Abstract
OBJECTIVE: We recently demonstrated that chronic treatment with brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) regulates energy expenditure in obese diabetic C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice. In this study, we investigated the acute effects of BDNF on energy expenditure.
DESIGN: After BDNF was singly administered to male db/db mice (aged 10–12 weeks), their body temperature and whole body glucose oxidation were measured. Their norepinephrine (NE) turnover and uncoupling protein (UCP) 1 expression in interscapular brown adipose tissue (BAT) were also analyzed.
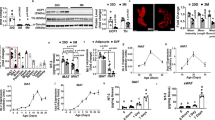
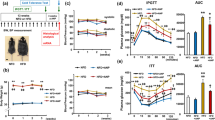
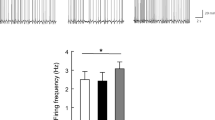
RESULTS: Even though the body temperatures of hyperphagic db/db mice dropped remarkably in a 24 h period after food deprivation, only a single subcutaneous administration of BDNF significantly prevented the reduction of body temperature. BDNF was also observed to have similar efficacy in cold exposure experiments at 15°C. Respiratory excretion of 14CO2 after intravenous injection of D-[14C(U)]-glucose was significantly increased by BDNF administration, indicating that BDNF increases whole-body glucose oxidation. BDNF administered intracerebroventricularly was also able to prevent the reduction of body temperature of db/db mice. To clarify the BDNF action mechanism we examined NE turnover in BAT. Four hours after a single administration, BDNF reduced NE content in the presence of the tyrosine hydroxylase inhibitor, α-methyl-P-tyrosine methyl ester, indicating enhanced NE turnover in BAT. BDNF also increased the expression of the UCP1 mRNA and protein in BAT.
CONCLUSION: These data indicate that BDNF rapidly regulates energy metabolism in obese diabetic animals, partly through activating the sympathetic nervous system and inducing UCP1 gene expression in BAT.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lindsay RM, Wiegand SJ, Altar CA, DiStefano PS . Neurotrophic factors: from molecule to man Trends Neurosci 1994 17: 182–190.
Skup MH . BDNF and NT-3 widen the scope of neurotrophin activity: pharmacological implications Acta Neurobiol Exp 1994 54: 81–94.
Barbacid M . Neurotrophic factors and their receptors Curr Opin Cell Biol 1995 7: 148–155.
Lewin GR, Barde YA . Physiology of the neurotrophins A Rev Neurosci 1996 19: 289–317.
Thoenen H, Castrén E, Berzaghi M, Blöchl A, Lindholm D . Recent advances in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders and cognitive dysfunction. In: Racagni G, Brunello N, Langer SZ (eds). International Academy for Biomedical Drug Research. Vol. 7: Karger: Basel 1994 197–203.
Sendtner M, Holtman B, Hughes RA . The response of motoneurons to neurotrophins Neurochem Res 1996 21: 831–841.
Yuen EC, Mobley WC . Therapeutic potential of neurotrophic factors for neurological disorders Ann Neurol 1996 40: 346–354.
Ono M, Ichihara J, Nonomura T, Itakura Y, Taiji M, Nakayama C, Noguchi H . Brain-derived neurotrophic factor reduces blood glucose level in obese diabetic mice but not in normal mice Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1997 238: 633–637.
Tonra JR, Ono M, Liu X, Garcia K, Jackson C, Yancopoulos GD, Wiegand SJ, Wong V . Brain derived neurotrophic factor improves blood glucose control and alleviates fasting hyperglycemia in C57BLKS-leprdb/leprdb mice Diabetes 1999 48: 588–594.
Ono M, Itakura Y, Nonomura T, Nakagawa T, Nakayama C, Taiji M, Noguchi H . Intermittent administration of brain-derived neurotrophic factor ameliorates glucose metabolism in obese diabetic mice Metabolism 2000 49: 129–133.
Nakagawa T, Tsuchida A, Itakura Y, Nonomura T, Ono M, Hirota F, Inoue T, Nakayama C, Taiji M, Noguchi H . Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) regulates glucose metabolism by modulating energy balance in diabetic mice Diabetes 2000 49: 436–444.
Collins S, Kuhn CM, Petro AE, Swick AG, Chrunyk BA, Surwit RS . Role of leptin in fat regulation Nature 1996 380: 667.
Gong D-W, He Y, Karas M, Reitman M . Uncoupling protein-3 is a mediator of thermogenesis regulated by thyroid hormone, β3-adrenergic agonists, and leptin J Biol Chem 1997 272: 24129–24132.
Kamohara S, Burcelin R, Halaas JL, Friedman JM, Charron MJ . Acute stimulation of glucose metabolism in mice by leptin treatment Nature 1997 389: 374–377.
Coleman DL, Hummel KP . Studies with the mutation, diabetes, in the mouse Diabetologia 1967 3: 238–248.
Coleman DL . Obese and diabetes: two mutant genes causing diabetes-obesity syndromes in mice Diabetologia 1978 14: 141–148.
Mayer J, Russell RE, Bates MW, Dickie MN . Basal oxygen consumption of hereditarily obese and diabetic mice Endocrinology 1952 50: 318–323.
Chen H, Charlat O, Tartaglia LA, Woolf EA, Weng X, Ellis SJ, Lakey ND, Culpepper J, Moore KJ, Breitbart RE, Duyk GM, Tepper RI, Morgenstern JP . Evidence that the diabetes gene encodes the leptin receptor: identification of a mutation in the leptin receptor gene in db/db mice Cell 1996 84: 491–495.
