Abstract
Evolution of pest resistance threatens the benefits of genetically engineered crops that produce Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) insecticidal proteins. Strategies intended to delay pest resistance are most effective when implemented proactively. Accordingly, researchers have selected for and analyzed resistance to Bt toxins in many laboratory strains of pests before resistance evolves in the field, but the utility of this approach depends on the largely untested assumption that laboratory- and field-selected resistance to Bt toxins are similar. Here we compared the genetic basis of resistance to Bt toxin Cry2Ab, which is widely deployed in transgenic crops, between laboratory- and field-selected populations of the pink bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella), a global pest of cotton. We discovered that resistance to Cry2Ab is associated with mutations disrupting the same ATP-binding cassette transporter gene (PgABCA2) in a laboratory-selected strain from Arizona, USA, and in field-selected populations from India. The most common mutation, loss of exon 6 caused by alternative splicing, occurred in resistant larvae from both locations. Together with previous data, the results imply that mutations in the same gene confer Bt resistance in laboratory- and field-selected strains and suggest that focusing on ABCA2 genes may help to accelerate progress in monitoring and managing resistance to Cry2Ab.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The insecticidal proteins produced by Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) kill some devastating insect pests, but cause little or no harm to humans and most other non-target organisms1,2. Farmers have used Bt toxins in insecticidal sprays for more than 70 years and in transgenic crops since 19963,4,5. In 2017, genetically engineered corn, cotton and soy producing Bt toxins were planted by millions of farmers on more than 100 million hectares worldwide5. The benefits of these Bt crops include pest suppression, reduced insecticide use, enhanced biological control, and increased farmer profits2,6,7,8,9,10,11. However, increasingly rapid evolution of pest resistance to Bt toxins has reduced these benefits12.
Strategies designed to delay pest resistance to Bt crops are most likely to succeed if they are implemented proactively, before resistance is widespread13,14. To provide the information needed to bolster the proactive development of such strategies, researchers have selected for and analyzed resistance to Bt toxins in many laboratory strains of pests4,15. The utility of this approach depends on the largely untested assumption that laboratory- and field-selected resistance are similar16.
Here we tested the hypothesis that the molecular genetic basis of resistance to Bt toxin Cry2Ab is similar in laboratory- and field-selected populations of one of the world’s most destructive pests of cotton, the pink bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella)17,18. Understanding the genetic basis of insect resistance to Cry2Ab is increasingly important for several reasons. While each of the first Bt crops produced a single toxin from the Cry1 family (e.g., Cry1Ac), most Bt crops grown now produce Cry2Ab in combination with one or more Cry1 toxins19. Whereas at least eight major lepidopteran pests have evolved resistance to Cry1 toxins in the field, field-evolved resistance to Cry2Ab has been reported only for pink bollworm in India and Helicoverpa zea in the United States12,20,21,22,23. In India, over 7 million farmers cultivated the largest area of Bt cotton (10.8 million ha) of any nation in 20165 and pink bollworm resistance to Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab produced by dual-toxin Bt cotton has caused severe economic losses20,21,24,25,26. Moreover, data reported previously on the genetic basis of resistance are extensive for Cry1 toxins12,15, but are relatively scarce and limited to laboratory-selected strains for Cry2Ab27,28,29. Resistance to Cry2Ab has been linked with mutations in an ATP-binding cassette transporter gene (ABCA2) in lab-selected strains of Helicoverpa armigera and Helicoverpa punctigera from Australia28, but we are not aware of any previous reports of the molecular genetic basis of field-evolved resistance to Cry2Ab.
Here we discovered that pink bollworm resistance to Cry2Ab is associated with mutations disrupting ABCA2 in a laboratory-selected strain from Arizona, USA, and in field-selected populations from India. Aberrant splicing of pre-mRNA was prevalent in the mutations affecting this gene in resistant pink bollworm from Arizona and India. Although one mutation was shared by some resistant larvae from both locations, the others differed between locations and were strikingly diverse in India. The results suggest that focusing on ABCA2 may help to accelerate progress in monitoring and managing field-evolved resistance to Cry2Ab.
Results
ABCA2 in Susceptible and Lab-Selected Resistant Pink Bollworm from Arizona
The full-length consensus PgABCA2 cDNA (GenBank accession no. MG637361) from two Arizona Cry2Ab-susceptible strains, APHIS-S and AZP-R, was identical and had 5,187 bp encoding a predicted protein of 1,729 aa (Supplementary Fig. S1). Similar to other ABC transporters in subfamily A, the proposed structure of PgABCA2 includes two transmembrane domains (TMD1 and TMD2) and two nucleotide-binding domains (NBD1 and NBD2) (Fig. 1a and Supplementary Fig. S1). Each transmembrane domain has six transmembrane helices and both nucleotide-binding domains have a catalytic core domain consisting of Walker A and B motifs and a structurally diverse α-helical domain containing the ABC transporter signature motif (also called Walker C motif) in the cytoplasm.
Mutations affecting PgABCA2 protein in Cry2Ab-resistant pink bollworm from Arizona and India. (a) The predicted PgABCA2 protein includes amino (N) and carboxyl (C) termini (pink), two transmembrane domains (TMD1 and TMD2), each consisting of 6 transmembrane regions (TM; orange), three extracellular loops (ECL; green), two intracellular loops (ICL; blue), and two nucleotide-binding domains (NBD; purple). Mutations affecting transcripts of resistant pink bollworm: Circles show premature stop codons from India (red), Arizona (yellow), or both (red and yellow). Triangles show in-frame indels from India (red) or Arizona (yellow). Numbers indicate the affected amino acids. (b) Full-length and partial PgABCA2 cDNAs were obtained by direct PCR sequencing, DNA sequencing of cDNA clones, and/or PacBio® DNA sequencing from susceptible (APHIS-S) and resistant, laboratory-selected (Bt4-R2) pink bollworm from Arizona, USA and India field-selected resistant populations (AM, CK, GAP, KT, and RK). The linear schematic (top) shows the predicted translated domain structure of the 5,187-bp full-length PgABCA2 coding sequence. The predicted protein includes amino- and carboxyl-termini (pink), transmembrane regions TM1-TM12 (orange), intracellular loops ICL1-ICL5 (blue), and extracellular loops ECL1-ECL6 (green). The domain structure connected to the exons that encode the respective domains is shown by dotted gray lines. Each predicted domain is numbered, with ECLs on top and ICLs numbered on bottom of protein schematic. Putative exons 1–31 are numbered, with grey exons indicating regions determined by direct PCR sequencing. Exons colored in light blue were further verified by sequencing cDNA clones (either by Sanger or PacBio® sequencing). Red bars indicate disruption sites within the full-length coding sequence and the red triangles indicate the location of premature stop codons shown to scale based on the linear schematic of the translated domain structure. Unique cDNA variants are indicated as a, b, c, etc.
We initially identified four transcript variants (Bt4-R2a to d) with mutations in PgABCA2 from cDNA sequencing of a pool of 10 larvae from the laboratory-selected Cry2Ab-resistant strain Bt4-R2 (Fig. 1, Supplementary Fig. S2, and Table 1). Each of these mutations affects exon 20: either a frameshift mutation introducing a premature stop codon truncating the PgABCA2 protein (Bt4-R2a, b, and d), or an in-frame deletion of exon 20 disrupting intracellular loop 4, transmembrane helix 9, and extracellular loop 5 (Bt4-R2c) (Fig. 1).
To test for differences between the susceptible APHIS-S strain and the resistant Bt4-R2 strain in genomic DNA (gDNA) near exon 20 of PgABCA2, we PCR amplified, cloned, and sequenced fragments from exon 18 to exon 21. Compared with APHIS-S, the gDNA from Bt4-R2 contained an indel mutation expected to disrupt the 3′ splice junction of exon 20 (Fig. 2a and Supplementary Fig. S2). This splice-site mutation includes a 7-bp insertion (GCGCGCC), followed by a 44-bp deletion that spans the exon-intron junction. We name this mutation “rA1” and refer to the allele containing this mutation as the rA1 allele. Because the rA1 mutation spans the exon-intron splice junction, the Bt4-R2a-d cDNA variants probably result from mis-splicing of intron 20. Further examination of nearby gDNA revealed that, relative to APHIS-S, Bt4-R2 also has a 1,129-bp insertion in intron 18 (Supplementary Fig. S2).
