Abstract
We performed a systematic review to assess whether being admitted during off-hours with non-ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) is associated with increased in-hospital mortality. Previous studies have demonstrated an inconsistent association between patient arrival time for NSTEMI and the subsequent clinical outcomes. All studies published up to November 10, 2014 on the association between time of admission and mortality among patients with NSTEMI were identified by searching the MEDLINE, COCHRANE, EMBASE and PUBMED databases. The characteristics and outcome data of the studies included in the systematic review were extracted. Summary odds ratios (ORs) and standardized mean differences (SMDs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using a random-effects model. Five cohort studies with a total of 129,548 patients met our inclusion criteria. The pooled analysis demonstrated that off-hours admission was not associated with increased in-hospital mortality (OR = 1.02 [95% CI (0.93–1.13)], P = 0.687). Furthermore, off-hours admission did not result in a longer door-to-balloon time (SMD = 0.37, [95%CI:−0.002 to 0.73], P = 0.051). The in-hospital mortality of patients admitted with NSTEMI during off-hours was similar to that of patients admitted during regular hours. Time of admission may not be a risk factor for increased in-hospital mortality.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
A number of studies have shown that patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) presenting during off-hours (weekday nights, weekends and holidays) have higher mortality compared to those presenting during regular hours and that patients with ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) have longer door-to-balloon times1. However, among patients with NSTEMI, findings regarding outcomes for patients admitted during off-hours are conflicting. While several studies showed an increased risk of death for patients admitted during off-hours2,3, others did not4,5,6. We postulated that patients admitted during off-hours may be at an increased risk of death. Therefore, we performed a systematic review to evaluate the available evidence on the association between off-hours admission and in-hospital mortality for patients with NSTEMI.
Methods
Search strategy
We performed a systematic search the MEDLINE, COCHRANE, EMBASE and PUBMED databases up to November 10, 2014 with no restriction on date or language. The following keywords were used: “NSTEMI”, “time”, “off-hours”, “weekend”, “admission” and “presentation”. References of relevant reports and review articles were also reviewed manually.
Inclusion criteria
Studies were eligible if they compared the clinical outcomes between patients with NSTEMI admitted during off-hours to those admitted during regular hours. Studies were excluded for the following reasons: (a) lack of data on mortality; (b) published in abstract form only; (e) inclusion of participants less than 18 years of age; and (d) not published in a peer-reviewed journal.
Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
Using a standardized data extraction protocol, two reviewers (X. T. Wang and J. Yan) independently extracted and collected the data. Disagreements or uncertainties were resolved by discussion of the two reviewers or by consultation with a third author (L. Li). When necessary, we attempted to contact the original authors for additional information. The extracted study characteristics included the first author, publication year, number of enrolled patients, study type, country, study period, definition of off-hours, variables adjusted for and outcomes. We also abstracted the adjusted relative risk estimates (odds ratios [ORs]) of mortality with the corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Quality assessment was performed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS)7, which consists of 3 domains: cohort selection, comparability and outcome. The maximum NOS score for an observational study is 9 points (4 points for selection, 2 points for comparability and 3 points for outcome).
Statistical analysis
A meta-analysis of the summary statistics from individual trials was performed using Stata software, version 12.0 (Stata Corporation, College Station, TX) by means of a DerSimonian and Laird random effects model8. The strength of the association between off-hours admission and in-hospital mortality for patients with NSTEMI was assessed by OR with 95% CI. The standardized mean difference (SMD) with 95% CI was used to express the pooled effect on measurement data. For continuous variables presented as medians with interquartile ranges (IQRs), the mean and standard deviation (SD) were estimated using the median and the estimator SD = IQR/1.359. The significance of the pooled OR and SMD was determined by the Z test. Heterogeneity among studies was evaluated by a chi-square-based Q-test10. We considered a PQ value < 0.1 as indicative of heterogeneity. For all other analyses, a P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. We performed subgroup analysis according to the definition of off-hours to explore the sources of heterogeneity among studies. Sensitivity analysis was performed by sequential omission of individual studies to assess the robustness of the results. Publication bias was evaluated by performing a linear regression of the standardized effect estimates against their precision according to the Egger’s test11.
