Abstract
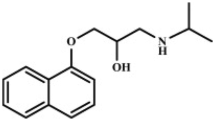
In this article, the binding interactions of a promising chloride channel blocker 9-methyl anthroate (9-MA) with a series of bile-salt aggregates of varying hydrophobicity have been thoroughly demonstrated. The altered photophysical properties of the fluorescent probe within the concerned microheterogeneous environments have been exploited spectroscopically to assess the communication between the aggregates and the guest. The contrived hydrophobic environment provided by the aggregates appreciably diminishes the water-assisted non-radiative decay channels and thus extends the fluorescence lifetime and the rotational relaxation time of the probe. NaDC aggregates, being more rigid and hydrophobic, provide a better protection to the bound guest from the external influence which is apparent from a much longer fluorescence lifetime and rotational correlation time for the encapsulated probe in NaDC aggregates compared to those in NaC and NaTC aggregates, as is further validated by fluorescence quenching experiments. Salt induced alterations of the binding behavior of the probe with the bile-salt aggregates have also been evaluated via fluorimetric studies, which conclude larger and tighter aggregate formation resulting in a superior degree of rigidity imposed on the aggregate-bound probe at high ionic strength of the medium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. J. O’Connor and R. G. Wallace, Physico-Chemical Behavior of Bile-salts, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 1985, 22, 1–111.
C. Bohne, Dynamics of Probe Interaction with Bile-salt Aggregates, in Organized Assemblies in Chemical Analysis: Bile Acid/Salt Surfactant Systems, ed. W. L. Hinze, JAI Press Inc., Stanford, 2000, pp. 147–166.>
J. P. Kratohvil, Size of bile-salt micelles: techniques, problems and results, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 1986, 26, 131–154.
A. F. Hofmann and K. J. Mysels, Bile salts as biological surfactants, Colloids Surf., 1987, 30, 145–173.
N. A. Mazer, M. C. Carey, R. F. Kwasnick and G. B. Benedek, Quasielastic Light Scattering Studies of Aqueous Biliary Lipid Systems: Size, Shape, and Thermodynamics of Bile-salt Micelles, Biochemistry, 1979, 18, 3064–3075.
D. M. Small, S. A. Penkett and D. Chapman, Studies on Simple and Mixed Bile-salt Micelles by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Lipids Lipid Metab., 1969, 176, 178–189.
D. M. Small, in The Bile-salts, ed. P. P. Nair and D. Kritchevsky, Plenum Press, New York, 1971, pp. 249–256.>
H. Kawamura, Y. Murata, T. Yamaguchi, H. Igimi, M. Tanaka, G. Sugihara and J. P. Kratohvil, Spin-Label Studies of Bile-salt Micelles, J. Phys. Chem., 1989, 93, 3321–3326.
E. Bottari, A. A. D’Archivio, M. R. Festa, L. Galantini and E. Giglio, Structure and Composition of Sodium Taurocholate Micellar Aggregates, Langmuir, 1999, 15, 2996–2998.
K. Matsuoka and Y. Moroi, Micelle Formation of Sodium Deoxycholate and Sodium Ursodeoxycholate (Part 1), Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids, 2002, 1580, 189–199.
S. M. Meyerhoffer and L. B. McGown, Microenvironments of Fluorescence Probes in Sodium Taurocholate and Sodium Taurodeoxycholate Bile-salt Media, Anal. Chem., 1991, 63, 2082–2086.
O. Rinco, M. C. Nolet, R. Ovans and C. Bohne, Probing the Binding Dynamics to Sodium Cholate Aggregates using Naphthalene Derivatives as Guests, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2003, 2, 1140–1151.
O. L. Waissbluth, M. C. Morales and C. Bohne, Influence of Planarity and Size on Guest Binding with Sodium Cholate Aggregates, Photochem. Photobiol., 2006, 82, 1030–1038.
R. Li, E. Carpentier, E. D. Newell, L. M. Olague, E. Heafey, C. Yihwa and C. Bohne, Effect of the Structure of Bile Salt Aggregates on the Binding of Aromatic Guests and the Accessibility of Anions, Langmuir, 2009, 25, 13800–13808.
M. Gomez-Mendoza, E. Nuin, I. Andreu, M. L. Marin and M. A. Miranda, Photophysical Probes to Assess the Potential of Cholic Acid Aggregates as Drug Carriers, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2012, 116, 10213–10218.
J. Rohacova, M. L. Marin, A. Martinez-Romero, L. Diaz, J. E. O’Connor, M. J. Gomez-Lechon, M. T. Donato, J. V. Castell and M. A. Miranda, Fluorescent Benzofurazan-Cholic Acid Conjugates for in Vitro Assessment of Bile Acid Uptake and Its Modulation by Drugs, ChemMedChem, 2009, 4, 466–472.
