Abstract
OBJECTIVES: To determine whether patterns of sleeping metabolic rate (SMR) are altered in obesity. Specifically to determine the relationship between changes in SMR and body weight, body mass index (BMI, kg/m2), and fat-free mass (FFM); and to compare resting metabolic rate (RMR) with SMR during different periods of sleep.
SUBJECTS: Eighteen healthy, pre-menopausal, obese (BMI >30, n=9) and non-obese (BMI <30, n=9), female subjects (six Caucasians and 12 African-Americans), with an average age of 36 y (range 22–45).
MEASUREMENTS: Total energy expenditure (TEE or 24 h EE), metabolic rate (MR), SMR (minimum, average and maximum) and resting metabolic rate (RMR) or resting energy expenditure (REE) measured by human respiratory chamber, and external mechanical work measured by a force platform within the respiratory chamber. Physical activity index (PAL) was derived as TEE/REE. Body composition was determined by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA).
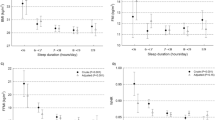
RESULTS: SMR decreased continuously during sleep and reached its lowest point just before the subject was awakened in the morning by the research staff. Although averages for RMR and SMR were similar, RMR was lower than SMR at the beginning of the sleeping period and higher than SMR in the morning hours. The rate of decrease in SMR was faster with increasing body weight (−0.829, P<0.0001), BMI (correlation factor −0.896, P<0.0001) and FFM (−0.798, P=0.001). The relationship between the slope of SMR decrease and BMI (y=−5×10−6x2+0.0002x−0.0028) is highly significant, with a P-value of <0.0001 and r2 value of 0.9622.
CONCLUSIONS: The rate of decline in metabolic rate during sleep is directly related to body weight, BMI and FFM. Average SMR tends to be lower than RMR in obese subjects and higher than RMR in non-obese subjects.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
FAO/WHO/UNU . 1985 Report of a joint expert consultation Energy and protein requirement WHO technical report series no. 724. WHO: Geneva
Fraser G, Trinder J, Colrain IM, Montgomery I . Effect of sleep and circadian cycle on sleep period energy expenditure J Appl Physiol 1989 66: 830–836.
Kreider MB, Buskirk ER, Bass DE . Oxygen consumption and body temperatures during the night J Appl Physiol 1958 12: 361–366.
Kreider MB, Iampietro PF . Oxygen consumption and body temperature during sleep in cold environments J Appl Physiol 1959 14: 765–767.
Palca JW, Walker JM, Berger RJ . Thermoregulation, metabolism and stages of sleep in cold-exposed men J Appl Physiol 1986 61: 940–947.
Robin ED, Whaley RD, Crump CH, Travis DM . Alveolar gas tensions, pulmonary ventilation and blood pH during physiologic sleep in normal subjects J Clin Invest 1958 37: 981–989.
Fontvieille AM, Rising R, Spraul M, Larson DE, Ravussin E . Relationship between sleep stages and metabolic rate in humans Am J Physiol 1994 267: E732–E737.
Brebbia DR, Altshuler KZ . Oxygen consumption rate and electroencephalographic stage of sleep Science Wash DC 1965 150: 1621–1623.
Ryan T, Mlynczak S, Erickson T, Man SFP, Man GCW . Oxygen consumption during sleep: influence of sleep stage and time of night Sleep 1989 12: 201–210.
Poehlman ET, Hortan ES . The impact of food intake and exercise on energy expenditure Nutr Rev 1989 47: 129–137.
Montgomery I, Trinder J, Paxton J . Energy expenditure and total sleep time: effect of physical exercise Sleep 1982 5: 159–168.
Seale JL, Conway JM . Relationship between overnight energy expenditure and BMR measured in a room-sized calorimeter Eur J Clin Nutr 1999 53: 107–111.
Westerterp K, Meijer G, Saris W, Soeters P, Winants Y, Hoor F . Physical activity and sleeping metabolic rate Med Sci Sports Exerc 1991 23: 166–170.
Hortan ES . Metabolic aspects of exercise and weight reduction Med Sci Sports Exerc 1986 18: 10–18.
Osterberg KL, Melby CL . Effect of acute resistance exercise on postexercise oxygen consumption and resting metabolic rate in young women Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 2000 10: 360.
Peterson HR, Rothschild M, Winberg CR, Feli RD McLeish KR, Pfeifer MA . Body fat and the activity of the autonomic nervous system New Engl J Med 1988 318: 1077–1083.
Poehlman ET . A review: exercise and its influence on resting metabolism in man Med Sci Sports Exerc 1989 21: 515–525.
Segal KR, Blando L, Ginsberg-Fellner F, Edano A . Postprandial thermogeneis at rest and postexercise before and after physical training in lean, obese, and mildly diabetic men Metab Clin Exp 1992 41: 868–878.
Weigle DS . Contribution of decreased body mass to diminished thermic effect of exercise reduced-obese men Int J Obes 1988 12: 567–578.
Fontvieille AM, Ferraro RT, Rising R, Spraul M, Larson DE, Ravussin E . Energy cost of arousal of sex, race and obesity Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1993 17: 705–709.
