Abstract
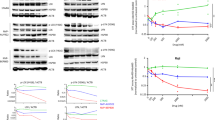
Temperature-sensitive mutants of BCR/ABL tyrosine kinase have been extensively used to study the mechanisms of cell transformation and signal transduction. However, little is known about the effect of temperature on the activity of wild-type BCR/ABL gene product. In this study, we demonstrate that in vivo tyrosine kinase activity of p210, p190 BCR/ABL and v-abl are temperature-sensitive when expressed in hematopoietic cells and decline when temperature is raised 2°C above normal range. In vitro tyrosine kinase activities of purified recombinant Abl and immunoprecipitated p210 BCR/ABL were also sensitive to increased temperature. Tyrosine phosphorylation of cellular proteins was markedly reduced in BCR/ABL transformed cells after 16 h at 39°C, whereas the expression of BCR/ABL was unchanged. Temperature-induced downregulation of BCR/ABL kinase activity was reversible when cells were shifted back to 37°C. The downregulation of Abl tyrosine kinase activity was not influenced by mutation or deletion of SH2 or SH3 domains or mutation of the GRB2 binding site. No increase in functional activity or expression of protein-tyrosine phosphatases, PTP-1B, SH-PTP1 or SH-PTP2 was detected in cells grown at 39°C. Temperature-induced downregulation in tyrosine kinase activity correlated with decline in phosphotyrosine-associated PI 3-kinase whereas there was no change in growth factor independence of transformed hematopoietic cells. In conclusion, Abl tyrosine kinase has intrinsic sensitivity to temperature and BCR/ABL expressed in hematopoietic cells is downregulated by increasing temperature 2°C. These observations provide a unique opportunity to identify cellular factor(s) which regulate BCR/ABL kinase in vivo and suggests possible novel treatment of CML by a mild hyperthermia.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramakrishnan L, Rosenberg N . abl genes Biochim Biophys Acta 1989 989: 209–224
Wiedemann LM, Karhi KK, Shivji MK, Rayter SI, Pegram SM, Dowden G, Bevan D, Will A, Galton DA, Chan LC . The correlation of breakpoint cluster region rearrangement and p210 phl/abl expression with morphological analysis of Ph-negative chronic myeloid leukemia and other myeloproliferative diseases Blood 1988 71: 349–355
Daley GQ, Van Etten RK, Baltimore D . Induction of chronic myelogenous leukemia in mice by the p210 bcr/abl gene of the Philadelphia chromosome Science 1990 247: 824–830
Daley GQ, Baltimore D . Transformation of an interleukin-3-dependent hematopoietic cell line by the chronic myelogenous leukemia-specific p210 bcr/abl protein Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1988 85: 9312–9316
Lugo TG, Pendergast AM, Muller AJ, Witte ON . Tyrosine kinase activity and transformation potency of bcr-abl oncogene products Science 1990 247: 1079–1082
Cortez D, Kadlec L, Pendergast AM . Structural and signalling requirements for BCR-ABL mediated transformation and inhibition of apoptosis Mol Cell Biol 1995 15: 5531–5541
Hariharan IK, Adams JM, Cory S . BCR-abl oncogene renders myeloid cell line factor independent Oncogene 1988 3: 387–399
Nishii K, Kabarowski JHS, Gibbons DL, Griffiths SD, Titley I, Wiedemann LM, Greaves MF . ts BCR-ABL kinase activation confers increased resistance to genotoxic damage via cell cycle block Oncogene 1996 13: 2225–2234
Cortez D, Stoica G, Pierce JH, Pendergast AM . The BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibits apoptosis by activating a Ras-dependent signaling pathway Oncogene 1996 13: 2589–2594
Cortez D, Reuther G, Pendergast AM . The BCR/abl tyrosine kinase activates mitogenic signaling pathways and stimulates G1-to S phase transition in hematopoietic cells Oncogene 1997 15: 2333–2342
