Abstract
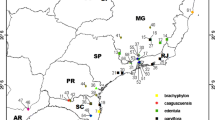
Multivariate morphometric analyses were performed on workers of Apis koschevnikovi from throughout their distribution in Malaysia, Borneo and Indonesia. Principal component analysis showed one morphocluster comprising bees from Kalimantan Indonesia, Sarawak, Sabah and the Malay Peninsula. The population is more homogeneous than A. cerana over the same geographical area, as seen from the average coefficient of variation in 12 characters in A. koschevnikovi (1.8%) compared to those same characters in A. cerana (4.3%). A. koschevnikovi is delimited to the tropical evergreen forest regions of Sumatera, Borneo, and the Malay Peninsula (Fig. 1). The altitudinal distributions show that A. koschevnikovi extends from sea level to about 1600 m. This significantly differs from A. nuluensis but not A. cerana. It appears that the range of A. koschevnikovi is diminishing because it is now either poorly represented or absent in several areas where it has been previously recorded.
Zusammenfassung
An Arbeiterinnen von Apis koschevnikovi aus deren gesamten Verbreitungsgebiet in Südostasien wurden multivariate morphometrische Analysen durchgeführt. Siebenundzwanzig morphologische Merkmale der Arbeiterinnen wurden nach der Methode von Ruttner (1988) vermessen, die verwendeten Merkmale enthielten Größenmessungen und Flügelwinkel. Hieraus wurden acht Hauptkomponenten abgeleitet, die insgesamt 78,7 % der Variation in den Daten repräsentierten. Die multivariaten Analysen der Proben von A. koschevnikovi zeigten klar, dass die Art aus einem einzigen anhand von nur 12 morphologischen Merkmalen abgrenzbaren Morphokluster zusammengesetzt ist.
Die Hauptkomponentenanalyse zeigte einen die Bienen von Sumatra, Borneo und der malayischen Halbinsel enthaltenden Morphokluster (Abb. 2 und 3). Die Population ist einheitlicher als die von A. cerana in dem gleichen Verbreitungsgebiet. Dies kann aus dem Vergleich der mittleren Varianzkoeffizienten von 12 gleichen Merkmalen ersehen werden, der bei A. koschevnikovi 1,8 %, bei A. cerana aber 4,3 % beträgt.
Die Höhenverteilung zeigt, dass von den 102 erfassten Fundorten von A. koschevnikovi 96 % niedriger als 1200 m und 4 % zwischen 1200 und 2700 m lagen (Tab. I und zusätzliches elektronisches Onlinematerial zur Verteilung von A. koschevnikovi auf Grundlage aller publizierter Nachweise). Diese Höhenverteilung ist nicht unterschiedlich von der sympatrischen A. cerana (χ2 = 6,9, df = 3, P = 0,0764). Sie ist aber signifikant verschieden von der Höhenverteilung der geographisch sympatrischen A. nuluensis, für die bisher nur drei Fundorte bekannt sind, die alle über 3000 m liegen (χ2 = 104,0, df = 3, P < 0,0001).
In zahlreichen Exkursionen im tropischen Regenwald über die letzten 10 Jahre in Thailand, Myanmar, Kambodscha and Vietnam konnte die Art A. koschevnikovi nicht nachgewiesen werden, ihr Vorkommen ist auf die Region des immergrünen Regenwaldes von Sundaland begrenzt (Abb. 1). Anscheinend ist das Verbreitungsgebiet von A. koschevnikovi im Schwinden, da diese in einigen Gebieten, in denen sie früher gefunden wurde, nun nur geringfügig vertreten ist oder vollständig fehlt.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arias M.C., Tingek S., Kelitu A., Sheppard W.S. (1996) Apis nuluensis Tingek, Koeniger and Koeniger, 1996 and its genetic relationship with sympatric species inferred from DNA sequences, Apidologie 27, 415–422.
Eltz T. (2004) Spatio-temporal variation of apine bee attraction to honeybaits in Bornean forests, J. Trop. Ecol. 20, 317–324.
Enderlein G. (1906) New honeybees and contribution to the distribution of the genus Apis, Stet. Entomol. Ztg. 67, 331–334 [in German].
Engel M.S. (1999) The taxonomy of recent and fossil honey bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae; Apis), J. Hymenopt. Res. 8, 165–196.