James WPT, Trayhurn P . An integrated view of the metabolic and genetic basis for obesity Lancet 1976 ii: 770–773.
Miller DS, Parsonage S . Resistance to slimming adaption or illusion? Lancet 1975 i: 773–775.
Rising R, Keys A, Ravussin E, Bogardus C . Concomitant interindividual variation in body temperature and metabolic rate Am J Physiol 1992 263 4 Pt 1: E730–734.
Rising R, Fontvieille AM, Larson DE, Spraul M, Bogardus C, Ravussin E . Racial difference in body core temperature between Pima Indian and Caucasian men Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1995 19: 1–5.
Albu J, Shur M, Curi M, Murphy L, Heymsfield SB, Pi-Sunyer FX . Resting metabolic rate in obese, premenopausal black women Am J Clin Nutr 1997 66: 531–538.
Gemert WG, Westerterp KR, Greve JWM, Soeters PB . Reduction of sleeping metabolic rate after vertical banded gastroplasty Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1998 22: 343–348.
Ravussin E, Lillioja S, Knowler WC, Christin L, Freymond D, Abbott WCH, Boyce Howard BV, Bogardus C . Reduced rate of energy expenditure as a risk factor for body-weight gain New Engl J Med 1988 318: 467–472.
Ravussin E, Gautier JF . Metabolic predictors of weight gain Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1999 23(Suppl): 37–41.
Weinsier RL, Hunter GR, Zuckerman PA, Redden DT, Darnell BE, Larson DE, Newcomer BR, Goran MI . Energy expenditure and free-living physical activity in black and white women: comparison before and after weight loss Am J Clin Nutr 2000 71: 1138–1146.
Afifi AK, Bergman RA . Basic nerosciences: a structural and functional approach Uban & Schwarzenberg: Munich 1986.
Weyer C, Snitker S, Rising R, Bogardus C, Ravussin E . Determinants of energy expenditure and fuel utilization in man: effects of body composition, age, sex, ethnicity and glucose tolerance in 916 subjects Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 23: 715–722.
Blaxter K . Energy metabolism in animal and man Cambridge University Press: New York 1989.
Fredrix EWHM, Soeters PB, Deerenberg IM, Kester ADM, Meyenfeldt MF, Saris WHM . Resting and sleeping energy expenditure in the elderly Eur J Clin Nutr 1990 44: 741–747.
Jéquier E, Acheson K, Schutz Y . Assessment of energy expenditure and fuel utilization in man A Rev Nutr 1987 7: 187–208.
Karklin A, Driver H, Buffenstein R . Restricted energy intake affects nocturnal body temperature and sleep patterns Am J Clin Nutr 1994 59: 346–349.
Garby L, Kurzer MS, Lammert O, Nielsen E . Energy expenditure during sleep in men and women: evaporative and sensible heat losses Hum Nutr Clin Nutr 1987 41: 225–233.
Goldberg GR, Prentice AM, Davies HL, Murgatroyd PR . Overnight and basal metabolic rates in men and women Eur J Clin Nutr 1988 42: 137–144.
Meijer G, Westerterp K, Saris W, Hoor F . Sleeping metabolic rate in relation to body composition and the menstrual cycle Am J Clin Nutr 1992 55: 637–640.
Meijer G, Westerterp K, Seyts GHP, Janssen GME, Saris WHIM, Hoor F . Body composition and sleeping metabolic rate in response to a 5-month endurance-training program in adults Eur J Appl Physiol 1991 62: 18–21.
Wang Z, Heshka S, Zhang K, Boozer CN, Heymsfield SB . Resting energy expenditure: systematic organization and critique of prediction methods Obes Res 2001 9: 331–336.
Wells JCK, Joughin C, Crisp JA, Cole TJ, Davies PSW . Comparison of measured sleeping metabolic rate and predicted basal metabolic rate in the first year of life Acta Paediatr 1996 85: 1013–1018.
Westerterp K, Meijer G, Schoffelen P, Janssen E . Body mass, body composition and sleeping metabolic rate before, during and after endurance training Eur J Appl Physiol 1994 69: 203–208.
Wong WW, Butte NF, Ellis KJ, Hergenroeder AC, Hill RB, Stuff JE, Smith EO . Pubertal African girls expend less energy at rest and during physical activity than Caucasian girls J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999 84: 906–911.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Grant P30 DK-26687 and by a Swiss National Science Foundation Post-Doctoral Fellowship to P Werner.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, K., Sun, M., Werner, P. et al. Sleeping metabolic rate in relation to body mass index and body composition. Int J Obes 26, 376–383 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801922
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801922
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Changes in Resting Energy Expenditure in Relation to Body Weight and Composition Following Gastric Restriction: A Systematic Review
Obesity Surgery (2016)
-
Associations of urinary phthalates with body mass index, waist circumference and serum lipids among females: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2004
International Journal of Obesity (2015)
-
Does practicing hatha yoga satisfy recommendations for intensity of physical activity which improves and maintains health and cardiovascular fitness?
BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine (2007)
-
Interindividual variability in sleeping metabolic rate in Japanese subjects
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2007)
-
Adiponectin Levels during Low‐ and High‐Fat Eucaloric Diets in Lean and Obese Women
Obesity Research (2005)