Albrecht T, Schwab R, Henkes M, Peschel C, Huber C, Aulitzky WE . Primary proliferating immature myeloid cells from CML patients are not resistant to induction of apoptosis by DNA damage and growth factor withdrawal Br J Haematol 1996 95: 501–507
Bedi A, Barber JP, Bedi GC, El-Deiry WS, Sidransky D, Vala MS, Akhtar AJ, Hilton J, Jones RJ . BCR-ABL-mediated inhibition of apoptosis with delay of G2/M transition after DNA damage: a mechanism of resistance to multiple anticancer agents Blood 1995 86: 1148–1158
Cambier N, Chopra R, Strasser A, Metcalf D, Elefanty AG . BCR-ABL activates pathways mediating cytokine independence and protection against apoptosis in murine hematopoietic cells in a dose-dependent manner Oncogene 1998 16: 349–357
Maguer-Satta V, Burl S, Liu L, Damen J, Chahine H, Krystal G, Eaves A, Eaves C . BCR-ABL accelerates C2-ceramide-induced apoptosis Oncogene 1998 16: 237–248
Engelman A, Rosenberg N . Isolation of temperature-sensitive Abelson virus mutants by site-directed mutagenesis Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1987 84: 8021–8025
Engelman A, Rosenberg N . Temperature-sensitive mutants of Abelson murine leukemia virus deficient in protein tyrosine kinase activity J Virol 1990 64: 4242–4251
LaMontagne KRJ, Flint AJ, Franza RB, Pendergast AM, Tonks NK . Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B antagonizes signalling by oncoprotein tyrosine kinase p210 bcr-abl in vivo Mol Cell Biol 1998 18: 2965–2975
Carlesso N, Griffin JD, Drucker B . Use of temperature-sensitive mutant to define the biological effects of p210/BCR/abl tyrosine kinase on proliferation of a factor-dependent murine myeloid cell line Oncogene 1994 9: 149–156
Kabarowski JHS, Allen PB, Wiedemann LM . A temperature sensitive p210 BCR-ABL mutant defines the primary consequences of BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase expression in growth factor dependent cells EMBO J 1994 13: 5887–5895
Cristau B, Schafer P, Pierce S . Heat shock enhances antigen processing and accelerates the formation of compact class II αβ dimers J Immunol 1994 152: 1546–1556
Duff GW, Durum SK . T cell proliferation induced by interleukin 1 is greatly increased by hyperthermia Clin Res 1982 30: 694–699
Kappel M, Diamant M, Hansen MB, Klokker M, Pedersen BK . Effects of in vitro hyperthermia on the proliferative response of blood mononuclear subsets and detection of interleukin 1 and 6, tumor necrosis factor alpha and interferon-gamma Immunology 1991 73: 304–308
Huang YH, Haegerstrand A, Frostegard J . Effects of in vitro hyperthermia on proliferative responses and lymphocyte activity Clin Exp Immunol 1996 103: 61–66
Palacios R, Steinmetz M . IL-3-dependent mouse clones that express B-220 surface antigen, contain Ig genes in germ-line configuration, and generate B lymphocytes in vivo Cell 1985 41: 727–734
McLaughlin J, Chianese E, Witte ON . In vitro transformation of immature hematopoietic cells by the P210 BCR/ABL oncogene product of the Philadelphia chromosome Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1987 84: 6558–6562
Daley GQ, McLaughlin J, Witte ON, Baltimore D . The CML-specific P210 bcr/abl protein, unlike v-abl, does not transform NIH/3T3 fibroblasts Science 1987 237: 532–535
Varticovski L, Daley GQ, Jackson P, Baltimore D, Cantley LC . Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in cells expressing abl oncogene variants Mol Cell Biol 1991 11: 1107–1113
Varticovski L, Druker B, Morrison D, Cantley LC, Roberts T . The CSF-1 receptor associates with and activates PI 3-kinase Nature 1989 342: 699–702
