Abstract
5-HT2C receptor (5HT2CR, serotonin-2C) RNA undergoes editing to produce several receptor variants, some with pharmacological differences. This investigation comprised two parts: the characterisation of 5-HT2CR RNA editing in a larger human control sample than previously examined, and a comparative study in subjects with schizophrenia. Secondary structure analysis of the putative edited region of the human 5-HT2CR gene predicted the existence of a double stranded (ds) RNA loop, essential for RNA editing in this receptor. RNA was then extracted from frontal cortex of five controls and five subjects with schizophrenia. RT-PCR products of the edited region were cloned and sequenced (n = 100). Reduced RNA editing, increased expression of the unedited 5-HT2C-INI isoform in schizophrenia (P = 0.001) and decreased expression of the 5-HT2C-VSV and 5-HT2C-VNV isoforms were detected in the schizophrenia group. In addition, two novel mRNA edited variants were identified: 5-HT2C-MNI and 5-HT2C-VDI. Screening of the 5-HT2CR gene did not reveal any mutations likely to disrupt the dsRNA loop, suggesting that the reduced RNA editing in schizophrenia may instead be caused by altered activity of the editing enzyme(s). Since the unedited 5-HT2C-INI is more efficiently coupled to G proteins than the other isoforms, its increased expression in schizophrenia may lead to enhanced 5-HT2CR-mediated effects. The results also illustrate that potentially important receptor alterations may occur in schizophrenia which are not detectable merely in terms of receptor abundance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Busatto GF, Kerwin RW . Perspectives on the role of serotonergic mechanisms in the pharmacology of schizophrenia J Psychopharmacol 1997 11: 3–12
Harrison PJ, East SZ . The serotonin 5-HT2A receptor and its gene in schizophrenia J Serotonin Res 2000 5: 1–6
Meltzer HY . The role of serotonin in antipsychotic drug action Neuropsychopharmacology 1999 21: 106S–115S
Burris KD, Breeding M, Sanders-Bush E . (+)Lysergic acid diethylamide, but not its non-hallucinogenic congeners, is a potent serotonin 5HT1C receptor agonist J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1991 258: 891–896
Sanders-Bush E, Breeding M . Choroid plexus epithelial cells in primary culture: a model of 5HT1C receptor activation by hallucinogenic drugs Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1991 105: 340–346
Segman RH, Ebstein RP, Heresco-Levy U, Gorfine M, Avnon M, Gur E et al. Schizophrenia, chronic hospitalization and the 5-HT2C receptor gene Psychiatr Genet 1997 7: 75–78
Holmes C, Arranz MJ, Powell JF, Collier DA, Lovestone S . 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptor polymorphisms and psychopathology in late onset Alzheimer's disease Hum Mol Genet 1998 7: 1507–1509
Sodhi MS, Arranz MJ, Curtis D, Ball DM, Sham P, Roberts GW et al. Association between clozapine response and allelic variation in the 5-HT2C receptor gene Neuroreport 1995 7: 169–172
Sodhi MS, Sham PC, Makoff A, Collier D, Arranz M, Munro J et al. Allelic variation of the serotonin 5-HT2C receptor in therapeutic response to clozapine—replication studies and meta-analysis Mol Psychiatry 1999 4 (Suppl 1): S94
Crossland N, East SZ, Burnet PWJ, Harrison PJ . An RT-PCR study of 5-HT2C receptor mRNA in schizophrenia Soc Neurosci Abs 1999 25: 2074
Tecott LH, Sun LM, Akana SF, Strack AM, Lowenstein DH, Dallman et al. Eating disorder and epilepsy in mice lacking 5-HT2C serotonin receptors Nature 1995 374: 542–546
Stam NJ, Vanderheyden P, van Alebeck C, Klomp J, de Boer T, van Delft A et al. Genomic organisation and functional expression of the gene encoding the human serotonin 5-HT2C receptor Eur J Pharmacol 1994 269: 339–348
Wang Q, O'Brien PJ, Chen CX, Cho DS, Murray JM, Nishikura K . Altered G protein-coupling functions of RNA editing isoform and splicing variant serotonin2C receptors J Neurochem 2000 74: 1290–1300
Burns CM, Chu H, Rueter SM, Hutchinson LK, Canton H, Sanders-Bush E et al. Regulation of serotonin-2C receptor G-protein coupling by RNA editing Nature 1997 387: 303–308
Niswender CM, Copeland SC, Herrick-Davis K, Emeson RB, Sanders-Bush E . RNA editing of the human serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine2C receptor silences constitutive activity J Biol Chem 1999 274: 9472–9478
