Abstract
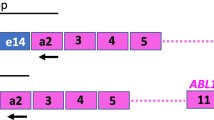
Monitoring of BCR-ABL transcripts has become established practice in the management of chronic myeloid leukemia. However, nucleic acid amplification techniques are prone to variations which limit the reliability of real-time quantitative PCR (RQ-PCR) for clinical decision making, highlighting the need for standardization of assays and reporting of minimal residual disease (MRD) data. We evaluated a lyophilized preparation of a leukemic cell line (K562) as a potential quality control reagent. This was found to be relatively stable, yielding comparable respective levels of ABL, GUS and BCR-ABL transcripts as determined by RQ-PCR before and after accelerated degradation experiments as well as following 5 years storage at −20°C. Vials of freeze-dried cells were sent at ambient temperature to 22 laboratories on four continents, with RQ-PCR analyses detecting BCR-ABL transcripts at levels comparable to those observed in primary patient samples. Our results suggest that freeze-dried cells can be used as quality control reagents with a range of analytical instrumentations and could enable the development of urgently needed international standards simulating clinically relevant levels of MRD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van der Velden VH, Hochhaus A, Cazzaniga G, Szczepanski T, Gabert J, van Dongen JJ . Detection of minimal residual disease in hematologic malignancies by real-time quantitative PCR: principles, approaches, and laboratory aspects. Leukemia 2003; 17: 1013–1034.
O'Brien SG, Guilhot F, Larson RA, Gathmann I, Baccarani M, Cervantes F et al. Imatinib compared with interferon and low-dose cytarabine for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 994–1004.
Capdeville R, Buchdunger E, Zimmermann J, Matter A . Glivec (STI571, imatinib), a rationally developed, targeted anticancer drug. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2002; 1: 493–502.
Le Coutre P, Kreuzer KA, Na IK, Schwarz M, Lupberger J, Holdhoff M et al. Imatinib in Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic phase CML patients: molecular and cytogenetic response rates and prediction of clinical outcome. Am J Hematol 2003; 73: 249–255.
Hughes TP, Kaeda J, Branford S, Rudzki Z, Hochhaus A, Hensley ML et al. Frequency of major molecular responses to imatinib or interferon alfa plus cytarabine in newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 1423–1432.
Mensink E, van de Locht A, Schattenberg A, Linders E, Schaap N, Geurts van Kessel A et al. Quantitation of minimal residual disease in Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukaemia patients using real-time quantitative RT-PCR. Br J Haematol 1998; 102: 768–774.
Olavarria E, Kanfer E, Szydlo R, Kaeda J, Rezvani K, Cwynarski K et al. Early detection of BCR-ABL transcripts by quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction predicts outcome after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2001; 97: 1560–1565.
Elmaagacli AH . Real-time PCR for monitoring minimal residual disease and chimerism in patients after allogeneic transplantation. Int J Hematol 2002; 76: 204–205.
Oehler VG, Radich JP . Monitoring bcr-abl by polymerase chain reaction in the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. Curr Oncol Rep 2003; 5: 426–435.
Freeman WM, Walker SJ, Vrana KE . Quantitative RT-PCR: pitfalls and potential. Biotechniques 1999; 26: 112–122, 124–125.
Keilholz U, Willhauck M, Rimoldi D, Brasseur F, Dummer W, Rass K et al. Reliability of reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)-based assays for the detection of circulating tumour cells: a quality-assurance initiative of the EORTC melanoma cooperative group. Eur J Cancer 1998; 34: 750–753.
Bolufer P, Barragan E, Sanz MA, Martin G, Bornstein R, Colomer D et al. Preliminary experience in external quality control of RT-PCR PML-RAR alpha detection in promyelocytic leukemia. Leukemia 1998; 12: 2024–2028.
Muller MC, Hordt T, Paschka P, Merx K, La Rosee P, Hehlmann R et al. Standardization of preanalytical factors for minimal residual disease analysis in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Acta Haematol 2004; 112: 30–33.