The rA1 mutation at the junction of exon and intron 20 in PgABCA2. (a) gDNA sequence for exon and intron 20 of the wild-type PgABCA2 allele (sA1) in the susceptible APHIS-S strain and the mutant rA1 allele from the Cry2Ab-resistant Bt4-R2 strain. The rA1 indel mutation has a 7-bp insertion (red letters) and 44-bp deletion (red dashes) in exon 20 (blue) and spanning the 5′ splice junction with intron 20 (not highlighted). The allele-specific primers rA1-F and rA1-R match the sequences highlighted in orange. (b) Allele-specific PCR using the primers in (a) yielded a 343-bp fragment from APHIS-S (sA1sA1), a 305-bp fragment from Bt4-R2 (rA1rA1), and both fragments in the offspring from crosses between the two strains (rA1sA1). Unprocessed image of agarose gel is shown in Supplementary Fig. S13.
To distinguish readily between the rA1 resistance allele from Bt4-R2 and the susceptible “sA1” allele from APHIS-S, we developed allele-specific PCR using primers that flank the rA1 mutation (Fig. 2 and Supplementary Table S1). These primers yielded a 343-bp fragment from APHIS-S individuals (sA1sA1), a 305-bp fragment from Bt4-R2 (rA1rA1), and both fragments in the Bt4-R2 X APHIS-S (rA1sA1) F1 offspring from biphasic linkage crosses detailed below (Fig. 2b).
Genetic Linkage between PgABCA2 and Resistance to Cry2Ab
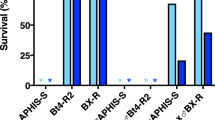
We tested for genetic linkage between PgABCA2 and resistance to Cry2Ab using backcross progeny obtained from single-pair crosses between Bt4-R2 (rA1rA1) and F1 (rA1sA1, from Bt4-R2 X APHIS-S) (Fig. 3 and Supplementary Table S2). From an initial set of 42 backcross families, we tested larval survival in bioassays with 1 microgram Cry2Ab per ml diet for 20 backcross families that each produced at least 10 progeny (mean = 28 neonates tested per family) (Supplementary Fig. S4). We used the allele-specific PCR described above to determine the PgABCA2 genotype of larvae.
Linkage analysis. Biphasic genetic linkage analysis was initiated with single-pair reciprocal crosses between F0 adults, with either a resistant Bt4-R2 female and a susceptible APHIS-S male (shown here) or a susceptible APHIS-S female and a resistant Bt4-R2 male. The resulting F1 progeny were backcrossed in single pairs with the resistant Bt4-R2 strain. Backcross (BC) progeny were tested either on diet containing 1 microgram Cry2Ab per mL diet or control diet. Survivors from 10 reciprocal backcross families (five F1 ♀ X Bt4-R2 ♂ and five Bt4-R2 ♀ X F1 ♂) were weighed and genotyped with allele-specific PCR.
In the 10 backcross families where the father was from Bt4-R2, the survivors on Cry2Ab-treated diet consisted of 125 rA1rA1 and 9 rA1sA1, which differs significantly from the ratio of 1:1 expected if resistance is not linked with PgABCA2 (Fisher’s exact test, P < 10−14) (Supplementary Table S2). Because crossing over in Lepidoptera occurs only in males, these results from backcross families with rA1rA1 fathers indicate linkage between resistance and the chromosome carrying PgABCA2. In the other 10 backcross families, where the father was an F1, the survivors on Cry2Ab-treated diet consisted of 113 rA1rA1 and 7 rA1sA1, which also differs significantly from the expected 1:1 ratio if resistance is not linked with PgABCA2 (Fisher’s exact test, P < 10−14) (Supplementary Table S2). Because crossing over occurs in males, the results from these 10 backcross families with rA1sA1 fathers indicate tight linkage between resistance and PgABCA2. Furthermore, in the backcross progeny that survived exposure to Cry2Ab, the proportion of individuals with genotype rA1rA1 was not higher for families with rA1rA1 fathers (0.93) where crossing over was not a factor, than for families with rA1sA1 fathers (0.94) where crossing over could occur, which implies tight linkage between resistance and PgABCA2. By contrast with the results described above, larvae from backcross families reared on untreated diet as controls consisted of 15 rA1rA1 and 12 rA1sA1, which does not differ significantly from the expected 1:1 ratio (Fisher’s exact test, P = 0.79).
For survivors on diet treated with Cry2Ab in the linkage analysis, mean larval weight (mg) was significantly lower for rA1sA1 (19, SE = 2.6) than rA1rA1 (27, SE = 0.5) (t-test, t = 3.8, df = 250, P = 0.0002) (Supplementary Fig. S4). However, larval weight on untreated diet was similar for rA1sA1 (26, SE = 1.9) and rA1rA1 (26, SE = 0.5, SE = 2.8) (t-test, t = 0.14, df = 41, P = 0.89). In addition, larval weight was lower on treated diet versus untreated diet for rA1sA1 (t-test, t = 2.2, df = 36, P = 0.03), but not for rA1rA1. Thus, in terms of larval weight, resistance to Cry2Ab was incomplete in the relatively rare rA1sA1 survivors, compared with complete resistance in the more abundant rA1rA1 survivors. The low level of resistance in rA1sA1 could reflect inheritance of resistance linked with PgABCA2 that was not completely recessive, a contribution to resistance from one or more mutations other than rA1, or both.
Single-molecule Long-read Sequencing of PgABCA2 cDNA
To check the accuracy of the genotypes assigned by PCR and to determine if Bt4-R2 has mutations in PgABCA2 other than the rA1 splice-site mutation, we used single-molecule, real-time sequencing to analyze barcoded PgABCA2 cDNA from 22 larvae: seven from APHIS-S as controls, and 15 backcross survivors from the linkage analysis (Fig. 3) that had been genotyped with allele-specific PCR (eight rA1rA1 and seven rA1sA1). We obtained a total of 369,672 reads, which yielded consensus sequences for 18 of the 22 larvae (Supplementary Table S3). For the other four larvae (two APHIS-S and two rA1rA1), the coverage was not deep enough to give reliable consensus sequences. For 16 of the 18 larvae with consensus sequences, the cDNA sequences confirmed the results from PCR in terms of the presence or absence of the rA1 mutation. As expected, the five APHIS-S larvae had only intact cDNA (sA1sA1), all of the transcripts from the six larvae genotyped by PCR as rA1rA1 had mutations affecting exon 20, and four of the six larvae genotyped by PCR as rA1sA1 each had at least one transcript with the rA1 mutation and one without it (Table 1 and Supplementary Table S3). For the other two larvae genotyped by PCR as rA1sA1 (rA1sA1-6 and rA1sA1-7), targeted sequencing yielded consensus reads with the intact sequence (sA1) in the region of the rA1 mutation, but not the expected rA1 mutation (Supplementary Table S3). However, subsequent cDNA cloning and Sanger sequencing confirmed the presence of the rA1 mutation. Thus, both of these larvae had transcripts with and without the rA1 mutation, confirming the PCR genotyping.
The long-read sequencing also revealed five previously unidentified transcript variants (Bt4-R2e to i), bringing the total of different cDNA variants in Bt4-R2 that disrupt PgABCA2 to nine, each having either one or two of the eight different cDNA mutations affecting exon 6 or one or more exons from 19 to 24 (Fig. 1 and Supplementary Fig. S2; Table 1 and Supplementary Table S3). Four of the 12 larval survivors from the backcross analyzed by targeting sequence shared a cDNA mutation (c.1090_1234del) that completely skips exon 6 (1,090–1,234 bp), yielding a frameshift and a premature stop codon at amino acid 373 (Fig. 1 and Supplementary Fig. S2; Table 1 and Supplementary Table S3). For one of these four larvae (rA1sA1-7), the transcript without the rA1 mutation lacked exon 6 and thus was not an intact, wild-type transcript. Therefore, when considering the entire PgABCA2 cDNA sequence (rather than just the region harboring the rA1 mutation), this individual had only disrupted transcripts, which may explain its ability to survive when exposed to Cry2Ab.