Fitzgerald LW, Iyer G, Conklin DS, Krause CM, Marshall A, Patterson JP et al. Messenger RNA editing of the human serotonin 5-HT2C receptor Neuropsychopharmacology 1999 21: 82S–90S
Scott J . A place in the world for RNA editing Cell 1995 81: 833–836
Higuchi M, Single FN, Kohler M, Sommer B, Sprengel R, Seeburg PH . RNA editing of AMPA receptor subunit GluR-B: a base-paired intron-exon structure determines position and efficiency Cell 1993 75: 1361–1370
Egebjerg J, Kukekov V, Heinemann SF . Intron sequence directs RNA editing of the glutamate receptor subunit GluR2 coding sequence Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994 91: 10270–10274
Lomeli H, Mosbacher J, Melcher T, Hoger T, Geiger JR, Kuner T et al. Control of kinetic properties of AMPA receptor channels by nuclear RNA editing Science 1994 266: 1709–1713
Brusa R, Zimmermann F, Koh DS, Feldmeyer D, Gass P, Seeburg PH et al. Early-onset epilepsy and postnatal lethality associated with an editing-deficient GluR-B allele in mice Science 1995 270: 1677–1680
Akbarian S, Smith MA, Jones EG . Editing for an AMPA receptor subunit RNA in prefrontal cortex and striatum in Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease and schizophrenia Brain Res 1995 699: 297–304
Lincoln SE, Daly MJ, Lander ES . PRIMER: a computer program for automatically selecting PCR primers. Version 0 5 MIT Center for Genome Research annd Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research 1991
Brodsky LI, Ivanov VV, Kalaydzidis Ya L, Leontovich AM, Nikolaev VK, Feranchuk SI et al. GeneBeeNET: Internetbased server for analyzing biopolymers structure Biochemistry 1995 60: 923–928
Orita M, Iwahana H, Kanazawa H, Hayashi K, Sekiya T . Detection of polymorphisms of human DNA by gel electrophoresis as single-strand conformation polymorphisms Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1989 86: 2766–2770
Sheffield VC, Beck JS, Kwitek AE, Sandstrom DW, Stone EM . The sensitivity of single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis for the detection of single base substitutions Genomics 1993 16: 325–332
Chomcynzski P, Saachi N . A single-step method for the isolation of RNA using the acid-phenol-chloroform method Anal Biochem 1987 162: 156–159
Eastwood SL, Heffernan J, Harrison PJ . Chronic haloperidol treatment differentially affects the expression of synaptic and neuronal plasticity-associated genes Mol Psychiatry 1997 2: 322–329
Corpet F . Multiple sequence alignment with hierarchical clustering Nucleic Acids Res 1988 16: 10881–10890
Acknowledgements
We thank Louise Lewis, Nicola Crossland, Simon East, Sharon Eastwood, Catherine Harmer, Anna Scarna (University Department of Psychiatry, Oxford) and Janet Mulchrone (Institute of Psychiatry, London) for their help at various stages of this project. In addition we thank Nigel Cairns and Nadeem Khan (MRC Brain Bank at the Institute of Psychiatry, London) for tissue from control subjects, and Ian Everall and David Cotter for help with tissue collection from three schizophrenia cases. The work was funded by the Stanley Foundation and a Medical Research Council Training Fellowship to MSS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sodhi, M., Burnet, P., Makoff, A. et al. RNA editing of the 5-HT2C receptor is reduced in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 6, 373–379 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000920
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000920
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Epitranscriptomic dynamics in brain development and disease
Molecular Psychiatry (2022)
-
Global landscape and genetic regulation of RNA editing in cortical samples from individuals with schizophrenia
Nature Neuroscience (2019)
-
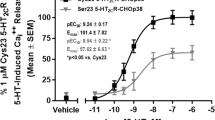
Serotonin 5-HT2C Receptor Cys23Ser Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Associates with Receptor Function and Localization In Vitro
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Mast Cell Serotonin Immunoregulatory Effects Impacting on Neuronal Function: Implications for Neurodegenerative and Psychiatric Disorders
Neurotoxicity Research (2015)
-
The role of 5-HT2C receptors in touchscreen visual reversal learning in the rat: a cross-site study
Psychopharmacology (2015)