Fuchs S., Koeniger N., Tingek S. (1996) The morphometric position of Apis nuluensis Tingek, Koeniger and Koeniger, 1996 within cavitynesting honey bees, Apidologie 27, 397–405.
Goetze G.K.L. (1964) The honeybee under natural and beekeeping conditions. Part 1. Systematics, reproduction and heritability, Monogr. Angew. Entomol. 19, 1–20 [in German].
Hadisoesilo S., Meixner M., Ruttner F. (1999) Geographic variation within Apis koschevnikovi Buttel-Reepen, 1906, in Borneo, Treubia 31, 299–306.
Hepburn R., Hepburn C. (2006) Bibliography of Apis cerana Fabricius (1793), Apidologie 37, 651–652.
Hepburn R., Hepburn C. (2007) Bibliography of Apis koschevnikovi Enderlein (1906), Apidologie 38, 507.
Hughes J.B., Round P.D., Woodruff D.S. (2003) The Indochinese-Sundaic faunal transition at the Isthmus of Kra: an analysis of resident forest bird species distributions, J. Biogeogr. 30, 569–580.
Johnson R.A., Wichern D.W. (2002) Applied Multivariate Statistical Analysis, 5th Edition, Prentice Hall, New Jersey.
Koeniger N., Koeniger G., Gries M., Tingek S., Kelitu A. (1996) Reproductive isolation of Apis nuluensis Tingek, Koeniger and Koeniger, 1996 by species specific mating time, Apidologie 27, 353–360.
Maa T.C. (1953) An enquiry into the systematics of the tribus Apidini or honey bees (Hymenoptera), Treubia 21, 525–640.
Mathew S., Mathew K. (1988) The ‘red’ bees of Sabah, Newsl. Beekeep, Trop. Subtrop. Countries 12, 10.
Otis G.W. (1997) Distributions of recently recognized species of honey bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae; Apis) in Asia, J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 69, 311–333.
Radloff S.E., Hepburn H.R., Fuchs S., Otis G.W., Hadisoesilo S., Hepburn C., Tan Ken (2005) Multivariate morphometric analysis of the Apis cerana populations of oceanic Asia, Apidologie 36, 475–492.
Raffiudin R., Crozier R.H. (2007) Phylogenetic analysis of honey bee behavioural evolution, Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 43, 543–552.
Rinderer T.E., Koeniger G., Tingek S., Mardan M.B. (1989) A morphological comparison of the cavity dwelling honeybees of Borneo Apis koschevnikovi (ButtelReepen, 1906) and Apis cerana (Fabricius, 1793), Apidologie 20, 405–411.
Ruttner F. (1988) Biogeography and Taxonomy of Honeybee, Springer, Berlin.
Ruttner F., Kauhausen D., Koeniger N. (1989) Position of the red honey bee, Apis koschevnikovi (Buttel-Reepen 1906), within the genus Apis, Apidologie 20, 395–404.
StatSoft, Inc. (2007) STATISTICA, version 8.1, www.statsoft.com.
Sulistianto A. (1990) Morphometric analysis of Indonesian honeybees, Thesis, University of Wales College of Cardiff, United Kingdom.
Takahashi J.I., Nakamura J., Sasaki M., Tingek A., Akimoto S. (2002) New haplotypes for the noncoding region of mitochondrial DNA in cavity nesting honey bees Apis koschevnikovi and Apis nuluensis, Apidologie 33, 25–31.
Tingek A., Mardan M.B., Rinderer T.E., Koeniger N., Koeniger G. (1988) Rediscovery of Apis vechti (Maa, 1953): the Saban honey bee, Apidologie 19, 97–102.
von Buttel-Reepen H. (1906) Contributions to the systematics biology as well as the historical and geographical distribution of honeybees (Apis mellifica L.) their variability and other Apis species, Mitt. Zool. Mus. Berlin 3, 117–201 [in German].
Voris H.K. (2000) Maps of Pleistocene sea levels in Southeast Asia: shorelines, river systems and time durations, J. Biogeogr. 27, 1153–1167.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript editor: Walter S. Sheppard
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hadisoesilo, S., Raffiudin, R., Susanti, W. et al. Morphometric analysis and biogeography of Apis koschevnikovi Enderlein (1906). Apidologie 39, 495–503 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1051/apido:2008029
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1051/apido:2008029