors and causes neurotoxicity. Ann Neurol 37: 373–380.
McMahon A, Wong BS, Iacopino AM, Ng MC, Chi S, German DC (1998). Calbindin-D28k buffers intracellular calcium and promotes resistance to degeneration in PC12 cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 54: 56–63.
Meeker RB, Robertson K, Barry T, Hall C (1999). Neurotoxicity of CSF from HIV-infected humans. J NeuroVirol 5: 507–518.
Mockel V, Fischer G (1994). Vulnerability to excitotoxic stimuli of cultured rat hippocampal neurons containing the calcium-binding proteins calretinin and calbindin D28K. Brain Res 648: 109–120.
Nath A, Geiger J (1998). Neurobiological aspects of human immunodeficiency virus infection: neurotoxic mechanisms. Prog Neurobiol 54: 19–33.
Nath A, Pauda RA, Geiger JD (1995). HIV-1 coat protein gp120-induced increases in levels of intrasynaptosomal calcium. Brain Res 678: 200–206.
Navia BA, Dafni U, Simpson D, Tucker T, Singer E, McArthur JC, Yiannoutsos C, Zaborski L, Lipton SA (1998). A phase I/II trial of nimodipine for HIV-related neurologic complications. Neurology 51: 221–228.
New DR, Ma M, Epstein LG, Nath A, Gelbard HA (1997). Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat protein induces death by apoptosis in primary human neuron cultures. NeuroVirol 3: 168–173.
Perrella O, Carrieri PB, Guarnaccia D, Soscia M (1992). Cerebrospinal fluid cytokines in AIDS dementia complex. J Neurol 239: 387–388.
Pulliam L, Clarke JA, McGuire D, McGrath MS (1994). Investigation of HIV-infected macrophage neurotoxin production from patients with AIDS dementia. Adv Neuroimmunol 4: 195–198.
Ranciat-McComb NS, Bland KS, Huschenbett J, Ramonda L, Bechtel M, Zaidi A, Michaelis ML (2000). Antisense oligonucleotide suppression of Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger activity in primary neurons from rat brain. Neurosci Lett 294: 13–16.
Storozhevykh T, Grigortsevich N, Sorokina E, Vinskaya N, Vergun O, Pinelis V, Khodorov B (1998). Role of Na2+/ca2+ exchange in regulation of neuronal ca2+ homeostasis requires re-evaluation. FEBS Lett 431: 215–218.
Thayer SA, Usachev YM, Pottorf WJ (2002). Modulating ca2+ clearance from neurons. Front Biosci 7: d1255-d1279.
Thurneysen T, Nicoll DA, Philipson KD, Porzig H (2002). Sodium/calcium exchanger subtypes NCX1, NCX2 and NCX3 show cell-specific expression in rat hippocampus cultures. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 107: 145–156.
Vergun O, Keelan J, Khodorov BI, Duchen MR (1999). Glutamate-induced mitochondrial depolarisation and perturbation of calcium homeostasis in cultured rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol 519(Pt 2): 451–466.
Wesselingh SL, Takahashi K, Glass JD, McArthur JC, Griffin JW, Griffin DE (1997). Cellular localization of tumor necrosis factor mRNA in neurological tissue from HIV-infected patients by combined reverse transcriptase/polymerase chain reaction in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry. J Neuroimmunol 74: 1–8.
Xiong H, Zeng YC, Lewis T, Zheng J, Persidsky Y, Gendelman HE (2000). HIV-1 infected mononuclear phagocyte secretory products affect neuronal physiology leading to cellular demise: relevance for HIV-1associated dementia. J NeuroVirol 6(Suppl 1): S14-S23.
Yeung MC, Pulliam L, Lau AS (1995). The HIV envelope protein gp120 is toxic to human brain-cell cultures through the induction of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. AIDS 9: 137–143.
Yu SP, Choi DW (1997). Na+-ca2+ exchange currents in cortical neurons: concomitant forward and reverse operation and effect of glutamate. Eur J Neurosci 9: 1273–1281.
Zheng J, Ghorpade A, Niemann D, Cotter RL, Thylin MR, Epstein L, Swartz JM, Shepard RB, Liu X, Nukuna A, Gendelman HE (1999a). Lymphotropic virions affect chemokine receptor-mediated neural signaling and apoptosis: implications for human immunodeficiency virus type 1-associated dementia. J Virol 73: 8256–8267.
Zheng J, Thylin MR, Ghorpade A, Xiong H, Persidsky Y, Cotter R, Niemann D, Che M, Zeng YC, Gelbard HA, Shepard RB, Swartz JM, Gendelman HE (1999b). Intracellular CXCR4 signaling, neuronal apoptosis and neuropathogenic mechanisms of HIV-1-associated dementia. J Neuroimmunol 98: 185–200.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by NIH grats MH62690, AI47749, and the UNC center for AIDS Research (P30-HD37260).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meeker, R.B., Boles, J.C., Robertson, K.R. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid from human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals facilitates neurotoxicity by suppressing intracellular calcium recovery. Journal of NeuroVirology 11, 144–156 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1080/13550280590922757
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/13550280590922757