Abstract
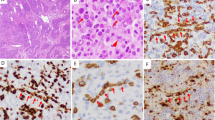
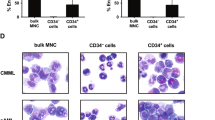
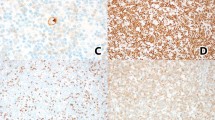
Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL) is a distinct biological and cytogenetic entity with a broad spectrum of morphological features (common type, small-cell variant and lymphohistiocytic variant). Few cell lines of ALCL are available and they all originate from primary tumors demonstrating the common type morphology (ie large-sized lymphoma cells). We established a new ALCL cell line (COST) from the peripheral blood of a patient with a small-cell variant of ALCL, at diagnosis. Cells growing in vitro and in SCID mice consisted of two populations, that is, small- and large-sized cells as seen in the patient's tumor. Both large and small malignant cells were positive for CD43/MT1 T-cell associated antigen, perforin, granzyme B and TIA-1, but negative for CD2, CD3, CD5, CD7, CD4 and CD8 antigens. Standard cytogenetic studies as well as multiplex FISH confirmed the presence of the canonical t(2;5)(p23;q35) translocation, but also revealed additional numerical and structural abnormalities. The COST cell line is the first ALCL small-cell variant cell line, and thus provides a potentially useful tool for further functional and molecular studies that should improve our understanding of the small-cell variant of ALCL, which is more frequently complicated by a leukemic phase.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stein H, Mason DY, Gerdes J, O'Connor N, Wainscoat J, Pallesen G et al. The expression of the Hodgkin's disease associated antigen Ki-1 in active and neoplastic lymphoid tissue: evidence that Reed–Sternberg cells and histiocytic malignancies are derived from activated lymphoid cells. Blood 1985; 66: 848–858.
Morris SW, Kirstein MN, Valentine MB, Dittmer KG, Shapiro DN, Saltman DL et al. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Science 1994; 263: 1281–1284.
Chan JKC, Ng CS, Hui PK, Leung TW, Lo ESF, Lau WH et al. Anaplastic large cell Ki-1 lymphoma. Delineation of two morphological types. Histopathology 1989; 15: 11–34.
Pileri S, Falini B, Delsol G, Stein H, Baglioni P, Poggi S et al. Lymphohistiocytic T-cell lymphoma CD30/Ki-1 + with high content of reactive histiocytes. Histopathology 1990; 16: 383–391.
Kinney MC, Collins RD, Greer JP, Whitlock JA, Sioutos N, Kadin ME . A small cell predominant variant of primary Ki-1 (CD30) + T-cell lymphoma. Am J Surg Pathol 1993; 17: 859–868.
Mann KP, Hall B, Kamino H, Borowitz MJ, Ratech H . Neutrophil-rich, Ki-1-positive anaplastic large-cell malignant lymphoma. Am J Surg Pathol 1995; 19: 407–416.
Benharroch D, Meguerian-Bedoyan Z, Lamant L, Amin C, Brugieres L, Terrier-Lacombe MJ et al. ALK-positive lymphoma: a single disease with a broad spectrum of morphology. Blood 1998; 91: 2076–2084.
Falini B . Anaplastic large cell lymphoma: pathological, molecular and clinical features. Br J Haematol 2001; 114: 741–760.
Delsol G, Ralfkiaer E, Stein H, Wright D, Jaffe E . Anaplastic large cell lymphomas. Primary systemic (T/Null cell type). In: Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H and Vardiman JW (eds). World Health Organization (WHO) Classification of Tumors. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon: IARC press, 2001, pp. 230–235.
Pulford K, Lamant L, Morris SW, Butler LH, Wood KM, Stroud D et al. Detection of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and nucleolar protein nucleophosmin (NPM)-ALK proteins in normal and neoplastic cells with the monoclonal antibody ALK1. Blood 1997; 89: 1394–1404.
Mason DY, Pulford KAF, Bischof D, Kuefer MU, Butler LH, Lamant L et al. Nucleolar localization of the nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase is not required for malignant transformation. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 1057–1062.
Lamant L, Meggetto F, Al Saati T, Brugières L, Bressac de Paillerets B, Dastugue N et al. High incidence of the t(2;5) (p23;q35) translocation in anaplastic large cell lymphoma and its lack of detection in Hodgkin's disease. Comparison of cytogenetic analysis, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction, and P-80 immunostaining. Blood 1996; 87: 284–291.
Cordell JL, Falini B, Erber WN, Ghosh KA, Abdulaziz Z, MacDonald S et al. Immunoenzymatic labeling of monoclonal antibodies using immune complexes of alkaline phosphatase and monoclonal anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP complexes). J Histochem Cytochem 1984; 32: 219–229.
Al Saati T, Galoin S, Gravel S, Lamant L, Roda D, Chittal SM et al. IgH and TcR γ gene rearrangements identified in Hodgkin's disease by PCR demonstrate lack of correlation between genotype, phenotype and Epstein–Barr virus status. J Pathol 1997; 181: 387–393.
Theriault C, Galoin S, Valmary S, Selves J, Lamant L, Roda D et al. PCR analysis of immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) and TCR-γ chain gene rearrangements in the diagnosis of lymphoproliferative disorders: results of a study of 525 cases. Mod Pathol 2000; 13: 1269–1279.