Results
Search results
Our search strategy retrieved 324 potentially relevant articles, 76 of which were reviewed as full articles. Five studies that met our inclusion criteria were included in our systematic review and meta-analysis. Figure 1 summarizes the process of identifying eligible studies2,3,4,5,6.
Study and patient characteristics
The characteristics of the selected studies are shown in Table 1, including author, publication year, number of enrolled patients, study type, country, study period, definition of off-hours, variables adjusted for, outcome assessed and NOS score. All included studies had a cohort design. Four studies2,3,4,6 were conducted in North America (United States and Canada) and one study5 was conducted in Asia. The total pooled study population was 129,548 patients. All included studies had reported multivariate adjusted ORs for in-hospital mortality for patients admitted during off-hours and those admitted during regular hours. In three studies, the definition of off-hours included weekday nights4,5,6, while in the other two studies, the definition of off-hours included only weekends and holidays2,3.
In-hospital mortality
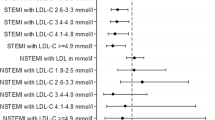
In-hospital mortality was reported in all 5 studies, providing data for 129,548 patients with NSTEMI2,3,4,5,6. There was no difference in the adjusted odds of death between patients admitted during off-hours and those admitted during regular hours (OR = 1.02 [95% CI (0.93–1.13)], P = 0.687) (Fig. 2). Significant heterogeneity was observed among the studies (PQ = 0.03). To explore the sources of heterogeneity, we performed subgroup analysis according to the definition of off-hours, with the following OR for death in patients admitted during off-hours: no weekday nights (OR = 0.96 [95% CI (0.91–1.02)], P = 0.187), heterogeneity PQ = 0.938; and weekday nights (OR = 1.22 [95% CI (0.84–1.79)], P = 0.296), heterogeneity PQ = 0.011.
Door-to-balloon time
A total of 4 studies reported door-to-balloon time and provided data for 84,007 participants. The door-to-balloon time in patients with NSTEMI who were admitted during off-hours was not longer than that for those who were admitted during regular hours (SMD = 0.37, [95% CI:−0.002 to 0.73], P = 0.051) (Fig. 3). There was significant heterogeneity among the studies (PQ < 0.001). We performed subgroup analysis according to the definition of off-hours to explore the sources of heterogeneity. The results were as follows: no weekday nights (SMD = 0.54, [95% CI: −0.07 to 1.15], P = 0.082), heterogeneity PQ < 0.001; and weekday nights (SMD = 0.19, [95% CI: 0.01 to 0.37], P = 0.036), heterogeneity PQ < 0.001.
Sensitivity analysis
A sensitivity analysis was performed by removing one study at a time. The corresponding combined ORs were not materially altered after the removal of any study, suggesting that our results have high robustness (Fig. 4).
Publication bias
Linear regression of the standard normal deviate against precision suggested that the intercept did not significantly deviate from zero (P = 0.303). Therefore, according to Egger’s test, the results showed no evidence of publication bias (Fig. 5).
Discussion
The major finding of this systematic review and meta-analysis is that in-hospital mortality of patients with NSTEMI admitted during off-hours was similar to those admitted during regular hours, even after adjusting for all patient covariates. Furthermore, off-hours admission did not result in longer door-to-balloon time; however, a subgroup analysis according to the definition of off-hours showed that weekday night admissions were associated with a longer door-to-balloon time. Off-hours admission may not be associated with a change in the risk of in-hospital mortality; however, significant heterogeneity was observed in the pooled analysis of individual study results.
According to our own survey of the literature, this is the first systematic review and meta-analysis to specifically assess the “off-hours effect” among NSTEMI patients. It is not entirely clear why admission during off-hours was not significantly associated with short-term mortality in this NSTEMI population.
