Abstract
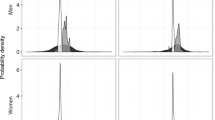
Demographic and socioeconomic differences between population sub-groups were analyzed, as a component of the EXPOLIS (Air Pollution Exposure Distributions Within Adult Urban Populations in Europe) Helsinki study, to explain variation in personal exposures to fine particles (PM2.5). Two-hundred one individuals were randomly selected among 25–55-year-old inhabitants of Helsinki Metropolitan area. Personal exposure samples and residential indoor, residential outdoor and workplace indoor microenvironment measurements of PM2.5 were collected between October 1996 and December 1997. Variation in PM2.5 personal exposures, between sociodemographic sub-groups, was best described by differences in occupational status, education and age. Lower occupational status, less educated and young participants had greater exposures than upper occupational status, more educated and older participants. Different workplace concentrations explained most of the socioeconomic differences, and personal day and night exposures and concentrations in home (but not workplace or outdoor concentrations) caused the PM2.5 exposure differences between age groups. Men had higher exposures and much larger exposure differences between the sociodemographic groups than women. No gender, socioeconomic or age differences were observed in home outdoor concentrations between groups. Exposure to tobacco smoke did not seem to create new differences between the sociodemographic groups; instead, it amplified the existing differences.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ROTKO, T., KOISTINEN, K., HÄNNINEN, O. et al. Sociodemographic descriptors of personal exposure to fine particles (PM2.5) in EXPOLIS Helsinki. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 10, 385–393 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jea.7500104
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jea.7500104
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Long-term ambient PM2.5 exposure associated with cardiovascular risk factors in Chinese less educated population
BMC Public Health (2021)
-
Personal PM2.5 exposures of husband and wife by residential characteristics in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia
Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health (2021)
-
Evaluation of intake fractions for different subpopulations due to primary fine particulate matter (PM2.5) emitted from domestic wood combustion and traffic in Finland
Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health (2011)
-
Opening the research agenda for selection of hot spots for human biomonitoring research in Belgium: a participatory research project
Environmental Health (2010)
-
Modeling residential fine particulate matter infiltration for exposure assessment
Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology (2009)