Abstract
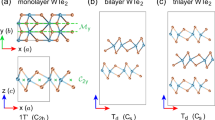
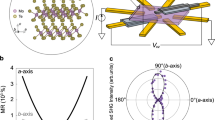
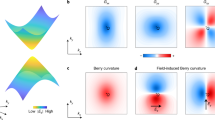
The Hall effect occurs only in systems with broken time-reversal symmetry, such as materials under an external magnetic field in the ordinary Hall effect and magnetic materials in the anomalous Hall effect (AHE)1. Here we show a nonlinear AHE in a non-magnetic material under zero magnetic field, in which the Hall voltage depends quadratically on the longitudinal current2,3,4,5,6. We observe the effect in few-layer Td-WTe2, a two-dimensional semimetal with broken inversion symmetry and only one mirror line in the crystal plane. Our angle-resolved electrical measurements reveal that the Hall voltage maximizes (vanishes) when the bias current is perpendicular (parallel) to the mirror line. The observed effect can be understood as an AHE induced by the bias current, which generates an out-of-plane magnetization. The temperature dependence of the Hall conductivity further suggests that both the intrinsic Berry curvature dipole and extrinsic spin-dependent scatterings contribute to the observed nonlinear AHE.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting the plots within this paper and other findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon request.
References
Nagaosa, N., Sinova, J., Onoda, S., MacDonald, A. H. & Ong, N. P. Anomalous Hall effect. Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 1539–1592 (2010).
Low, T., Jiang, Y. & Guinea, F. Topological currents in black phosphorus with broken inversion symmetry. Phys. Rev. B 92, 235447 (2015).
Sodemann, I. & Fu, L. Quantum nonlinear Hall effect induced by Berry curvature dipole in time-reversal invariant materials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 216806 (2015).
Zhang, Y., van den Brink, J., Felser, C. & Yan, B. Electrically tuneable nonlinear anomalous Hall effect in two-dimensional transition-metal dichalcogenides WTe2 and MoTe2. 2D Mater. 5, 044001 (2018).
Shi, L.-k. & Song, J. C. W. Symmetry, spin-texture, and tunable quantum geometry in a WTe2 monolayer. Phys. Rev. B 99, 035403 (2019).
You, J.-S., Fang, S., Xu, S.-Y., Kaxiras, E. & Low, T. Berry curvature dipole current in the transition metal dichalcogenides family. Phys. Rev. B 98, 121109 (2018).
Landau, L. D., Lifshitz, E. M. & Pitaevskii, L. P. Statistical Physics (Pergamon, Oxford, 1999).
Shen, Y. R. The Principles of Nonlinear Optics (Wiley, Hoboken, 2002).
Brown, B. E. The crystal structures of WTe2 and high-temperature MoTe2. Acta Crystallogr. 20, 268–274 (1966).
Song, Q. et al. The in-plane anisotropy of WTe2 investigated by angle-dependent and polarized Raman spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 6, 29254 (2016).
Ali, M. N. et al. Large, non-saturating magnetoresistance in WTe2. Nature 514, 205–208 (2014).
Soluyanov, A. A. et al. Type-II Weyl semimetals. Nature 527, 495–498 (2015).
Wang, Y. et al. Gate-tunable negative longitudinal magnetoresistance in the predicted type-II Weyl semimetal WTe2. Nat. Commun. 7, 13142 (2016).
Fatemi, V. et al. Magnetoresistance and quantum oscillations of an electrostatically tuned semimetal-to-metal transition in ultrathin WTe2. Phys. Rev. B 95, 041410 (2017).
Qian, X., Liu, J., Fu, L. & Li, J. Quantum spin Hall effect in two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. Science 346, 1344–1347 (2014).
Tang, S. et al. Quantum spin Hall state in monolayer 1Tʹ-WTe2. Nat. Phys. 13, 683–687 (2017).
Fei, Z. et al. Edge conduction in monolayer WTe2.Nat. Phys. 13, 677–682 (2017).
Wu, S. et al. Observation of the quantum spin Hall effect up to 100 kelvin in a monolayer crystal. Science 359, 76–79 (2018).
Fei, Z. et al. Ferroelectric switching of a two-dimensional metal. Nature 560, 336–339 (2018).