Data regarding the “off-hours effect” in AMI are conflicting. Previous analyses revealed that patients with MI and heart failure who were admitted during off-hours had significantly higher adjusted in-hospital mortality12,13,14. These results were thought to be attributable to delayed reperfusion. Ting and colleagues found that admission during off-hours can increase the delay in reperfusion15. However, several other studies provided evidence that off-hours admission was not associated with in-hospital mortality in patients with MI16,17,18. The association between off-hours admission and mortality has also been evaluated in intensive care units (ICUs) and the results suggested that patients admitted to the ICU over the weekend have a higher risk of dying than those admitted on weekdays19. The lower level of staffing and intensity of care over the weekend may account for this finding19.
The importance of time to intervention to establish reperfusion is well-recognized in the STEMI population. In contrast, the optimal time to intervention has not clearly been elucidated in those with NSTEMI20. An early invasive strategy has not been shown to result in lower mortality in patients with NSTEMI. A related study suggested that the overall relationship between delay times and in-hospital mortality was generally not strong for patients with NSTEMI21. Our findings show that in patients with NSTEMI admitted during off-hours, door-to-balloon time may not be prolonged and in-hospital mortality may not increase.
A subgroup analysis of studies whose definition of off-hours included weekday nights showed that weekday night admissions were associated with a longer door-to-balloon time. Physicians have been shown to perform psychomotor tasks less proficiently at night22 and there are fewer health care professionals and experienced workers at night. We suspect that these factors might result in a longer door-to-balloon time. However, weekday night admissions were not associated with a change in in-hospital mortality. As long as a similar intensity of medical therapy is maintained, including the rates of antithrombotic therapy, antiplatelet therapy and beta blocker use, possible delays in the timing of invasive treatment strategies for patients with NSTEMI do not result in a significantly increased death risk. However, a recent study found that off-hours admission was significantly associated with higher complication rates, especially ventricular arrhythmias and gastrointestinal bleeding23. Physicians should pay attention to this phenomenon and implement preventive measures. Regardless of the time of presentation, patients should have the same likelihood of receiving evidence-based treatment and timely reperfusion therapies and hospitals should have the same number of hospital staff with the same level of expertise working at all times.
For better interpretation of the results, some limitations in this study should be acknowledged. First, the results were derived from observational studies; therefore, as with all observational data, residual confounding is possible. Second, the study population was not randomized. The patients’ baseline characteristics may confound the difference in mortality between patients admitted during off-hours and regular hours. Third, due to insufficient data, the following variables were not assessed: door-to-needle-time, composite major complications and risk score. However, we believe that in-hospital mortality is one of the best tools to assess differences between the results of admission during regular hours and off-hours. Fourth, 5 studies were not enough to assess whether being admitted with NSTEMI during off-hours was associated with increased in-hospital mortality. The differences observed in this meta-analysis may have been caused by chance due to the small sample sizes of the included studies. Thus, the results regarding the relationship between off-hours admission and in-hospital mortality should be interpreted with caution. Finally, we were only able to compare in-hospital outcomes. It is unknown whether longer-term mortality is different between patients admitted during regular hours and those admitted during off-hours.
Conclusions
In conclusion, our systematic review suggests that off-hours admission has limited impact on in-hospital mortality and door-to-balloon time among patients admitted with NSTEMI. Time of admission may not be a risk factor for increased in-hospital mortality.
Additional Information
How to cite this article: Wang, X. et al. Is there an association between time of admission and in-hospital mortality in patients with non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction? A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 5, 14409; doi: 10.1038/srep14409 (2015).
References
Sorita, A. et al. Off-hour presentation and outcomes in patients with acute myocardial infarction: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 348, f7393 (2014).
Ryan, J. W. et al. Optimal timing of intervention in non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndromes: insights from the CRUSADE (Can Rapid risk stratification of Unstable angina patients Suppress ADverse outcomes with Early implementation of the ACC/AHA guidelines) Registry. Circulation 112, 3049–3057 (2005).