Although we initially identified only 4 individuals (rA1sA1-1, rA1sA1-2, rA1sA1-6 and rA1sA1-7) with cDNA mutation that completely skip exon 6, we found 6 more individuals (two homozygous: rA1rA1-3, rA1rA1-5 and 4 heterozygous: rA1sA1-2, rA1sA1-3, rA1sA1-4 and rA1sA1-5) when we changed the conditions to include shorter subreads in the Long Amplicon Analysis (Supplementary Table S3). We cloned and Sanger sequenced the gDNA from three individuals (rA1sA1-3, rA1sA1-4 and rA1sA1-6) and found no changes in gDNA corresponding to the observed loss of exon 6 in cDNA (Supplementary Fig. S5).
Including the results from the initial sequencing of 10 pooled resistant larvae and next generation sequencing of 15 individual survivors from the linkage analysis (Table 1 and Supplementary Table S3), mis-splicing is implicated in each of the eight different cDNA mutations in Bt4-R2. Comparison of the Bt4-R2 genomic DNA sequence and the transcript variants at exon 20 revealed that the indel mutation at the splice junction disrupted the 5′ GT intron signature sequence and introduced several cryptic splice sites in the pre-mRNA (Table 1 and Supplementary Fig. S6). The indel mutation thus caused mis-splicing of the Bt4-R2 pre-mRNA and produced nine transcript variants with disruptions in exons 19–24 (Table 1 and Supplementary Fig. S6).
Mutations in PgABCA2 Associated with Field-Selected Resistance to Bt Cotton in India
To determine if mutations in PgABCA2 are associated with field-selected resistance to Cry2Ab, we compared cDNA from field-collected pink bollworm larvae from India that were either susceptible or resistant to Cry2Ab. We collected the three susceptible larvae from a non-Bt cotton field in Akola, Maharashtra (AMH-1, AMH-2, and AMH-3) in 201030, five years before resistance to Cry2Ab was detected in India (Fig. 4). During December 2015 and January 2016, after pink bollworm resistance to Cry2Ab was widespread in India20,25, we collected 11 larvae as fourth instars from fields of dual-toxin Bt cotton at seven sites in India (Fig. 4). We identified these larvae as resistant because immunoassays confirmed that the bolls from which they were collected produced both Cry2Ab and Cry1Ac (Supplementary Table S4). We obtained sufficient material for full-length cDNA sequencing for all three susceptible larvae and eight resistant larvae from five sites in India (AM-8, CK-1, GAP-3, KT-1, KT-8, KT-10, RK-1, and RK-11).
Pink bollworm sampling sites in India. After widespread resistance to Cry2Ab was reported in India, Cry2Ab-resistant larvae were collected in 2015 and 2016 as fourth instars from dual-toxin cotton producing Cry2Ab and Cry1Ac from seven districts of four states: Ahmednagar and Jalna, Maharashtra (AM and JM), Karimnagar, Telangana (KT), Guntur, Andhra Pradesh (GAP), and Chitradurga, Raichur and Yadgir, Karnataka (CK, RK and YK) (red). Several years before resistance to Cry2Ab was detected in India, Cry2Ab-susceptible larvae were collected in 2010 from non-Bt cotton in Akola, Maharashtra (AMH) (green).
The consensus cDNA sequences of PgABCA2 were identical for the three susceptible larvae from India and the susceptible APHIS-S strain from Arizona (Supplementary Fig. S7). Conversely, the eight resistant larvae from five sites in India yielded 19 distinct PgABCA2 transcript variants, each severely disrupted by one to three mutations (Fig. 1 and Table 2). Collectively, the eight resistant larvae from India harbored 17 different cDNA mutations, and a total of 40 mutations including several that occurred in more than one larva (Table 2). The disruptive effects of these 40 PgABCA2 cDNA mutations are expected throughout the encoded protein (Fig. 1).
The most common cDNA mutation in the resistant larvae from India was loss of exon 6, exactly the same mutation as in the four larvae from Bt4-R2 described above (Table 1 and Fig. 1). This mutation occurred in 75% (6 of 8) of the resistant larvae from India representing all four states studied here (Table 2). In 18 clones from four resistant larvae from India with this cDNA mutation, we found no changes in the corresponding gDNA at or near the exon/intron boundaries of exon 6 (Supplementary Figs S8–S11 and Table 3), which implicates alternative splicing. Thus, in a lab-selected strain from Arizona and field-selected populations from India, pink bollworm resistance to Cry2Ab is associated with mis-splicing that omits exon 6 of PgABCA2.
By contrast, we did not detect the rA1 splice-site mutation from Arizona in any of the 11 resistant larvae from India. We did not find any mutations in exon 20 in full-length PgABCA2 cDNA sequences from the eight resistant larvae from India noted above. In addition, the rA1 mutation was not detected with allele-specific PCR in four of the resistant larvae mentioned above (AM-8, CK-1, KT-1, and RK-1) or in three additional resistant larvae from India that were not fully sequenced (GAP-2, JM-9, and YK-1).
Including 4 of the 19 distinct PgABCA2 cDNA sequences that occurred in larvae from two to three sites each, we found a total of 24 mutant transcripts (Table 2). The four transcript variants detected at more than one site are: CK-1a, KT-1a, and RK-1b with stop codons at amino acids 282 and 373; CK-1d and KT-1c with stop codons at amino acids 303 and 373; GAP-3a and RK-11c with a stop codon at amino acid 524; and CK-1c and KT-1c with in-frame deletions causing the loss of amino acids 280–315 (Fig. 1 and Table 2).
Sequencing of gDNA fragments from five resistant larvae from India revealed that five out of the six different cDNA mutations examined involved mis-splicing of pre-mRNA (Table 3). Four entail introduction of 5′ and/or 3′ alternative splice sites and the fifth is skipping of exon 6 described above (Table 3, Supplementary Figs S8–11). In each of these cDNA mutations, except for skipping of exon 6, the corresponding gDNA had splice-site mutations that either disrupted the native splice site or introduced alternative splice sites (Table 3). For example, in one larva (GAP-3), the native 5′ GT dinucleotide splice site of intron 8 was changed to AT, causing the splicing machinery to use a cryptic GT splice site within exon 8 (Supplementary Fig. S9 and Table 3). In two larvae (CK-1 and RK-1), a large DNA insertion within exon 4 introduced several alternative splice sites (Table 3, Supplementary Figs S8 and S11). Only one of the six different cDNA mutations examined did not involve mis-splicing of pre-mRNA (Table 3). This mutation has the same 5-bp deletion in exon 17 in both gDNA and cDNA (Table 3 and Supplementary Fig. S12).
Discussion
The results reported here enable the first direct comparison of the genetic basis of laboratory- and field-selected resistance to Cry2Ab, which is deployed widely in Bt cotton and Bt corn. We discovered that mutations disrupting the ABC transporter gene PgABCA2 are associated with resistance to Cry2Ab in both laboratory- and field-selected pink bollworm, a global pest of cotton. Genetic linkage analysis revealed that >10,000-fold resistance to Cry2Ab in a laboratory-selected strain from Arizona (Bt4-R2) is tightly linked with a disruptive indel mutation (rA1) in PgABCA2. In field-selected Cry2Ab-resistant pink bollworm from India, we did not find this mutation, but all of the 24 transcript variants from eight larvae collected from five field sites showed severe disruption of PgABCA2, including 19 distinct variants with one to three mutations each. Moreover, the most common cDNA mutation in field-selected populations from India, which entails mis-splicing that omits exon 6 and introduces a stop codon at amino acid 373, also occurred in Bt4-R2. This was the only mutation shared between Arizona and India. The other mutations were mostly from splice-site mutations that lead to mis-splicing of PgABCA2 and were more diverse in India. The differences in PgABCA2 resistance mutations between India and Arizona could reflect the difference in geographic origin, laboratory versus field selection, or both.
Mis-splicing of PgABCA2 pre-mRNA was prevalent in Cry2Ab-resistant larvae from both field- and laboratory-selected pink bollworm. Each of the eight different mutations in resistant larvae from Arizona involves mis-splicing of PgABCA2 (Table 1). For India, we found 17 different cDNA mutations in eight resistant larvae (Table 2). Evaluation of the corresponding gDNA sequences for 6 of these 17 cDNA mutations revealed that all but one are caused by mis-splicing (Table 3). Previous work showed that mis-splicing of cadherin pre-mRNA is associated with pink bollworm resistance to Bt toxin Cry1Ac in laboratory- and field-selected pink bollworm30,31. Also, in laboratory-selected H. armigera, mis-splicing of cadherin and ABCC2 is associated with resistance to Cry1Ac32,33,34. Together with the previous data, our new results suggest that mis-splicing may be a common underlying cause of both field- and laboratory-selected resistance to Bt toxins.