Van Dongen JJM, Langerak AW, Brüggemann M, Evans PAS, Hummel M, Lavender FL et al. Design and standardization of PCR primers and protocols for detection of clonal immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene recombinations in suspect lymphoproliferations: report of the BIOMED-2 Concerted Action BMH4-CT98-3936. Leukemia 2003; 17: 2257–2317.
Mitelman F . ISCN 1995. An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature. Basel, Switzerland: Karger, 1995.
Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Stein H, Banks PM, Chan JKC, Cleary ML et al. A revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: A proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Blood 1994; 84: 1361–1392.
Chhanabhai M, Britten C, Klasa R, Gascoyne RD . T(2;5) positive lymphoma with peripheral blood involvement. Leukemia Lymphoma 1998; 28: 415–422.
Bayle C, Charpentier A, Duchayne E, Manel AM, Pages MP, Robert A et al. Leukaemic presentation of small cell variant anaplastic large cell lymphoma: report of four cases. Br J Haematol 1999; 104: 680–688.
Villamor N, Rozman M, Esteve J, Aymerich M, Colomer D, Aguilar JL et al. Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma with rapid evolution to leukemic phase. Ann Hematol 1999; 78: 478–482.
Duchayne E, Demur C, Dastugue N, Robert A, Delsol G . Lymphome anaplasique: forme leucémique de la variante ‘à petites cellules’ chez un enfant. Hematologia 2000; 6: 85–88.
Lesesve JF, Buisine J, Gregoire MJ, Raby P, Lederlin P, Bene MC et al. Leukaemic small cell variant anaplastic large cell lymphoma during pregnancy. Clin Lab Haematol 2000; 22: 297–301.
Epstein AL, Kaplan HS . Biology of the human malignant lymphomas. Establishment in continuous cell culture and heterotransplantation of diffuse histiocytic lymphomas. Cancer 1974; 34: 1851–1872.
Fisher P, Nacheva E, Mason DY, Sherrington PD, Hoyle C, Hayhoe FGK et al. A Ki-1 (CD30)-positive human cell line (Karpas 299) established from a high-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, showing a 2;5 translocation and rearrangement of the T-cell receptor β-chain gene. Blood 1988; 72: 234–240.
Su IJ, Balk SP, Kadin ME . Molecular basis for the aberrant expression of T cell antigens in postthymic T cell malignancies. Am J Pathol 1988; 132: 192–198.
Morgan R, Smith SD, Hecht BK, Christy V, Mellentin JD, Warnke R et al. Lack of involvement of the c-fms and N-myc genes by chromosomal translocation (2;5)(p23;q35) common to malignancies with features of so-called malignant histiocytosis. Blood 1989; 73: 2155–2164.
Barbey S, Gogusev J, Mouly H, Le Pelletier O, Smith W, Richard S et al. DEL cell line: a ‘malignant histiocytosis’ CD30+ t(5;6)(q35;p21) cell line. Int J Cancer 1990; 45: 546–553.
Shimakage M, Dezawa T, Tamura S, Tabata T, Aoyagi N, Koike M et al. A Ki-1-positive cell line expressing Epstein–Barr virus antigens, established from a child with Ki-1-positive lymphoma. Intervirology 1993; 36: 215–224.
Pasqualucci L, Wasik M, Teicher BA, Flenghi L, Bolognesi A, Stirpe F et al. Antitumor activity of anti-CD30 immunotoxin (Ber-H2/saporin) in vitro and in severe combined immunodeficiency disease mice xenografted with human CD30+ anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Blood 1995; 85: 2139–2146.
Del Mistro A, Leszl A, Bertorelle R, Calabro ML, Panozzo M, Menin C et al. A CD30-positive T cell line established from an aggressive anaplastic large cell lymphoma, originally diagnosed as Hodgkin's disease. Leukemia 1994; 8: 1214–1219.
Kim H, Pangalis GA, Payne BC, Kadin ME, Rappaport H . Ultrastructural identification of neoplastic histiocytes–monocytes: an application of a newly developed cytochemical technique. Am J Pathol 1982; 106: 204–223.
Acknowledgements
We thank Michel March for his excellent technical work performing immunohistochemistry, Daniel Roda and Jeanine Boye. We acknowledge the paediatrician, Dr Alain Robert for providing us clinical data. This work was supported by the ‘Ligue Contre le Cancer’, Comités de la Haute-Garonne et de l'Aveyron.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lamant, L., Espinos, E., Duplantier, M. et al. Establishment of a novel anaplastic large-cell lymphoma-cell line (COST) from a ‘small-cell variant’ of ALCL. Leukemia 18, 1693–1698 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403464
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403464
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Peptides derived from the dependence receptor ALK are proapoptotic for ALK-positive tumors
Cell Death & Disease (2015)
-
Phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate regulates invasion through binding and activation of Tiam1
Nature Communications (2014)
-
Inhibition of Rac controls NPM–ALK-dependent lymphoma development and dissemination
Blood Cancer Journal (2011)
-
Activation of Rac1 and the exchange factor Vav3 are involved in NPM-ALK signaling in anaplastic large cell lymphomas
Oncogene (2008)
-
Serpin A1 is overexpressed in ALK+ anaplastic large cell lymphoma and its expression correlates with extranodal dissemination
Leukemia (2006)