Summary
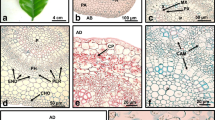
Structure and ultrastructure changes that occurred during tissue culture of upper explants of hypocotyl (adjacent to cotyledons) of 10-d-old seedlings of Gentiana cruciata were studied. The explants were cultured on Murashige and Skoog induction medium supplemented with 1.0 mg l−1 dicamba +0.1 mg l−1 naphthaleneacetic acid +2.0 mg l−1 benzyladenine +80.0 mg l−1 adenine sulfate. The initial response of the explant and callus formation were ultrastructurally analyzed during the first 11 d of culture. After 6–8 wk, various methods were employed to collect evidence of indirect somatic embryogenesis. After 48 h of culture, the earliest cell response was cell division of epidermis and primary cortex. There were numerous disturbances of karyo- and cytokinesis, leading to formation of multinuclear cells. With time, the divisions ceased, and cortex cells underwent strong expansion, vacuolization and degradation. About the 6th day of culture, callus tissue proliferated and the initial divisions of vascular cylinder cells were observed. Their division appeared normal. Cells originating from that tissue were small, weakly vacuolated, with dense cytoplasm containing active-looking cell organelles. Numerous divisions occurred in the vascular cylinder, which led to its expansion and the formation of embryogenic callus tissue. During the 6–8th wk of culture, in the proximal end of the explant, masses of somatic embryos were formed from outer parts of intensively proliferating tissue.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhojwani, S. S.; Razadan, M. K. Plant tissue culture: theory and practice. Ireland: Elsevier Science Publishers; 1983:159–180.
Brown, D. C. W.; Finstad, K. I.; Watson, E. M. Somatic embryogenesis in herbaceous dicots. In: Thorpe, T. A., ed. In vitro embryogenesis in plants. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1995:345–416.
Canhoto, J. M.; Lopes, M. L.; Cruz, G. S. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in myrtle (Myrtaceae). Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 57:13–21; 1999.
Canhoto, J. M.; Mesquita, J. F.; Cruz, G. S. Ultrastructural changes in cotyledons of pineapple guava (Myrtaceae) during somatic embryogenesis. Ann. Bot. 78:513–521; 1996.
Collings, D. A.; Emons, A. M. C. Microtubule and actin filament organization during acentral divisions in potato suspension cells. Protoplasma 207:158–168; 1999.
Cruz, G. S.; Canhoto, J. M.; Abreu, M. A. V. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from zygotic embryos of Feijoa sellowiana Berg. Plant Sci. 66:263–270; 1990.
Dudits, D.; Bögre, L.; Györgyey, J. Molecular and cellular approaches to the analysis of plant embryo development from somatic cells in vitro. J. Cell Sci. 99:475–484; 1991.
Fehér, A.; Pasternak, T.; Miskolczi, P.; Ayaydin, F.; Dudits, D. Induction of the embryogenic pathway in somatic plant cells. In: Sorvari S.; Karhu, S.; Kanervo, E.; Pihakashi, S., eds. IV International symposium on in vitro culture and horticultural breeding. Acta Hort. 560: 293–298; 2001.
Fiore, M. C.; Trabace, T.; Sunseri, F. High frequency of plant regeneration in sunflower from cytoledons via somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Rep. 16:295–298; 1997.
Fiuk, A.; Rajkiewicz, M.; Rybezyński, J. J. In vitro culture of Gentiana kurroo (Royle). Biotechnologia 3:267–274, 2003 [English summary].
Halperin, V. Attainment and retention of morphogenetic capacity in vitro. In: Vasil, I. K., ed. Cell culture and somatic cell genetic of plants. New York: Academic Press; 1986:3–47.
Hakman, I.; Fowke, L. C.; von Arnold, S.; Errikson, T. The development of the somatic embryos in tissue cultures initiated from immature embryos of Picea abies (Norway spruce). Plant Sci. 38:53–59; 1985.
Hakman, I.; von Arnold, S. Plantlet regeneration through somatic embryogenesis in Picea abies (Norway spruce). J. Plant Physiol. 121:149–158; 1985.
Jacobsen, H. J. Biochemical mechanisms of plant hormone activity. In: Evans, D. A.; Sharp, W. R.; Ammirato, P. V.; Yamada, Y., eds. Handbook of plant cell culture: Techniques for propagation and breeding, 1. New York: Macmillian; 1983:672–695.
Katsuta, J.; Shibaoka, H. The roles of cytoskeleton and the cell wall in nuclear positioning in tobacco BY-2 cells. Plant Cell Physiol. 29:403–413; 1988.
Komamine, A.; Matsumoto, M.; Tsukahara, M.; Fujiwara, A.; Kawahara, R.; Ito, M.; Smith, J.; Nomura, K.; Fujimura, T. Mechanism of somatic embryogenesis in cell cultures—physiology, biochemistry, and molecular biology. In: Thorpe, T. A., ed. In Vitro embryogenesis in plants. Dordrecht; Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1990:307–313.
Lloyd, C. W.; Lowe, S. B.; Peace, G. W. The model of action of 2,4-D in counteracting the elongation of carrot cells grown in culture. J. Cell Sci. 45:257–268; 1980.
Mathews, H. Morphogenetic responses from in vitro cultured seedling explants of mung bean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek). Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 11:233–240; 1987.