Similar to the results here revealing resistance to Cry2Ab is associated with mutations in PgABCA2 in both laboratory- and field-selected pink bollworm, previous work shows laboratory-selected resistance to Cry2Ab is associated with the homologous genes in H. armigera and H. punctigera from Australia28. In Australia, where field populations remain susceptible to Cry2Ab35, the three resistance alleles detected in H. armigera result in premature truncation of ABCA2, while the sole reported H. punctigera resistance allele has a 14-bp deletion that causes missense mutations28. Like the prevalent role of mis-splicing in pink bollworm resistance to Cry2Ab, our analysis of the previously reported sequences28 indicates mis-splicing is also implicated in two of the three mutations in H. armigera. Ha2Ab-R01 has an 8-bp insertion at the 5′-end of exon 16 and complete skipping of this exon while Ha2Ab-R02 has a 5-bp deletion at the 5′-end of exon 18 and involves an alternative 5′ splice site. Using CRISPR/Cas9 to edit HaABCA2 in H. armigera, each of the two introduced frameshift mutations caused >100-fold resistance to Cry2Ab36. This gene editing also eliminated binding of Cry2Ab to brush border membrane vesicles of H. armigera, demonstrating that ABCA2 is required for such binding36.
In addition to the association between resistance to Cry2Ab and mutations in ABCA2 in three species of Lepidoptera noted above, resistance to Bt toxins in two other families is linked with mutations in two other ABC transporter proteins. Resistance to Cry1 toxins is associated with mutations disrupting ABCC2 in eight lepidopteran pests37,38,39,40,41 and resistance to Cry3Aa is genetically linked with a 4-bp deletion in ABCB1 in the coleopteran Chrysomela tremula42. The association between resistance to Cry toxins and mutations affecting ABC transporters in at least 11 species of insects indicates a key role for these proteins in the Cry toxin mode of action, which may include directly binding toxin or promoting toxin oligomerization and pore formation37,41,43,44,45,46,47.
Results from previous work related to this study show that in both laboratory-selected strains from Arizona and field-selected pink bollworm populations from India, resistance to Cry1Ac is associated with mutations disrupting a gene encoding a cadherin protein (PgCad1) that binds this toxin in the midgut of susceptible larvae30,48,49,50. Similar to the results with Cry2Ab reported here, the mutations affecting PgCad1 were more diverse in the field-selected populations from India than in several lab-selected strains from Arizona. Whereas only four mutant cadherin alleles were found in pink bollworm from five laboratory-selected strains from Arizona, eight cadherin resistance alleles and 19 transcript isoforms were identified from just eight individuals collected from two field-selected populations in India30. Thus, both analyses support the conclusion that laboratory selection may be useful for identifying the genes conferring resistance to Bt toxins, but the resistance alleles are likely to be more diverse in field populations. Unlike the results here with Cry2Ab, none of the Cry1Ac resistance mutations in pink bollworm were shared between Arizona and India.
The diverse mutations in PgABCA2 and PgCad1 associated with resistance to Cry2Ab and Cry1Ac, respectively, in field-selected populations of pink bollworm imply that it would not be efficient to screen for specific resistance alleles, as has been done previously51,52. Moreover, monitoring by screening DNA would miss the critical mis-splicing variants associated with resistance to Bt toxins in this study and in previous work.
Conversely, monitoring methods such as the F1 screen, which can readily identify field-collected individuals with diverse and previously unknown resistance mutations, could be especially useful. In the F1 screen, each field-collected adult is allowed to mate in a single pair with an adult from a strain that is homozygous for a recessive resistance mutation16,53. This approach can detect any recessive resistance alleles in the field-collected adults that occur at the same locus as the recessive mutations in the laboratory-selected strain, as well as non-recessive mutations at any locus15,16. In addition to the F1 screen, the use of next generation sequencing is promising for monitoring variants associated with resistance in the field. This approach allowed us to multiplex cDNA samples from 22 individuals and obtain sequencing information from essentially single molecules of full-length PgABCA2 cDNA without post-sequencing assembly. Furthermore, long read sequencing identified five PgABCA2 transcript variants (Bt4-R2e-i) not previously found by cloning and Sanger sequencing. Even though we identified several PgABCA2 mutations in gDNA from resistant larvae from India using traditional PCR, cloning, and Sanger sequencing, this method is laborious and not practical for monitoring the diverse mutations in the field. Given that PgABCA2-mediated resistance to Cry2Ab occurred in pink bollworm populations from Arizona and India, long read sequencing focusing on this gene could provide a valuable alternative to the F1 screen for monitoring resistance to Cry2Ab in this cosmopolitan pest.
Whereas refuges of non-Bt host plants have helped to delay pest resistance to Bt crops generally, and particularly for the pink bollworm in the United States and China12,54, the scarcity of such refuges probably contributed to the rapid evolution of pink bollworm resistance to both Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab in India21,55,56. Currently, in some regions of India, no Bt toxins in commercialized transgenic cotton are effective against pink bollworm20,21. However, the genetically modified toxins Cry1AbMod and Cry1AcMod are effective against laboratory-selected strains of pink bollworm from Arizona resistant to Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab57,58. Because the loci harboring mutations conferring resistance to these toxins are the same in laboratory- and field-selected pink bollworm, we hypothesize that these modified toxins would also kill field-selected resistant larvae from India. Nonetheless, Bt cotton producing these modified toxins is not available and no transgenic cotton effective against resistant pink bollworm in India is likely to be available in the next several years. This difficult situation underscores the value of proactively implementing resistance management to sustain the efficacy of Bt crops.
Materials and Methods
Insect Strains and Rearing
We used three strains of pink bollworm from Arizona: APHIS-S, AZP-R and Bt4-R2. APHIS-S is a susceptible strain that has been reared in the laboratory for more than 30 years without exposure to Bt toxins or other insecticides59,60. AZP-R, derived from 10 populations collected from Arizona cotton fields in 1997, has 1,500–3,100-fold resistance to Cry1Ac conferred primarily by the r2 cadherin allele, but only two-fold resistance to Cry2Ab61,62. Relative to APHIS-S, Bt4-R2 had 28-fold resistance to Cry1Ac conferred by the mutant cadherin allele r4, and >10,000-fold resistance to Cry2Ab27,63. Bt4-R2 was derived from the Bt4R strain and selected in the laboratory for resistance to Cry2Ab27. In Bt4-R2, inheritance of resistance to Cry1Ac (10 micrograms Cry1Ac per ml diet) and Cry2Ab (0.1, 0.3, 1 and 10 microgram Cry2Ab per ml diet) was recessive based on results of 21-day diet bioassays27,50. All larvae were reared on wheat germ diet64 at 26 °C with 14 h light:10 h dark.
Genetic Linkage Analysis and Diet Bioassays
We tested the genetic linkage between the PgABCA2 rA1 allele and resistance to Cry2Ab by exploiting the biphasic nature of the genetic linkage in Lepidoptera65. We first set up 40 F0 single-pair crosses between APHIS-S (sA1sA1) and Bt4-R2 (rA1rA1) for both ♀ Bt4-R2 x ♂ APHIS-S and ♀ APHIS-S x ♂ Bt4-R2 reciprocal crosses. From each cross, F1 eggs were collected and neonates were reared individually on untreated artificial diet until pupation. To generate backcross families, surviving F1 pupae (n = 22 from ♀ Bt4-R2 x ♂ APHIS-S and n = 20 from ♀ APHIS-S x ♂ Bt4-R2) were sexed and paired with a Bt4-R2 pupa of the opposite sex. A total of 5 informative F1 backcross families were chosen for each reciprocal cross (A, B, C, D and E from ♀ Bt4-R2 x ♂ APHIS-S and F, G, H, I and J from ♀ APHIS-S x ♂ Bt4-R2). We used diet incorporation bioassays to evaluate the susceptibility of neonates from backcross families on either untreated diet or on 1 microgram Cry2Ab per mL diet27,62. After 12 d at 26 °C, we scored all insects for survival and weighed the live insects. Cry2Ab protoxin from Jie Zhang [as described in Fabrick et al.27 was used for all bioassays.
RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
We extracted total RNA from pink bollworm using TRI Reagent (Invitrogen-Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA) and cDNA was prepared using 1 μg of total RNA and random hexamer primers with the ThermoScript RT-PCR system (Invitrogen-Life Technologies) according to the manufacturer’s instruction. RNA used for PCR and cloning was from dissected alimentary tracts pooled from either 3 or 10 fourth instar larvae.
PCR Amplification of PgABCA2 cDNA
Prior to the availability of a pink bollworm midgut transcriptome66, we used degenerate PCR to amplify the PgABCA2 cDNA sequence. Degenerate oligonucleotide primers (Supplementary Table S1) were designed using the consensus degenerate hybrid oligonucleotide primer (CODEHOP) strategy67 from eight different insect ABCA family members, including Aedes aegypti (XP_001662816), Anopheles sinensis (KFB51284), Bombyx mori (ALE60402), Culex quinquefasciatus (XP_001851807), Drosophila ananassae (XP_001967055), Danaus plexippus (EHJ70360), Helicoverpa armigera (ALF46272), and Tribolium castaneum (XP_008199153). Sequences were aligned using Clustal Omega (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/), and conserved blocks were prepared using the Block Maker software (http://blocks.fhcrc.org/blocks/make_blocks.html). Blocks were then used by CODEHOP program (https://virology.uvic.ca/virology-ca-tools/j-codehop/) to design degenerate primers with the default parameters. All primers were purchased from Integrated DNA Technology (IDT, Coralville, IA).
We used the primer combinations 1pgABCA2-5 + 8pgABCA2-3 and 4pgABCA2-5 + 27pgABCA2-3 (Supplementary Table S1) to amplify two internal PgABCA2 cDNA fragments from APHIS-S. PCR was performed with 2.5 U Takara ExTaq Premix (Takara Bio USA Inc., Mountain View, CA), 2 μM of each sense and antisense primer, and 0.3 µg cDNA using a Biometra TProfessional gradient Thermocycler (Biometra, Germany) at: 95 °C for 3 min (1 cycle); 40 cycles of 95 °C for 45 s, 50 °C for 1 min and 72 °C for 2 min; then 72 °C for 5 min. Nested PCR amplification was carried using one microliter of primary PCR product using the primer combinations 2pgABCA2-5 + 6pgABCA2-3 and 15pgABCA2-5 + 23pgABCA2-3, respectively (Supplementary Table S1). PCR products cloned into pCR®2.1-TOPO® (Invitrogen-Life Technologies) were sequenced by the Arizona State University DNA Lab (Tempe, AZ) and confirmed as PgABCA2 using BLAST (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi).
Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends (RACE)
The partial cDNA sequences obtained from degenerate PCR allowed for design of PgABCA2-specific sense and antisense primers (Supplementary Table S1) and were used for 5′- and 3′-RACE according to Invitrogen’s GeneRacer™ kit protocol. For 5′-RACE, cDNA was reverse transcribed using supplied random hexamer primer from 1 µg of total RNA from APHIS-S and used as templates for PCR. Semi-nested PCR amplification was used, including a first round with the GeneRacer™ 5′ Primer and 32pgABCA2-3 and the second using GeneRacer™ 5′ Nested Primer and 32pgABCA2-3. For 3′-RACE, APHIS-S total RNA was reverse transcribed using GeneRacer™ Oligo-dT Primer and nested PCR was run using 37pgABCA2-5 and the GeneRacer™ 3′ Primer followed by fully-nested amplification using 38pgABCA2-5 and the GeneRacer™ 3′ Nested Primer. PCR products were cloned into pCR®2.1-TOPO® and sequenced as indicated above.
Sanger Sequencing of the Full-Length PgABCA2 Coding Region
Oligonucleotide primers, 55pgABCA2-5 and 60pgABCA2-3 (Supplementary Table S1), corresponding to the 5′- and 3′-ends of PgABCA2 were used to amplify the full-length coding sequence from APHIS-S cDNA described earlier. PCR was performed using 1.25 U SuperTaqTM DNA polymerase (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) and 0.4 μM primers at: 94 °C for 2 min (1 cycle); 40 cycles of 94 °C for 30 s, 60 °C for 30 s and 68 °C for 6 min; then 72 °C for 5 min. PCR products were A-tailed with 1 U of Takara ExTaq and separated by agarose gel electrophoresis. A band of ~5 kb was gel-purified and multiple attempts were made to clone into several cloning vectors optimized for cloning long PCR amplicons and to minimize “leaky” expression of genes. Unfortunately, no PgABCA2-positive E. coli clones were obtained, suggesting that the insert may be cytotoxic to bacteria.
Because of difficulties with cloning the full-length PgABCA2 coding region, we verified the 55pgABCA2-5 + 60pgABCA2-3 PCR products by direct sequencing. PCR products were treated with ExoSAP-IT™ PCR Product Cleanup Reagent (Affymetrix, Inc. Santa Clara, CA) according to manufacturer’s protocol and sequenced directly with oligonucleotide primers, 63pgABCA2-3 through 78pgABCA2-5 (Supplementary Table S1). Similarly, we amplified the full-length coding sequence from cDNA prepared from Bt4-R2 and PCR products were directly sequenced and compared with the APHIS-S PgABCA2 sequence. The full-length coding sequence of PgABCA2 from APHIS-S, AZP-R, and Bt4-R2 are deposited in the GenBank public database (MG637361).
To further validate differences within the PgABCA2 cDNA sequences from APHIS-S and Bt4-R2, three overlapping, partial fragments corresponding to nucleotides 1–1,744, 1,656–3,403, and 3,326–5,187 were PCR amplified and cloned into pCR®2.1-TOPO®. Several clones corresponding to each fragment were Sanger sequenced. The PgABCA2 cDNA sequences that were unique after sequencing these clones were identified as “variants”. We used Mutalyzer 2.0.26 (https://mutalyzer.nl/description-extractor)68 and Description Extractor69 to detect all sequence changes (≥2 bp) found within the Bt4-R2 cDNA variants and all mutations were annotated based on nomenclature and recommendations provided by Human Genome Variation Society (http://www.HGVS.org/varnomen)70. Changes resulting from single nucleotide polymorphisms were excluded from our analysis.
Extraction of gDNA, PCR and Cloning
gDNA was extracted from pools of ten APHIS-S and Bt4-R2 using the PUREGENE DNA Isolation Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. We extracted gDNA from the remaining tissues (e.g. larvae minus gut tracts) from the same 10 individuals that were used for RNA extractions. gDNA was similarly extracted from India and Arizona individuals for PCR genotyping and Sanger sequencing.
Because exon-intron junctions are unknown for the PgABCA2 gene, we used Splign, (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sutils/splign/splign.cgi)71 and the H. armigera ABCA2 coding sequence (KP219763) with its corresponding genomic locus (NW_018395393.1) to predict intron positions in PgABCA2. The primers 91pgABCA2-5 and 92pgABCA2-3 (Supplementary Table S1) located in the exons flanking the rA1 mutation were used to amplify genomic fragments from APHIS-S and Bt4-R2 and the gDNA products were cloned into pCR®2.1-TOPO® and sequenced as above. To check genomic DNA corresponding to exon 6 region (1,090-1,234 bp) in Bt4-R2, two different sets of primers were used (143pgABCA2-5 + 106pgABCA2-3 and 95pgABCA2-5 + 90pgABCA2-3).
Allele-Specific PCR
Based on the location of the rA1 mutation in the gDNA, we used allele-specific PCR and primers 83pgABCA2-5 and 84pgABCA2-3 (hereafter referred to as rA1-F and rA1-R) (Supplementary Table S1) that flank the rA1 mutation to genotype backcross survivors obtained from biphasic linkage crosses. Reactions contained 0.1 μg gDNA, 2X SaphireAmp® polymerase premix (Takara Bio USA Inc., Mountain View, CA), and 0.2 μM of both sense and antisense primers. PCR was run using the following conditions: 94 °C for 1 min (1 cycle); 25 cycles of 98 °C for 5 s, 60 °C for 5 s and 72 °C for 5 s. PCR products and 1 kb Plus DNA Ladder (ThermoFisher Scientific) were separated using 3% agarose gel electrophoresis to differentiate size of mutant (rA1) and wild-type (sA1) DNA bands. To validate allele-specific PCR, amplified products were cloned and sequenced from Bt4-R2 (n = 4) and APHIS-S (n = 4).
