Abstract
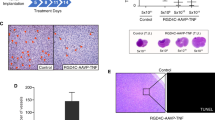
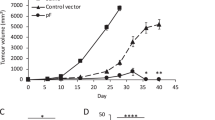
Gene therapy using adenoviral (Ad) vector containing herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase (AxCAHSV-tk) followed by the administration of ganciclovir (GCV) has been a promising therapy for cancer including malignant gliomas. However, there remain numerous problems to overcome, such as the high immunogenicity and toxicity of Ad vector. To optimize the therapy, we investigated whether a conjugation of our original cationic liposomes and Ad vectors reduces viral antigenicity and maintains the antitumor activity in mouse experimental (subcutaneous and intracranial) glioma models. Our original liposomes consist of N-(α-trimethylammonioacetyl)-didodecyl-D-glutamate chloride, dilauroyl phosphatidylcholine, and dioleoyl phosphatidyl-ethanolamine in a molar ratio of 1:2:2. AxCAHSV-tk and GCV showed a remarkable inhibition of experimental glioma growth. The growth-inhibitory effect decreased in mice previously immunized with another Ad vector (AxCALacZ). In contrast, the conjugation of AxCAHSV-tk and liposomes did not diminish the growth-inhibitory effect. Furthermore, the conjugation reduced antigenicity for Ad vector in vivo. These findings suggest that suicide gene therapy, using a conjugation of AxCAHSV-tk and our liposomes, is a feasible approach for human cancer gene therapy, especially malignant gliomas.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ryuke Y, Mizuno M, Natsume A et al. The transduction efficiency of adenoviral vectors increases by associating with cationic liposomes on human glioma cells Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2000 40: 256–260
Natsume A, Mizuno M, Ryuke Y et al. Cationic liposomes conjugation to recombinant adenoviral vector reduces viral antigenicity Jpn J Cancer Res 2000 91: 363–367
Wilkins RH, Ketcham AS . Studies of glioma in mice: 1. Experiments concerning glioma growth and hepatic mitotic activity J Natl Cancer Inst 1964 32: 871–880
Oldfield EH, Ram Z, Culver KW et al. Gene therapy for the treatment of brain tumors using intra-tumoral transduction with the thymidine kinase gene and intravenous ganciclovir Hum Gene Ther 1993 4: 39–69
Ram Z, Culver KW, Oshiro EM et al. Therapy of malignant brain tumors by intratumoral implantation of retroviral vector-producing cells Nat Med 1997 3: 1354–1361
Beer SJ, Matthews CB, Stein CS et al. Poly (lactic–glycolic) acid copolymer encapsulation of recombinant adenovirus reduced immunogenicity in vivo Gene Ther 1998 5: 740–746
Kreuzer J, Denger S, Reifers F et al. Adenovirus-assisted lipofection: efficient in vitro gene transfer of luciferase and cytosine deaminase to human smooth muscle cells Atherosclerosis 1996 124: 49–60
Raja-Walia R, Webber J, Naftilan J, Chapman GD, Naftilan AJ . Enhancement of liposome-mediated gene transfer into vascular tissue by replication deficient adenovirus Gene Ther 1995 2: 521–530
Rainov NG, Ikeda K, Qureshi NH et al. Intraarterial delivery of adenovirus vectors and liposome–DNA complexes to experimental brain neoplasms Hum Gene Ther 1999 20: 311–318
Lambright ES, Force SD, Lanuti ME et al. Efficacy of repeated adenoviral suicide gene therapy in a localized murine tumor model Ann Thorac Surg 2000 70: 1865–1870
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mizuno, M., Ryuke, Y. & Yoshida, J. Cationic liposomes conjugation to recombinant adenoviral vectors containing herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene followed by ganciclovir treatment reduces viral antigenicity and maintains antitumor activity in mouse experimental glioma models. Cancer Gene Ther 9, 825–829 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700503
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700503
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Liposome size and charge optimization for intraarterial delivery to gliomas
Drug Delivery and Translational Research (2016)
-
Current advances in developing cationic lipid-based nanoparticles as a vehicle for improving adenoviral gene delivery
Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation (2016)
-
Co-delivery of Adenovirus and Carmustine by Anionic Liposomes with Synergistic Anti-tumor Effects
Pharmaceutical Research (2012)
-
Microencapsulation of PEGylated Adenovirus within PLGA Microspheres for Enhanced Stability and Gene Transfection Efficiency
Pharmaceutical Research (2007)