Michaux-Ferrière, N.; Carron, M. P. Histology of early somatic embryogenesis in Heavea brasiliensis: The importance of the timing of subculturing. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 19:243–256; 1989.
Mikuŀa, A.; Fiuk, A.; Rybczyński, J. J. Induction, maintenance and preservation of embryogenic competence of Gentiana cruciata L. cultures. Acta Biol Crac. Ser. Botanica 47:227–236; 2005a.
Mikuŀa, A.; Rybczyński, J. J. Somatic embryogenesis of Gentiana genus. I. The effect of the preculture treatment and primary explant origin on somatic embryogenesis of: Gentiana cruciata (L.), G. pannonica (Scop.), and G. tibetica (King). Acta Physiol. Plant. 23:15–25; 2001.
Mikuŀa, A.; Rybczyński, J. J.; Latkowska, M. J. Somatic embryogenesis of Gentiana cruciata (L.) and G. tibetica (King) in long-term suspension cultures. Proceedings of the 1st international symposium. Liquid system for in vitro mass propagation of plants, 29 May–2 June 2002, Norway; 2002a: 96–97.
Mikuŀa, A.; Rybczyński, J. J.; Skierski, J.; Latkowska, H. J.; Fiuk, A. Somatic embryogenesis of Gentiana cruciata and Gentiana tibetica embryogenic cell suspension. In: Hvoslef-Eide, A. K.; Preil, W., eds. Liquid culture systems for in vitro plant propagation. The Netherlands, Springer; 2005b;345–358.
Mikuŀa, A.; Rybczyński, J. J.; Tykarska, T.; Kuraś, M. Somatic embryogenesis of Gentiana genus. II. Scanning and ultrastructural analysis of early stages of somatic embryogenesis in liquid medium. Biol. Bull. Poznań 38:53–57; 2001.
Mikuŀa, A.; Skierski, J.; Rybczyński, J. J. Somatic embryogenesis of Gentiana genus. III. Characterisation of tree-year-old embryogenic suspension of Gentiana pannonica (Scop.) originated from various seedling explants. Acta Physiol. Plant. 24:311–322; 2002b.
Mikuŀa, A.; Tykarska, T.; Kuraś, M.; Iwanowska, A.; Rybczyński, J. J. Studies on the morphogenic potential of gentians in cell suspension. Proceedings of the international symposium ‘Breeding research on medicinal and aromatic plants,’ 30 June–4 July, 1996, Quedlinburg, Germany; 1996a:290–295.
Mikuŀa, A.; Tykarska, T.; Rybczyński, J.; Kuraś, M. Ultrastructural analysis of initial stages of defifferentiation of root explants of Gentiana cruciata seedlings. Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 71:287–297; 2002c.
Mikuŀa, A.; Tykarska, T.; Zielińska, M.; Rybczyński, J.; Kuraś, M. Ultrastructural changes in zygotic embryos of Gentiana punctata (L.) during initiation and formation of callus tissue and somatic embryos. Acta Biol. Cracoviensia Bot. 46:1–12; 2004.
Mikuŀa, A.; Wesoŀowska, M.; Kapusta, J.; Skrzypezak, L.; Rybezyński, J. J. Cytomorphological studies on somatic embryogenesis of Gentiana tibetica (King) and G. cruciata (L.). Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 65:47–51; 1996b.
Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15:473–497; 1962.
Özcan, S.; Barghehi, M.; Firek, S.; Draper, J. Efficient adventitious shoot regeneration and somatic embryogenesis in pea. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 34:271–277; 1993.
Pierson, E. S.; van Lammeren, A. A. M.; Schel, J. H. N.; Staritsky, G. In vitro development of embryoids from punched leaf discs of Coffea canephora. Protoplasma 115:208–216; 1983.
Puigderrajols, P.; Mir, G.; Molinas, M. Ultrastructure of early secondary embryogenesis by multicellular and unicellular pathways in Cork Oak (Quercus suber L.). Ann. Bot. 87:179–189; 2001.
Reynolds, E. S. Use of lead citrate at high pH as electron opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17:208–213; 1963.
Rodriguez, A. P. M.; Wetzstein, H. Y. A morphological and histological comparison of the initiation and development of pecan (Carya illinoinensis) somatic embryogenic cultures induced with naphthaleneacetic acid or 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Protoplasma 204:1–83; 1998.
Santos, I.; Guimarąes, I.; Salema, R. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration of Nerium oleander. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 37:83–86; 1994.
Tomar, U. K.; Gupta, S. C. Somatic embryogenesis and organogenesis in callus cultures of a tree legume—Albizia richardiana King. Plant Cell Rep. 7:70–73; 1988.
Verdeil, J. L.; Hocher, V.; Huel, C.; Grosdemange, F.; Escoute, J.; Ferriere, N.; Nicole, M. Ultrastructural changes in coconut calli associated with the acquisition of embryogenic competence. Ann. Bot. 88:9–18; 2001.
Warren, G. S. The cell biology of plant cell culture systems. In: Fowler, M. W.; Warren, G. S.; Moo-Young, M., eds. Plant biotechnology. Comprehensive biotechnology second supplement. New York: Pergamon Press; 1992:1–17.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mikuŀa, A., Tykarska, T., Kuraś, M. et al. Somatic embryogenesis of Gentiana cruciata (L.): Histological and ultrastructural changes in seedling hypocotyl explant. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 41, 686–694 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1079/IVP2005678
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1079/IVP2005678