Targeted PgABCA2 Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
We used Single Molecule, Real-Time (SMRT®) sequencing on a PacBio® RSII (Pacific Biosciences, Menlo Park, CA) to sequence PgABCA2 cDNA from 22 pink bollworm larvae. Fifteen larvae were survivors obtained from backcross families on 1 microgram Cry2Ab per mL diet, including 7 genotyped by allele-specific PCR as rA1rA1 and 8 genotyped as rA1sA1. APHIS-S larvae were taken directly from our rearing colony on November 17, 2016.
Total RNA was extracted and cDNA was prepared from individual 4th instar larvae (excluding head) as previously described, except we used a gene-specific primer (150pgABCA2-3; Supplementary Table S1) to enrich the cDNA for PgABCA2. Because of limited available tissue and low abundance of the PgABCA2 transcript, we used nested PCR to generate amplicon templates for library preparation. Initial PCR amplification was performed with primers 158pgABCA2-5 and 150pgABCA2-3 (Supplementary Table S1) using SuperTaqTM DNA polymerase (Applied Biosystems). Nested amplification was carried out with barcode-tailed PCR primers, 163pgABCA2-5 and 166pgABCA2-3 (Supplementary Table S1). The symmetric barcode-tailed PCR primers were designed based on the PacBio® multiplex PCR primer guidelines (http://www.2einteractive.com/pacbio/Shared-Protocol-PacBio-Barcodes-for-SMRT-Sequencing.pdf).
Prior to SMRTbellTM library preparation, ~5 kb PCR products were gel purified with QIAquick® Gel extraction kit (Qiagen, Germantown, MD) and quantified using QubitTM dsDNA High Sensitivity Assay Kit with the QubitTM 2.0 Fluorometer (ThermoFisher Scientific). Barcoded samples (n = 22) were pooled in equimolar concentrations and SMRTbellTM libraries were prepared with 0.5 µg of the pooled amplicons following the standard procedures for blunt ligation of hairpin adapters using SMRTbellTM Template Prep Kit 1.0 (Pacific Biosciences). DNA sequencing was performed on the PacBio® RSII sequencer using P6-P4 enzyme chemistry at the University of Arizona, Arizona Genomics Institute (Tucson, Arizona). Data were captured using 3-hour movies. Sequence data are deposited in the NCBI TSA under the accession SRP126193, associated with BioProject PRJNA421207.
We initially processed the raw sequences through the PacBio SMRT® portal (v2.3.0), in which sequences were filtered for a minimum of two passes and a minimum predicted accuracy of 90%. We used Long Amplicon Analysis (LAA v2) protocol to identify and report abundance of differing clusters of sequencing reads within a single library. Custom LAA settings included: minimum subread length = 4,000; maximum number of subreads = 1000; barcode score = 30; ignore primer sequence = 30; trim ends = 0; only most supported = 0; cluster per gene family = y; phase alleles = y; split results = y. We also processed the raw sequences by LAA analysis using slightly modified settings to include shorter subreads (minimum subread length = 3000). The latter analysis allowed us to sample more reads and to specifically identify reads containing the exon 6 deletion. Resulting consensus sequences were manually inspected (for length and subread coverage to exclude spurious artifact sequences) and mapped to the PgABCA2 cDNA plus strand using Geneious R10 (Biomatters Inc., Newark, NJ).
Pink Bollworm Field Collections
We analyzed putatively resistant pink bollworm larvae collected from December 11, 2015 to January 3, 2016 at seven sites in four states of India (Fig. 4). Fourth instars were collected by opening mature cotton bolls collected arbitrarily from cotton fields reported to be planted with dual-toxin Bt cotton producing Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab. Fourth instar larvae were saved in RNAlater® (Ambion-Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA). We used EnviroLogix QuantiPlateTM ELISA kits (Portland, ME) for Cry1Ab/Cry1Ac and Cry2A to estimate the concentration of Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab in maternal tissue from cotton bolls for which survivors were recovered. ELISAs were conducted according to manufacturer’s protocols on boll material stored frozen at −20 °C for 2–4 months prior to analysis. Toxins provided with the kit were used as positive controls, single samples were run, and concentrations were expressed as micrograms Cry toxin per gram wet tissue.
DNA Screening of Populations from India for PgABCA2 r A1 Allele
We extracted gDNA from the head portion of seven pink bollworm survivors on Bollgard II® that remained following RNA extraction and performed rA1-specific PCR as described above. PCR products were separated on 3% agarose gels and visually inspected for PgABCA2 product size different from control samples (APHIS-S and Bt4-R2).
Sequencing of PgABCA2 DNA from Field-Collected Resistant and Susceptible Pink Bollworm from India
Genomic DNA, total RNA and cDNA were prepared from pink bollworm recovered from Bollgard II® cotton bolls from India as described above. We extracted total RNA from 8 individuals (AM-8, CK-1, GAP-3, KT-1, KT-8, KT-10, RK-1 and RK-11), and cDNA was synthesized using the PgABCA2-specific primer, 60pgABCA2-3. cDNA from three pink bollworm samples (AMH-1, AMH-2 and AMH-3) collected 3 November 2010 on non-Bt cotton bolls at the Panjabrao Deshmukh Agricultural University Cotton Research Station in Akola, Maharashtra served as susceptible control samples30. Full-length PgABCA2 cDNA was first amplified using 55pgABCA2-5 and 60pgABCA2-3 primers and SuperTaqTM DNA polymerase (Applied Biosystems) followed by nested amplification with 104pgABCA2-5 and 105pgABCA2-3. PCR products were separated by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis to confirm presence of a single amplicon and remainder of samples were used for Sanger sequencing of PgABCA2 PCR products using sequencing primers described above.
PgABCA2 PCR sequence reads were mapped to the reference PgABCA2 cDNA sequence from AMH using Geneious R10 and variation was observed in traces showing multiple overlapping sequencing. We amplified and cloned cDNAs corresponding to these variable regions into pCR®2.1-TOPO® or pCR-XL-TOPO® and plasmid DNA was sequenced. Specifically, for CK-1 and GAP-3, 61pgABCA2-5 and 125pgABCA2-3 amplified a fragment corresponding to putative exons 2–18. For samples KT-1, KT-8, KT-10, RK-1 and RK-11 samples, overlapping fragments were amplified using primers 104pgABCA2-5 and 169pgABCA2-3 and 70pgABCA2-5 and 169pgaBCA-3 spanning exons 1–16 and 13–31, respectively. The PgABCA2 cDNA variants from India that differed by ≥2 bp and unique from the AMH consensus sequence were further analyzed using Mutalyzer and were annotated based on nomenclature and recommendations provided by the Human Genome Variation Society70. We checked the gDNA regions that overlapped with some mutations from several of the putative resistant samples from India (AM-8, CK-1, GAP-3, KT-1 and RK-1). To amplify the gDNA, we used primers 124pgABCA2-5 and 125pgABCA2-3 for AM-8, 191pgABCA2-5 and 192pgABCA2-3 for CK-1, 174pgABCA2-5 and 185pgABCA2-3 for GAP-3, 49pgABCA2-5 and 89pgABCA2-3, 104pgABCA2-5 and 89pgABCA2-3, 64pgABCA2-5 and 120pgABCA2-3, and 121pgABCA2-5 and 123pgABCA2-3 for RK-1 (Supplementary Table S1). To amplify a common region overlapping the mis-splicing observed in exon 6, primers 96pgABCA2-5 and 90pgABCA2-3 were used to amplify gDNA from CK-1, KT-1 and RK-1 (Supplementary Table S1). The partial gDNA sequences were cloned into pCR®2.1-TOPO® or pCR-XL-TOPO® and sequenced.
References
Mendelsohn, M., Kough, J., Vaituzis, Z. & Matthews, K. Are Bt crops safe? Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 1003–1009, https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0903-1003 (2003).
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Genetically Engineered Crops: Experiences and Prospects (National Academies Press, Washington, DC, 2016).
Sanahuja, G., Banakar, R., Twyman, R. M., Capell, T. & Christou, P. Bacillus thuringiensis: a century of research, development and commercial applications. Plant Biotechnol. J. 9, 283–300, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7652.2011.00595.x (2011).
Pardo-López, L., Soberón, M. & Bravo, A. Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal three-domain Cry toxins: mode of action, insect resistance and consequences for crop protection. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 37, 3–22, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2012.00341.x (2013).