Gyenes, G. T. et al. Use and timing of coronary angiography and associated in-hospital outcomes in Canadian non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients: insights from the Canadian Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events. Can. J. Cardiol. 29, 1429–1435 (2013).
Jneid, H. et al. Impact of time of presentation on the care and outcomes of acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 117, 2502–2509 (2008).
Kim, S. S. et al. Impact of patients’ arrival time on the care and in-hospital mortality in patients with non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Am. J. Cardiol. 113, 262–269 (2014).
Pollack, C. V., Jr. et al. Non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction patients who present during off hours have higher risk profiles and are treated less aggressively, but their outcomes are not worse: a report from Can Rapid Risk Stratification of Unstable Angina Patients Suppress ADverse Outcomes with Early Implementation of the ACC/AHA Guidelines CRUSADE initiative. Crit. Pathw. Cardiol . 8, 29–33 (2009).
Wells, G. et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. Available at: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp. (Accessed: 10th November 2014).
DerSimonian, R. & Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control. Clin. Trials 7, 177–188 (1986).
Higgins, J. P. & Green, S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions, version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration.(2011) Available at: http://www.cochrane-handbook.org. (Accessed: 18th March 2015).
Higgins, J. P. & Thompson, S. G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 21, 1539–1558 (2002).
Egger, M., Davey Smith, G., Schneider, M. & Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315, 629–634 (1997).
Magid, D. J. et al. Relationship between time of day, day of week, timeliness of reperfusion and in-hospital mortality for patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. JAMA 294, 803–812 (2005).
Kostis, W. J. et al. Weekend versus weekday admission and mortality from myocardial infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 356, 1099–1109 (2007).
Horwich, T. B. et al. Weekend hospital admission and discharge for heart failure: association with quality of care and clinical outcomes. Am. Heart J. 158, 451–458 (2009).
Ting, H. H. et al. Factors associated with longer time from symptom onset to hospital presentation for patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Arch. Intern. Med. 168, 959–968 (2008).
Hong, J. S., Kang, H. C. & Lee, S. H. Comparison of Case Fatality Rates for Acute Myocardial Infarction in Weekday vs Weekend Admissions in South Korea. Circulation Journal 74, 496–502 (2010).
Ortolani, P. et al. Clinical comparison of “normal-hours” vs “off-hours” percutaneous coronary interventions for ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Am. Heart J. 154, 366–372 (2007).
Berger, A. et al. Comparison of in-hospital mortality for acute myocardial infarction in Switzerland with admission during routine duty hours versus admission during out of hours (insight into the AMIS plus registry). Am. J. Cardiol. 101, 422–427 (2008).
Cavallazzi, R. et al. Association between time of admission to the ICU and mortality: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Chest 138, 68–75 (2010).
Anderson, J. L. et al. 2012 ACCF/AHA focused update incorporated into the ACCF/AHA 2007 guidelines for the management of patients with unstable angina/non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 61, e179–347 (2013).
Ting, H. H. et al. Delay from symptom onset to hospital presentation for patients with non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Arch. Intern. Med. 170, 1834–1841 (2010).
Rollinson, D. C. et al. The effects of consecutive night shifts on neuropsychological performance of interns in the emergency department: a pilot study. Ann. Emerg. Med. 41, 400–406 (2003).
Sorita, A. et al. Off-hour admission and outcomes for patients with acute myocardial infarction undergoing percutaneous coronary interventions. Am. Heart J. 169, 62–68 (2015).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Yangchun Liu and Tao Liu for their helpful comments in regards to this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.L., S.Q. and S.Y.H. defined the research theme. W.X.T., Y.J. and Y.H.F. designed the methods, analyzed the data, interpreted the results and wrote the manuscript. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Yan, J., Su, Q. et al. Is there an association between time of admission and in-hospital mortality in patients with non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction? A meta-analysis. Sci Rep 5, 14409 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14409
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14409
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.