D. Fuentealba, K. Thurber, E. Bovero, T. C. S. Pace and C. Bohne, Effect of sodium chloride on the binding of polyaromatic hydrocarbon guests with sodium cholate aggregates, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2011, 10, 1420–1430.
S. Mandal, S. Ghosh, D. Banik, C. Banerjee, J. Kuchlyan and N. Sarkar, An Investigation into the Effect of the Structure of Bile-salt Aggregates on the Binding Interactions and ESIHT Dynamics of Curcumin: A Photophysical Approach To Probe Bile-salt Aggregates as a Potential Drug Carrier, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2013, 117, 13795–13807.
T. Mondal, S. Ghosh, A. K. Das, A. K. Mandal and K. Bhattacharyya, Salt Effect on the Ultrafast Proton Transfer in Niosome, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2012, 116, 8105–8112.
D. Sarkar, D. Ghosh, P. Das and N. Chattopadhyay, Electrostatic Pushing Effect: A Prospective Strategy for Enhanced Drug Delivery, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2010, 114, 12541–12548.
M. J. Davila, S. Aparicio, R. Alcalde, B. García and J. M. Leal, On the properties of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium octylsulfate ionic liquid, Green Chem., 2007, 9, 221–232.
P. Garidel, A. Hildebrand, R. Neubert and A. Blume, Thermodynamic Characterization of Bile-salt Aggregation as a Function of Temperature and Ionic Strength Using Isothermal Titration Calorimetry, Langmuir, 2000, 16, 5267–5275.
L. Hao, R. Lu, D. G. Leaist and P. R. Poulin, Aggregation Number of Aqueous Sodium Cholate Micelles from Mutual Diffusion Measurements, J. Solution Chem., 1997, 26, 113–125.
S. M. Meyerhoffer and L. B. McGown, Fluorescent Probe Studies of Metal Salt Effects on Bile-salt Aggregation, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1991, 113, 2146–2149.
A. Ganguly, S. Jana, S. Ghosh, S. Dalapati and N. Guchhait, Solvent modulated photophysics of 9-methyl anthroate: Exploring the effect of polarity and hydrogen bonding on the emissive state, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 2013, 112, 237–244.
J. R. Lakowicz, Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, Plenum, New York, 1999.
C. Reichardt, Solvatochromic Dyes as Solvent Polarity Indicators, Chem. Rev., 1994, 94, 2319–2358.
R. L. Scott, Some comments on the Benesi–Hildebrand equation, Recl. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas, 1956, 75, 787–789.
N. Ghosh, R. Mondal and S. Mukherjee, Hydrophobicity Is the Governing Factor in the Interaction of Human Serum Albumin with Bile-salts, Langmuir, 2015, 31, 1095–1104.
A. Ganguly, B. K. Paul, S. Ghosh, S. Dalapati and N. Guchhait, Interaction of a potential chloride channel blocker with a model transport protein: A spectroscopic and molecular docking investigation, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014, 16, 8465–8475.
B. K. Paul, N. Ghosh and S. Mukherjee, Prototropic Transformation and Rotational-Relaxation Dynamics of a Biological Photosensitizer Norharmane inside Nonionic Micellar Aggregates, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2014, 118, 11209–11219.
A. Ganguly, S. Ghosh and N. Guchhait, Interaction of triblock co-polymer micelles with phospholipid-bilayer: A spectroscopic investigation using a potential chloride channel blocker, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015, 17, 6597–6605.
G. Li and L. B. McGown, A New Approach to Polydispersity Studies of Sodium Taurocholate and Sodium Taurodeoxycholate Aggregates Using Dynamic Fluorescence Anisotropy, J. Phys. Chem., 1993, 97, 6745–6752, and references therein.
Z. Shi, P. G. Debenedetti and F. H. Stillinger, Relaxation processes in liquids: Variations on a theme by Stokes and Einstein, J. Chem. Phys., 2013, 138, 12A526.
G. Esposito, E. Giglio, N. V. Pavel and A. Zanobit, Size and Shape of Sodium Deoxycholate Mlcellar Aggregates, J. Phys. Chem., 1987, 91, 356–362.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganguly, A., Ghosh, S. & Guchhait, N. Modulated photophysics of an anthracene-based fluorophore within bile-salt aggregates: the effect of the ionic strength of the medium on the aggregation behavior. Photochem Photobiol Sci 14, 2168–2178 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5pp00280j
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c5pp00280j