Lee GH, Proenca R, Montez JM, Carroll KM, Darvishzadeh JG, Lee JI, Friedman JM . Abnormal splicing of the leptin receptor in diabetic mice Nature 1996 379: 632–635.
Campfield LA, Smith FJ, Guisez Y, Devos R, Burn P . Recombinant mouse OB protein: evidence for a peripheral signal linking adiposity and central neural networks Science 1995 269: 546–549.
Halaas JF, Gajiwala KS, Maffei M, Cohen SL, Chait BT, Rabinowitz D, Lallone RL, Burley SK, Friedman JM . Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene Science 1995 269: 543–546.
Simonson DC, Rossetti L, Giaccari A, DeFronzo RA . Glucose toxicity. In: Alberti KGMM, Zimmet P, DeFronzo RA (eds). International textbook on diabetes mellitus, 2nd edn. Wiley: West Sussex 1997 713–744.
Valenzuela DM, Maisonpierre PC, Glass DJ, Rojas E, Nunez L, Kong Y, Gies DR, Stitt TN, Ip NY, Yancopoulos GD . Alternative forms of rat TrkC with different functional capabilities Neuron 1993 10: 963–974.
Poduslo JF, Curran GL . Permiability at the blood-brain and blood-nerve barriers of the neurotrophic factors: NGF, CNTF, NT-3, BDNF Mol Brain Res 1996 36: 280–286.
Pan W, Banks WA, Fasold MB, Bluth J, Kastin AJ . Transport of brain-derived neurotrophic factor across the blood-brain barrier Neuropharmacology 1998 37: 1553–1561.
Lyons WE, Mamounas LA, Ricaurate GA, Coppala V, Reid SW, Bora SH, Wihler C, Koliatsos VE, Tessarollo L . Brain-derived neurotrophic factor-deficient mice develop aggressiveness and hyperphagia in conjunction with brain serotonergic abnormalities Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999 96: 15239–15244.
Kernie SG, Liebl DJ, Parada LF . BDNF regulates eating behavior and locomotor activity in mice EMBO J 2000 19: 1290–1300.
Pelleymounter MA, Cullen MJ, Baker MB, Hecht R, Winters D, Boone T, Collins F . Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in ob/ob mice Science 1995 269: 540–543.
Schwartz MW, Seeley RJ, Campfield LA, Burn P, Baskin DG . Identification of targets of leptin action in rat hypothalamus J Clin Invest 1996 98: 1101–1106.
Elmquist JK, Ahima RS, Maratos-Flier E, Flier JS, Saper CB . Leptin activates neurons in ventrobasal hypothalamus and brainstem Endocrinology 1997 138: 839–842.
Fei H, Okano HJ, Li C, Lee G-H, Zhao C, Darnell R, Friedman JM . Anatomic localization of alternatively spliced leptin receptors (Ob-R) in mouse brain and other tissues Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997 94: 7001–7005.
Hetherington AW, Ranson SW . The spontaneous activity and food intake of rats with hypothalamic lesions Am J Physiol 1942 136: 609–617.
Nonogaki K . New insight into sympathetic regulation of glucose and fat metabolism Diabetologia 2000 43: 533–549.
Saito M, Minokoshi Y, Shimazu T . Accelerated norepinephrine turnover in peripheral tissues after ventromedial hypothalamic stimulation in rats Brain Res 1989 481: 298–303.
Satoh N, Ogawa Y, Katsuura G, Numata Y, Masuzaki H, Yoshimasa Y, Nakao K . Satiety effect and sympathetic activation of leptin are mediated by hypothalamic melanocortin system Neurosci Lett 1998 249: 107–110.
Commins SP, Marsh DJ, Thomas SA, Watson PM, Padgett MA, Palmiter R, Gettys TW . Norepinephrine is required for leptin effects on gene expression in brown and white adipose tissue Endocrinology 1999 140: 4772–4778.
Jacobsson A, Stadler U, Glotzer MA, Kozak LP . Mitochondrial uncoupling protein from mouse brown fat. Molecular cloning, genetic mapping, and mRNA expression J Biol Chem 1985 260: 16250–16254.
Chinookoswong N, Wang JL, Shi ZQ . Leptin restores euglycemia and normalizes glucose turnover in insulin-deficient diabetes in the rat Diabetes 1999 48: 1487–1492.
Shimomura I, Hammer RE, Ikemoto S, Brown MS, Goldstein JL . Leptin reverses insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus in mice with congenital lipodystrophy Nature 1999 401: 73–76.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mr Masayuki Satoh (Sumitomo Chemical, Osaka, Japan) for conducting the glucose oxidation analysis. This study was supported by Sumitomo Pharmaceuticals Co. Ltd, Osaka, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsuchida, A., Nonomura, T., Ono-Kishino, M. et al. Acute effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on energy expenditure in obese diabetic mice. Int J Obes 25, 1286–1293 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801678
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801678
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Serum and plasma levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in individuals with eating disorders (EDs): a systematic review and meta-analysis
Journal of Eating Disorders (2022)
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF): a multifaceted marker in chronic kidney disease
Clinical and Experimental Nephrology (2022)
-
Roles of myokines in exercise-induced improvement of neuropsychiatric function
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2019)
-
Serum Levels of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Are Associated with Diabetes Risk, Complications, and Obesity: a Cohort Study from Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Molecular Neurobiology (2016)
-
Agonistic effect of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) and its metabolites on brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) through molecular docking simulation
Lipids in Health and Disease (2012)