Saldanha J, Gerlich W, Lelie N, Dawson P, Heermann K, Heath A . An international collaborative study to establish a World Health Organization international standard for hepatitis B virus DNA nucleic acid amplification techniques. Vox Sang 2001; 80: 63–71.
Saldanha J, Heath A . Collaborative study to calibrate hepatitis C virus genotypes 2–6 against the HCV International Standard, 96/790 (genotype 1). Vox Sang 2003; 84: 20–27.
Dybul M, Fauci AS, Bartlett JG, Kaplan JE, Pau AK . Guidelines for using antiretroviral agents among HIV-infected adults and adolescents. Ann Intern Med 2002; 137: 381–433.
Beillard E, Pallisgaard N, van der Velden VH, Bi W, Dee R, van der Schoot E et al. Evaluation of candidate control genes for diagnosis and residual disease detection in leukemic patients using ‘real-time’ quantitative reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RQ-PCR) – a Europe against cancer program. Leukemia 2003; 17: 2474–2486.
Gabert J, Beillard E, van der Velden VH, Bi W, Grimwade D, Pallisgaard N et al. Standardization and quality control studies of ‘real-time’ quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction of fusion gene transcripts for residual disease detection in leukemia – a Europe against cancer program. Leukemia 2003; 17: 2318–2357.
Guo JQ, Lin H, Kantarjian H, Talpaz M, Champlin R, Andreeff M et al. Comparison of competitive-nested PCR and real-time PCR in detecting BCR-ABL fusion transcripts in chronic myeloid leukemia patients. Leukemia 2002; 16: 2447–2453.
Kirkwood TB . Predicting the stability of biological standards and products. Biometrics 1977; 33: 736–742.
Tydeman M, Kirkwood T . Design and analysis of accelerated degradation tests for the stability of biological standards I. Properties of maximum likelihood estimators. J Biol Stand 1984; 12: 195–214.
Van Der Velden VH, Boeckx N, Gonzalez M, Malec M, Barbany G, Lion T et al. Differential stability of control gene and fusion gene transcripts over time may hamper accurate quantification of minimal residual disease – a study within the Europe Against Cancer Program. Leukemia 2004; 18: 884–886.
Hughes TP, Deininger MW, Hochhaus A, Branford S, Radich JP, Kaeda J et al. Monitoring CML patients responding to treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors – review and recommendations for ‘harmonizing’ current methodology for detecting BCR-ABL transcripts and kinase domain mutations and for expressing results. Blood 2006; 108: 28–37.
Gorre ME, Mohammed M, Ellwood K, Hsu N, Paquette R, Rao PN et al. Clinical resistance to STI-571 cancer therapy caused by BCR-ABL gene mutation or amplification. Science 2001; 293: 876–880.
Hochhaus A, Kreil S, Corbin AS, La Rosee P, Muller MC, Lahaye T et al. Molecular and chromosomal mechanisms of resistance to imatinib (STI571) therapy. Leukemia 2002; 16: 2190–2196.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the SANCO commission grant no. SI2.129294 (99CVF2-016), and national grants notably ARC no. 5484, PACA Canceropôle funding and a grant from the French Ministry of Employment and Solidarity for the: ‘Innovative and Expensive Diagnostic and Therapeutic Tools Programme’. MS was under a temporary contract from Canceropôle PACA. DG was supported by Leukaemia Research Fund of Great Britain. GC was supported by Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website (http://www.nature.com/leu)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saldanha, J., Silvy, M., Beaufils, N. et al. Characterization of a reference material for BCR-ABL (M-BCR) mRNA quantitation by real-time amplification assays: towards new standards for gene expression measurements. Leukemia 21, 1481–1487 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404716
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404716
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Harmonization of molecular monitoring of CML therapy in Europe
Leukemia (2009)