Sajadi, E. et al. Gate-induced superconductivity in a monolayer topological insulator. Science 362, 922–925 (2018).
Fatemi, V. et al. Electrically tunable low density superconductivity in a monolayer topological insulator. Science 362, 926–929 (2018).
Ma, Q. et al. Observation of the nonlinear Hall effect under time-reversal-symmetric conditions. Nature 565, 337–342 (2019).
Luo, Y. et al. Hall effect in the extremely large magnetoresistance semimetal WTe2. Appl. Phys. Lett. 107, 182411 (2015).
Olbrich, P. et al. Room-temperature high-frequency transport of Dirac fermions in epitaxially grown Sb2Te3- and Bi2Te3-based topological insulators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 096601 (2014).
Yu, H., Wu, Y., Liu, G.-B., Xu, X. & Yao, W. Nonlinear valley and spin currents from Fermi pocket anisotropy in 2D crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 156603 (2014).
Edelstein, V. M. Spin polarization of conduction electrons induced by electric current in two-dimensional asymmetric electron systems. Solid State Commun. 73, 233–235 (1990).
Lee, J., Wang, Z., Xie, H., Mak, K. F. & Shan, J. Valley magnetoelectricity in single-layer MoS2. Nat. Mater. 16, 887–891 (2017).
Mak, K. F., Xiao, D. & Shan, J. Light–valley interactions in 2D semiconductors. Nat. Photon. 12, 451–460 (2018).
MacNeill, D. et al. Control of spin–orbit torques through crystal symmetry in WTe2/ferromagnet bilayers. Nat. Phys. 13, 300–305 (2016).
MacNeill, D. et al. Thickness dependence of spin–orbit torques generated by WTe2. Phys. Rev. B 96, 054450 (2017).
Tian, Y., Ye, L. & Jin, X. Proper scaling of the anomalous Hall effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 087206 (2009).
Ye, L. et al. Massive Dirac fermions in a ferromagnetic kagome metal. Nature 555, 638–642 (2018).
Xu, S.-Y. et al. Electrically switchable Berry curvature dipole in the monolayer topological insulator WTe2. Nat. Phys. 14, 900–906 (2018).
Wang, L. et al. One-dimensional electrical contact to a two-dimensional material. Science 342, 614–617 (2013).
Chang, T.-R. et al. Prediction of an arc-tunable Weyl Fermion metallic state in MoxW1−xTe2. Nat. Commun. 7, 10639 (2016).
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by ARO Award W911NF-17-1-0605 for sample fabrication and transport measurements, and the US Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy Sciences under award no. DESC0013883 for optical measurements. It was also partially supported by the Cornell Center for Materials Research with funding from the NSF MRSEC program (DMR-1719875) for the low-temperature studies. This work was performed in part at Cornell NanoScale Facility, an NNCI member supported by NSF Grant NNCI-1542081. We also thank the David and Lucille Packard Fellowship and a Sloan Fellowship (K.F.M.) for support and G. Stiehl for fruitful discussions on the crystal symmetry properties of multilayer Td-WTe2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.K. and T.L. fabricated the devices. E.S., T.L. and K.K. developed the experimental set-up and performed the measurements. K.K., T.L. and K.F.M. analysed the data. J.S. and K.F.M. developed the model and wrote the paper. All the authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figures 1–7, Supplementary Tables 1,2, Supplementary Notes 1–5, Supplementary References 1–3
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, K., Li, T., Sohn, E. et al. Nonlinear anomalous Hall effect in few-layer WTe2. Nat. Mater. 18, 324–328 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-019-0294-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-019-0294-7
This article is cited by
-
Real space characterization of nonlinear hall effect in confined directions
npj Computational Materials (2024)
-
Room-temperature flexible manipulation of the quantum-metric structure in a topological chiral antiferromagnet
Nature Physics (2024)
-
Intrinsic supercurrent non-reciprocity coupled to the crystal structure of a van der Waals Josephson barrier
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Angle-resolved transport non-reciprocity and spontaneous symmetry breaking in twisted trilayer graphene
Nature Materials (2024)
-
A tunable room-temperature nonlinear Hall effect in elemental bismuth thin films
Nature Electronics (2024)