Abstract
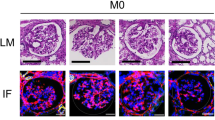
The molecular mechanism of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN), the most common primary renal glomerular disease worldwide, is unknown. HIGA (high serum IgA) mouse is a valid model of IgAN showing almost all of the pathological features, including mesangial cell proliferation. Here we elucidate a pattern of gene expression associated with IgAN by analyzing the diseased kidneys on cDNA microarrays. In particular, we showed an enhanced expression of several genes regulating the cell cycle and proliferation, including growth factors and their receptors, as well as endothelial differentiation gene-5 (EDG5), a receptor for sphingosine 1-phosphate (SPP). One of the growth factors, platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) induces a marked upregulation of EDG5 in proliferative mesangial cells, and promotes cell proliferation synergistically with SPP. The genomic approach allows us to identify families of genes involved in a process, and can indicate that enhanced PDGF-EDG5 signaling plays an important role in the progression of IgAN.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Emancipator SN, Lamm ME . IgA nephropathy: pathogenesis of the most common form of glomerulonephritis Lab Invest 1989 60: 168–183
Miyawaki S, Muso E, Takeuchi E, Matsushima H, Shibata Y, Sasayama S et al. Selective breeding for high serum IgA levels from noninbred ddY mice: isolation of a strain with an early onset of glomerular IgA deposition Nephron 1997 76: 201–207
Muso E, Yoshida H, Takeuchi E, Yashiro M, Matsushima H, Oyama A et al. Enhanced production of glomerular extracellular matrix in a new mouse strain of high serum IgA ddY mice Kidney Int 1996 50: 1946–1957
Orth SR, Ritz E, Suter-Crazzolara C . Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is expressed in the human kidney and is a growth factor for human mesangial cells Nephrol Dial Transplant 2000 15: 589–595
Kallincos NC, Pollard AN, Couper JJ . Evidence for a functional hepatocyte growth factor receptor in human mesangial cells Regul Pept 1998 74: 137–142
Thomas S, Vanuystel J, Gruden G, Rodriguez V, Burt D, Gnudi L et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptors in human mesangium in vitro and in glomerular disease J Am Soc Nephrol 2000 11: 1236–1243
Shankland SJ, Pippin J, Flanagan M, Coats SR, Nangaku M, Gordon KL et al. Mesangial cell proliferation mediated by PDGF and bFGF is determined by levels of the cyclin kinase inhibitor p27Kip1 Kidney Int 1997 51: 1088–1099
Ennulat D, Brown CA, Brown SA . Mitogenic effects of epidermal growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor on canine and equine mesangial cells in vitro Am J Vet Res 1997 58: 1308–1313
Yamabe H, Osawa H, Kaizuka M, Tsunoda S, Shirato K, Tateyama F et al. Platelet-derived growth factor, basic fibroblast growth factor, and interferon gamma increase type IV collagen production in human fetal mesangial cells via a transforming growth factor-beta-dependent mechanism Dial Transplant 2000 15: 872–876
Yokomizo T, Izumi T, Chang K, Takuwa Y, Shimizu T . A G-protein-coupled receptor for leukotriene B4 that mediates chemotaxis Nature 1997 387: 620–624
Suzuki S, Kuroda T, Kazama JI, Imai N, Kimura H, Arakawa M et al. The leukotriene B4 receptor antagonist ONO-4057 inhibits nephrotoxic serum nephritis in WKY rats J Am Soc Nephrol 1999 10: 264–270
Pizzinat N, Girolami JP, Parini A, Pecher C, Ordener C . Serotonin metabolism in rat mesangial cells: involvement of a serotonin transporter and monoamine oxidase A Kidney Int 1999 56: 1391–1399
Okazaki H, Ishizaka N, Sakurai T, Kurokawa K, Goto K, Kumada M et al. Molecular cloning of a novel putative G protein-coupled receptor expressed in the cardiovascular system Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1993 190: 1104–1109
An S, Zheng Y, Bleu T . Sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced cell proliferation, survival, and related signaling events mediated by G protein-coupled receptors Edg3 and Edg5 J Biol Chem 2000 275: 288–296
Pyne S, Pyne NJ . Sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling in mammalian cells Biochem J 2000 349: 385–402
Goetzl EJ, An S . A subfamily of G protein-coupled cellular receptors for lysophospholipids and lysosphingolipids Adv Exp Med Biol 1999 469: 259–264
An S . Molecular identification and characterization of G protein-coupled receptors for lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine 1-phosphate Ann NY Acad Sci 2000 905: 25–33
Coroneos E, Martinez M, McKenna S, Kester M . Differential regulation of sphingomyelinase and ceramidase activities by growth factors and cytokines. Implications for cellular proliferation and differentiation J Biol Chem 1995 270: 23305–23309
Kubo S, Kim ST, Takasugi M, Kuroiwa A . Pathogenetic mechanisms involved in mesangial interposition in IgA nephropathy Nephron 1994 68: 308–313