ISAAA. Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops in 2017: Biotech crop adoption surges as economic benefits accumulate in 22 years. ISAAA Brief No. 53 (ISAAA, Ithaca, NY).
Hutchison, W. D. et al. Areawide suppression of European corn borer with Bt maize reaps savings to non-Bt maize growers. Science 330, 222–225, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1190242 (2010).
Tabashnik, B. E. et al. Suppressing resistance to Bt cotton with sterile insect releases. Nat. Biotechnol. 28, 1304–1307, https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1704 (2010).
Naranjo, S. E. Impacts of Bt transgenic cotton on integrated pest management. J. Agric. Food Chem. 59, 5842–5851, https://doi.org/10.1021/jf102939c (2011).
Lu, Y., Wu, K., Jiang, Y., Guo, Y. & Desneux, N. Widespread adoption of Bt cotton and insecticide decrease promotes biocontrol services. Nature 487, 362–365, https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11153 (2012).
Downes, S. et al. A perspective on management of Helicoverpa armigera: transgenic Bt cotton, IPM, and landscapes. Pest Manag. Sci. 73, 485–492, https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.4461 (2017).
Dively, G. P. et al. Regional pest suppression associated with widespread Bt maize adoption benefits vegetable growers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 115, 3320–3325, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1720692115 (2018).
Tabashnik, B. E. & Carrière, Y. Surge in insect resistance to transgenic crops and prospects for sustainability. Nat. Biotechnol. 35, 926–935, https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3974 (2017).
Fitt, G. P. An Australian approach to IPM in cotton: integrating new technologies to minimise insecticide dependence. Crop Protection 19, 793–800, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-2194(00)00106-X (2000).
Tabashnik, B. E., Mota-Sanchez, D., Whalon, M. E., Hollingworth, R. M. & Carrière, Y. Defining terms for proactive management of resistance to Bt crops and pesticides. J. Econ. Entomol. 107, 496–507 (2014).
Wu, Y. Chapter Six - Detection and mechanisms of resistance evolved in insects to Cry toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis in Advances in Insect Physiology Vol. 47 (eds. Dhadialla, T. S., & Gill, S. S.) 297–342 (Academic Press, 2014).
Zhang, H. et al. Diverse genetic basis of field-evolved resistance to Bt cotton in cotton bollworm from China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109, 10275–10280, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1200156109 (2012).
Henneberry, T. J. & Naranjo, S. E. Integrated management approaches for pink bollworm in the southwestern United States. Integrated Pest Manag. Rev. 3, 31–52, https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1009673622862 (1998).
Centre for Agriculture and Biosciences International. Invasive species compendium: Datasheet report for Pectinophora gossypiella (pink bollworm). (CABI, 2016).
Carrière, Y., Crickmore, N. & Tabashnik, B. E. Optimizing pyramided transgenic Bt crops for sustainable pest management. Nat. Biotechnol. 33, 161–168, https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3099 (2015).
Kranthi, K. R. Pink bollworm strikes Bt-cotton. Cotton Statistics & News, 1–6 (2015).
Mohan, K. S. An area-wide approach to pink bollworm management on Bt cotton in India – a dire necessity with community participation. Curr. Sci. 112, 10 (2017).
Ali, M. I. & Luttrell, R. G. Susceptibility of bollworm and tobacco budworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to Cry2Ab2 insecticidal protein. J. Econ. Entomol. 100, 921–931 (2007).
Dively, G. P., Venugopal, P. D. & Finkenbinder, C. Field-evolved resistance in corn earworm to Cry proteins expressed by transgenic sweet corn. PLoS ONE 11, e0169115, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0169115 (2016).
Dhurua, S. & Gujar, G. T. Field-evolved resistance to Bt toxin Cry1Ac in the pink bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella (Saunders) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae), from India. Pest Manag. Sci. 67, 898–903, https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.2127 (2011).
Naik, V. C. et al. Field-evolved resistance of pink bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella (Saunders) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae), to transgenic Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) cotton expressing crystal 1Ac (Cry1Ac) and Cry2Ab in India. Pest Manag. Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.5038 (2018).
Mohan, K. S., Ravi, K. C., Suresh, P. J., Sumerford, D. & Head, G. P. Field resistance to the Bacillus thuringiensis protein Cry1Ac expressed in Bollgard® hybrid cotton in pink bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella (Saunders), populations in India. Pest Manag. Sci. 72, 738–746, https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.4047 (2016).
Fabrick, J. A. et al. Multi-toxin resistance enables pink bollworm survival on pyramided Bt cotton. Sci. Rep. 5, 16554, https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16554 (2015).
Tay, W. T. et al. Insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cry2Ab is conferred by mutations in an ABC transporter subfamily A protein. PLoS Genet. 11, e1005534, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005534 (2015).
Song, X., Kain, W., Cassidy, D. & Wang, P. Resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cry2Ab in Trichoplusia ni is conferred by a novel genetic mechanism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81, 5184–5195, https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00593-15 (2015).
Fabrick, J. A. et al. Alternative splicing and highly variable cadherin transcripts associated with field-evolved resistance of pink bollworm to Bt cotton in India. PLoS ONE 9, e97900, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0097900 (2014).
Fabrick, J. A., Mathew, L. G., Tabashnik, B. E. & Li, X. Insertion of an intact CR1 retrotransposon in a cadherin gene linked with Bt resistance in the pink bollworm. Pectinophora gossypiella. Insect Mol. Biol. 20, 651–665, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2583.2011.01095.x (2011).
Zhang, H., Tang, M., Yang, F., Yang, Y. & Wu, Y. DNA-based screening for an intracellular cadherin mutation conferring non-recessive Cry1Ac resistance in field populations of Helicoverpa armigera. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 107, 148–152, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2013.06.007 (2013).
Zhao, J., Jin, L., Yang, Y. & Wu, Y. Diverse cadherin mutations conferring resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cry1Ac in Helicoverpa armigera. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 40, 113–118, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2010.01.001 (2010).
Xiao, Y. et al. Mis-splicing of the ABCC2 gene linked with Bt toxin resistance in Helicoverpa armigera. Sci. Rep. 4, 6184, https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06184 (2014).
Downes, S., Walsh, T. & Tay, W. T. Bt resistance in Australian insect pest species. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 15, 78–83, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cois.2016.04.002 (2016).
Wang, J. et al. CRISPR/Cas9 mediated genome editing of Helicoverpa armigera with mutations of an ABC transporter gene HaABCA2 confers resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry2A toxins. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 87, 147–153, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2017.07.002 (2017).
Heckel, D. G. Learning the ABCs of Bt: ABC transporters and insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis provide clues to a crucial step in toxin mode of action. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 104, 103–110, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2012.05.007 (2012).
Coates, B. S. & Siegfried, B. D. Linkage of an ABCC transporter to a single QTL that controls Ostrinia nubilalis larval resistance to the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Fa toxin. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 63, 86–96, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2015.06.003 (2015).
Tabashnik, B. E. ABCs of insect resistance to Bt. PLoS Genet. 11, e1005646, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005646 (2015).
Banerjee, R. et al. Mechanism and DNA-based detection of field-evolved resistance to transgenic Bt corn in fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda). Sci. Rep. 7, 10877, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09866-y (2017).
Tanaka, S. et al. Bombyx mori ABC transporter C2 structures responsible for the receptor function of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Aa toxin. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 91, 44–54, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2017.11.002 (2017).
Pauchet, Y., Bretschneider, A., Augustin, S. & Heckel, D. G. A P-Glycoprotein is linked to resistance to the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry3Aa toxin in a leaf beetle. Toxins (Basel) 8, https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8120362 (2016).
Atsumi, S. et al. Single amino acid mutation in an ATP-binding cassette transporter gene causes resistance to Bt toxin Cry1Ab in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109, E1591–1598, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1120698109 (2012).
Bretschneider, A., Heckel, D. G. & Pauchet, Y. Three toxins, two receptors, one mechanism: Mode of action of Cry1A toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis in Heliothis virescens. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 76, 109–117, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2016.07.008 (2016).
Ocelotl, J. et al. ABCC2 is associated with Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac toxin oligomerization and membrane insertion in diamondback moth. Sci. Rep. 7, 2386, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-02545-y (2017).