Susa M, Keeler ML, Varticovski L . Platetet-derived growth factor activates membrane-associated phosphatidyinositol 3-kinase and mediates its translocation from the cytosol J Biol Chem 1992 267: 22951–22956
Jain SK, Susa-Spring M, Carlesso N, Druker B, Varticovski L . PI 3-kinase activation in BCR/abl-transformed hematopoietic cells does not require interaction of p85 SH2 domains with p210 BCR/abl Blood 1996 88: 1542–1550
Sattler M, Salgia R, Shrikhande G, Verma S, Choi JL, Rohrschneider LR, Griffin JD . The phosphatidylinositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase SHIP and the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 form a complex in hematopoietic cells which can be regulated by BCR/ABL and growth factors Oncogene 1997 15: 2379–2384
Jain SK, Langdon WY, Varticovski L . Tyrosine phosphorylation of p120cbl in BCR/abl transformed hematopoietic cells mediates enhanced Association with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase Oncogene 1997 14: 2217–2228
Skorski T, Kanakaraj P, Nieborowska-Skorska M, Ratajczak MZ, Wen SC, Zon G, Gewirtz AM, Perussia B, Calabretta B . Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase activity is regulated by BCR/ABL and is required for the growth of Philadelphia chromosome-positive cells Blood 1995 86: 726–736
Klucher KM, Lopez DV, Daley GQ . Secondary mutation maintains the transformed state in BaF3 cells with inducible BCR/ABL expression Blood 1998 91: 3927–3934
Fincham VJ, Wyke JA . Localization of temperature-sensitive transformation mutations and back mutations in the Rous sarcoma virus src gene J Virol 1986 58: 694–699
Lugo TG, Witte ON . The bcr/abl oncogene transforms Rat-1 cells and cooperates with c-myc Mol Cell Biol 1989 9: 1263–1270
Jackson P, Baltimore D . N-terminal mutations activate the leukemogenic potential of the myristoylated form of c-abl EMBO J 1989 8: 449–456
Daley GQ, Van Etten RA, Jackson PK, Bernards A, Baltimore D . Nonmyristoylated Abl proteins transform a factor-dependent hematopoietic cell line Mol Cell Biol 1992 12: 1864–1871
Skorski T, Kanakaraj P, Skoska MN, Ratajczak MZ, Wen S-C, Zon G, Gewirtz AM, Perussia B, Calabretta B . Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity is regulated by BCR/ABL and is required for the growth of Philadelphia chromosome-positive cells Blood 1995 86: 726–736
Pendergast A-M, Quilliam LA, Cripe LD, Bassing CH, Dai Z, Li N, Batzer A, Rabun KM, Der CJ, Schlessinger J, Gishizky ML . BCR-ABL-induced oncogenesis is mediated by direct interaction with the SH2 domain of the GRB-2 adaptor protein Cell 1993 75: 175–185
Pendergast A, Muller AJ, Havlik MH, Maru Y, Witte ON . BCR sequences essential for transformation by the BCR-ABL oncogene bind to the Abl SH2 regulatory domain in a non-phosphotyrosine-dependent manner Cell 1991 66: 161–171
Voncken JW, Kaartinen V, Pattengale PK, Germeraad WTV, Groffen J, Heisterkamp N . BCR/ABL p210 and p190 cause distinct leukemia in transgenic mice Blood 1995 86: 4603–4611
Varticovski L, Harrison-Findik D, Keeler ML, Susa M . Role of PI 3-kinase in mitogenesis Biochim Biophys Acta 1994 1226: 1–11
Skorski T, Bellacosa A, Nieborowska-Skorska M, Majewski M, Martinez R, Choi JK, Trotta R, Wlodarski P, Perrotti D, Chan TO, Wasik MA, Tsichlis PN, Calabretta B . Transformation of hematopoietic cells by BCR/ABL requires activation of a PI-3k/Akt-dependent pathway EMBO J 1997 16: 6151–6161
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, S., de Aos, I., Inai, Y. et al. Inactivation of wild-type BCR/ABL tyrosine kinase in hematopoietic cells by mild hyperthermia. Leukemia 14, 845–852 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401759
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401759