Efficient antibacterial activity of hydroxyapatite through ROS generation motivated by trace Mn(iii) coupled H vacancies†
Abstract
Hydroxyapatite (HA) has attracted wide attention for medical application due to its biocompatibility and bioactivity. However, the infection problems of HA remain among the leading reasons for implantation failure. Thus, it is urgent to endow HA biomaterials with antibacterial activity. Herein, the high antibacterial activity was achieved by introducing trace Mn3+ and H vacancy 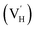 couples in HA through a facile heat-treatment strategy in air. The theoretical results indicated that Mn3+ was preferentially substituted for the Ca(2) site in the HA structure with a charge-compensating H vacancy appearing at the adjacent OH− site. The antibacterial tests showed that Mn-HA possessed antibacterial activity towards both E. coli and S. aureus with trace Mn content at the ppm level, and implied that Mn3+ and
couples in HA through a facile heat-treatment strategy in air. The theoretical results indicated that Mn3+ was preferentially substituted for the Ca(2) site in the HA structure with a charge-compensating H vacancy appearing at the adjacent OH− site. The antibacterial tests showed that Mn-HA possessed antibacterial activity towards both E. coli and S. aureus with trace Mn content at the ppm level, and implied that Mn3+ and 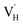 centers may play an important role in the antibacterial process. The Mn3+ and
centers may play an important role in the antibacterial process. The Mn3+ and 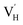 couples in Mn-HA, serving as oxidative and reductive centers respectively, could then collectively participate in the CoQ/CoQH2 redox cycling and synergistically facilitate the accumulation of CoQ˙− and ROS radicals. This enhanced ROS production was the main factor to endow Mn-HA with efficient antibacterial activity. Moreover, the in vitro bioactivity assay showed that Mn-HA materials exhibited enhanced osteogenic activity and good biocompatibility. Therefore, this work not only provides a feasible method to control the oxidation state of Mn elements in HA, but also proposes a novel trace Mn3+-doped HA for potential applications in tissue engineering.
couples in Mn-HA, serving as oxidative and reductive centers respectively, could then collectively participate in the CoQ/CoQH2 redox cycling and synergistically facilitate the accumulation of CoQ˙− and ROS radicals. This enhanced ROS production was the main factor to endow Mn-HA with efficient antibacterial activity. Moreover, the in vitro bioactivity assay showed that Mn-HA materials exhibited enhanced osteogenic activity and good biocompatibility. Therefore, this work not only provides a feasible method to control the oxidation state of Mn elements in HA, but also proposes a novel trace Mn3+-doped HA for potential applications in tissue engineering.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...