Tanaka, S. et al. The ATP-binding cassette transporter subfamily C member 2 in Bombyx mori larvae is a functional receptor for Cry toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis. FEBS J. 280, 1782–1794, https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.12200 (2013).
Zhou, Z. et al. Identification of ABCC2 as a binding protein of Cry1Ac on brush border membrane vesicles from Helicoverpa armigera by an improved pull-down assay. MicrobiologyOpen 5, 659–669, https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.360 (2016).
Morin, S. et al. Three cadherin alleles associated with resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis in pink bollworm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 5004–5009, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0831036100 (2003).
Fabrick, J. A. & Tabashnik, B. E. Binding of Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cry1Ac to multiple sites of cadherin in pink bollworm. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 37, 97–106, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2006.10.010 (2007).
Fabrick, J. A. & Tabashnik, B. E. Similar genetic basis of resistance to Bt toxin Cry1Ac in boll-selected and diet-selected strains of pink bollworm. PLoS ONE 7, e35658, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0035658 (2012).
Tabashnik, B. E. et al. DNA screening reveals pink bollworm resistance to Bt cotton remains rare after a decade of exposure. J. Econ. Entomol. 99, 1525–1530, https://doi.org/10.1603/0022-0493-99.5.1525 (2006).
Gahan, L. J., Gould, F., López, J. D. Jr., Micinski, S. & Heckel, D. G. A polymerase chain reaction screen of field populations of Heliothis virescens for a retrotransposon insertion conferring resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin. J. Econ. Entomol. 100, 187–194 (2007).
Gould, F. et al. Initial frequency of alleles for resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxins in field populations of Heliothis virescens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 3519–3523 (1997).
Wan, P. et al. Hybridizing transgenic Bt cotton with non-Bt cotton counters resistance in pink bollworm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 114, 5413–5418, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1700396114 (2017).
Stone, G. D. Biotechnology and the political ecology of information in India. Hum. Organ. 63, 127–140, https://doi.org/10.17730/humo.63.2.jgvu7rlfafk9jwf9 (2004).
Choudhary, B. G., K. Bt cotton in India: A country profile. ISAAA Series of Biotech Crop Profiles (ISAAA, Ithaca, NY, 2010).
Soberón, M. et al. Engineering modified Bt toxins to counter insect resistance. Science 318, 1640–1642, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1146453 (2007).
Tabashnik, B. E. et al. Efficacy of genetically modified Bt toxins alone and in combinations against pink bollworm resistant to Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab. PLoS ONE 8, e80496, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0080496 (2013).
Liu, Y. B., Tabashnik, B. E., Meyer, S. K., Carrière, Y. & Bartlett, A. C. Genetics of pink bollworm resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cry1Ac. J. Econ. Entomol. 94, 248–252, https://doi.org/10.1603/0022-0493-94.1.248 (2001).
Bartlett, A. C. Resistance of the pink bollworm to Bt transgenic cotton. In Proceedings, Beltwide Cotton Conferences. National Cotton Council of America, Memphis, TN. pp 766–767 (1995).
Tabashnik, B. E. et al. Frequency of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis in field populations of pink bollworm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 12980–12984, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.24.12980 (2000).
Tabashnik, B. E. et al. Asymmetrical cross-resistance between Bacillus thuringiensis toxins Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab in pink bollworm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 11889–11894, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0901351106 (2009).
Fabrick, J. A., Forlow Jech, L. & Henneberry, T. J. Novel pink bollworm resistance to the Bt toxin Cry 1Ac: effects on mating, oviposition, larval development and survival. J. Insect Sci. 9, 24, https://doi.org/10.1673/031.009.2401 (2009).
Bartlett, A. C. & Wolf, W. W. Pectinophora gossypiella. Handbook of Insect Rearing. Vol. 2 (eds Singh, P. & Moore, R. F.) 415–430 (Elsevier Scientific Publishing Co., Amsterdam, 1985).
Heckel, D. G., Gahan, L. J., Liu, Y. B. & Tabashnik, B. E. Genetic mapping of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxins in diamondback moth using biphasic linkage analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 8373–8377 (1999).
Tassone, E. E. et al. Sequencing, de novo assembly and annotation of a pink bollworm larval midgut transcriptome. Gigascience 5, 28, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13742-016-0130-9 (2016).
Rose, T. M., Henikoff, J. G. & Henikoff, S. CODEHOP (COnsensus-DEgenerate Hybrid Oligonucleotide Primer) PCR primer design. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 3763–3766 (2003).
Wildeman, M., van Ophuizen, E., den Dunnen, J. T. & Taschner, P. E. Improving sequence variant descriptions in mutation databases and literature using the Mutalyzer sequence variation nomenclature checker. Hum. Mutat. 29, 6–13, https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.20654 (2008).
Vis, J. K., Vermaat, M., Taschner, P. E., Kok, J. N. & Laros, J. F. An efficient algorithm for the extraction of HGVS variant descriptions from sequences. Bioinformatics 31, 3751–3757, https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv443 (2015).
den Dunnen, J. T. et al. HGVS recommendations for the description of sequence variants: 2016 update. Hum. Mutat. 37, 564–569, https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.22981 (2016).
Kapustin, Y., Souvorov, A., Tatusova, T. & Lipman, D. Splign: algorithms for computing spliced alignments with identification of paralogs. Biol. Direct 3, 20, https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6150-3-20 (2008).
Acknowledgements
We thank D. LeRoy, B. Hefner, G. Unnithan, and A. Yelich for excellent technical assistance and D. Kudrna and D. Copetti and other staff of the Arizona Genomics Institute at the University of Arizona for assistance with PacBio® RSII sequencing. We thank Jie Zhang for kindly providing Cry2Ab. This research was supported by CRIS base funding to USDA ARS, National Program 304 - Crop Protection & Quarantine (Project #2020-22620-022-00D), DuPont Pioneer (Agreement #58-3K95-4-1666), Agriculture and Food Research Initiative Competitive Grant 2018-67013-27821 from the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture, the Max-Planck-Gesellschaft, the CSIRO Health and Biosecurity (R-8681-1), and CSIRO Land and Water. Mention of trade names or commercial products in this article is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the U. S. Department of Agriculture. USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.G.M., X.L., B.E.T. and J.A.F. designed the study. L.G.M., J.P., B.M., L.R.C., J.Z. and J.A.F. performed the experiments. L.G.M., X.L., B.E.T. and J.A.F. analyzed the data. L.G.M., Y.C., X.L., B.E.T. and J.A.F. wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
This is a cooperative investigation between the USDA Agricultural Research Service, the University of Arizona, the Indian Council of Agricultural Research, the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization, and the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology. DuPont Pioneer provided partial support to J.A.F., B.E.T., and Y.C. for this work. J.A.F. is coauthor of a patent “Cadherin Receptor Peptide for Potentiating Bt Biopesticides” (patent numbers: US20090175974A1, US8354371, WO2009067487A2, WO2009067487A3). B.E.T. is a coauthor of a patent on modified Bt toxins, “Suppression of Resistance in Insects to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry Toxins, Using Toxins that do not Require the Cadherin Receptor” (patent numbers: CA2690188A1, CN101730712A, EP2184293A2, EP2184293A4, EP2184293B1, WO2008150150A2, WO2008150150A3). All other authors declare no potential conflict of interest. Bayer CropScience, Dow AgroSciences, Monsanto, FMC, Gowan, and Syngenta did not provide funding to support this work, but may be affected financially by publication of this paper and have funded other work by some of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Mathew, L.G., Ponnuraj, J., Mallappa, B. et al. ABC transporter mis-splicing associated with resistance to Bt toxin Cry2Ab in laboratory- and field-selected pink bollworm. Sci Rep 8, 13531 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31840-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31840-5
This article is cited by
-
The evaluation of resistance risk to Cry2Ab and cross-resistance to other insecticides in Helicoverpa armigera
Journal of Pest Science (2024)
-
Molecular profiling of resistance alleles in Pectinophora gossypiella (Saunders) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) collected from different locations
Egyptian Journal of Biological Pest Control (2023)
-
Genome-wide analysis reveals distinct global populations of pink bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella)
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Knockout of ABC transporter gene ABCA2 confers resistance to Bt toxin Cry2Ab in Helicoverpa zea
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Functional Diversity of the Lepidopteran ATP-Binding Cassette Transporters
Journal of Molecular Evolution (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.