Matsuda M, Shikata K, Makino H, Sugimoto H, Ota K, Akiyama K et al. Gene expression of PDGF and PDGF receptor in various forms of glomerulonephritis Am J Nephrol 1997 17: 25–31
Nakajima M, Hewitson TD, Mathews DC, Kincaid SP . Platelet-derived growth factor mesangial deposits in mesangial IgA glomerulonephritis Nephrol Dial Transplant 1991 6: 11–16
Niemir ZI, Stein H, Noronha IL, Kruger C, Andrassy K, Ritz E et al. PDGF and TGF-beta contribute to the natural course of human IgA glomerulonephritis Kidney Int 1995 48: 1530–1541
Wang MB, Billings KR, Venkatesan N, Hall FL, Srivatsan ES . Inhibition of cell proliferation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines with antisense cyclin D1 Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1998 119: 593–599
Oren R, Takahashi S, Doss C, Levy R, Levy S . TAPA-1, the target of an antiproliferative antibody, defines a new family of transmembrane proteins Mol Cell Biol 1990 10: 4007–4015
Uda S, Yoshimura A, Sugenoya Y, Inui K, Taira T, Ideura T . Mesangial proliferative nephritis in man is associated with increased expression of the cell survival factor, Bcl-2 Am J Nephrol 1998 18: 281–295
Sandau KB, Brune B . Up-regulation of Bcl-2 by redox signals in glomerular mesangial cells Cell Death Differ 2000 7: 118–125
Del Sal G, Ruaro ME, Philipson L, Schneider C . The growth arrest-specific gene, gas1, is involved in growth suppression Cell 1992 70: 595–607
Rouault JP, Rimokh R, Tessa C, Paranhos G, Ffrench M, Duret L et al. BTG1, a member of a new family of antiproliferative genes EMBO J 1992 11: 1663–1670
Motohashi K, Shibata S, Ozaki Y, Yatomi Y, Igarashi Y . Identification of lysophospholipid receptors in human platelets: the relation of two agonists, lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine 1-phosphate FEBS Lett 2000 468: 189–193
Gonda K, Okamoto H, Takuwa N, Yatomi Y, Okazaki H, Sakurai T et al. The novel sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor AGR16 is coupled via pertussis toxin-sensitive and -insensitive G-proteins to multiple signaling pathways Biochem J 1999 337: 67–75
Couser WG, Johnson RJ . Mechanisms of progressive renal disease in glomerulonephritis Am J Kidney Dis 1994 23: 193–198
Inoue CN, Epstein M, Foster HG, Hotta O, Kondo Y, Iinuma K . Lysophosphatidic acid and mesangial cells: implications for renal diseases Clin Sci (Colch) 1999 96: 431–436
Yatomi Y, Ruan F, Hakomori S, Igarashi Y . Sphingosine-1-phosphate: a platelet-activating sphingolipid released from agonist-stimulated human platelets Blood 1995 86: 193–202
Yatomi Y, Yamamura S, Ruan F, Igarashi Y . Sphingosine 1-phosphate induces platelet activation through an extracellular action and shares a platelet surface receptor with lysophosphatidic acid J Biol Chem 1997 272: 5291–5297
Benton AM, Gerrard JM, Michiel T, Kindom SE . Are lysophosphatidic acids or phosphatidic acids involved in stimulus activation coupling in platelets? Blood 1982 60: 642–649
Rupprecht HD, Dann P, Sukhatme VP, Sterzel RB, Coleman DL . Effect of vasoactive agents on induction of Egr-1 in rat mesangial cells: correlation with mitogenicity Am J Physiol 1992 263: 623–636
Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB . Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery Genome Res 1996 6: 791–806
Katsuma S, Shiojima S, Hirasawa A, Suzuki Y, Ikawa H, Takagaki K et al. Functional genomic search of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR) using microarrays with normalized cDNA library Meth Enzymol 2001 345: 585–600
Dong G, Loukinova E, Chen Z, Gangi L, Chanturita TI, Liu ET et al. Molecular profiling of transformed and metastatic murine squamous carcinoma cells by differential display and cDNA microarray reveals altered expression of multiple genes related to growth, apoptosis, angiogenesis, and the NF-kappaB signal pathway Cancer Res 2001 61: 4797–4808
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs S Stojilkovic (National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, National Institutes of Health) and GE Smyth (Research Laboratories, Nippon Shinyaku Co) for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported in part by research grants from the Scientific Fund of the Ministry of Education, Science, and Culture of Japan, the Japan Health Science Foundation and Ministry of Human Health and Welfare, the Organization for Pharmaceutical Safety and Research (OPSR), and a Grant for Liberal Harmonious Research Promotion System from the Science and Technology Agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katsuma, S., Shiojima, S., Hirasawa, A. et al. Genomic analysis of a mouse model of immunoglobulin A nephropathy reveals an enhanced PDGF–EDG5 cascade. Pharmacogenomics J 1, 211–217 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500043
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500043