Abstract
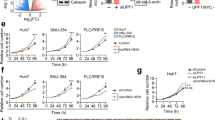
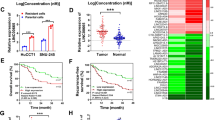
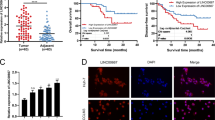
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common histological class of primary liver cancer with dismal prognosis. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are increasingly documented as participators in cancers. Present study aimed to explore the role of long intergenic nonprotein-coding RNA 467 (LINC00467) in HCC. LINC00467 was upregulated in HCC samples in TCGA database, and was confirmed to be elevated in HCC cell lines. Functionally, LINC00467 depletion impeded proliferation and invasion, induced apoptosis, and promoted cellular sensitivity to Axitinib in HCC. Mechanistically, LINC00467 performed as a sponge of microRNA (miR)-509-3p and upregulated the expression of platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA) in HCC cells. In conclusion, our study illustrated that LINC00467 promoted proliferation and invasion, impedes apoptosis, and contributed to Axitinib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma through miR-509-3p/PDGFRA, indicating LINC00467 as a promising biological target for HCC treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elserag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2557–76.
Liu K, Wu X, Zang X, Huang Z, Lin Z, Tan W, et al. TRAF4 regulates migration, invasion and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition via PI3K/AKT signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Res. 2017;25:1329–40.
Innes H, Barclay ST, Hayes PC, Fraser A, Dillon JF, Stanley A, et al. The risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients with hepatitis C and sustained viral response: role of the treatment regimen. J Hepatol. 2017;68:S0168827817324297.
Zhang B, Zhang X, Zhou T, Liu J. Clinical observation of liver cancer patients treated with axitinib and cabozantinib after failed sorafenib treatment: a case report and literature review. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16:215–8.
Chan SL, Yeo W, Mo F, Chan AWH, Koh J, Li L, et al. A phase 2 study of the efficacy and biomarker on the combination of transarterial chemoembolization and axitinib in the treatment of inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2017;123:3977–85.
Lin AY, Fisher G, So S, Tang C, Levitt L. A phase II study of imatinib mesylate (IM) in patients (pts) with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:4223.
Bartoschek M, Pietras K. PDGF family function and prognostic value in tumor biology. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;503:984–90.
Patel SH, Kneuertz PJ, Delgado M, Cohen C, Sarmiento J, Staley CA, et al. Association of tumor PDGFR-α and PDGFR-β expression and survival after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:220.
Lavorgna G, Vago R, Sarmini M, Montorsi F, Salonia A, Bellone M. Long non-coding RNAs as novel therapeutic targets in cancer. Pharmacol Res. 2016;110:131–8.
Schmitt A, Chang H. Long noncoding RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell. 2016;29:452–63.
Huang R, Wang X, Zhang W, Zhangyuan G, Jin K, Yu W, et al. Down-regulation of LncRNA DGCR5 correlates with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;40:707.
Pan Y, Li C, Chen J, Zhang K, Chu X, Wang R, et al. The emerging roles of long noncoding RNA ROR (lincRNA-ROR) and its possible mechanisms in human cancers. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;40:219–29.
Tang J, Zhuo H, Zhang X, Jiang R, Ji J, Deng L, et al. A novel biomarker Linc00974 interacting with KRT19 promotes proliferation and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e1549.
Yang H, Zhong Y, Xie H, Lai XB, Xu M, Nie Y, et al. Induction of the liver cancer-down-regulated long noncoding RNA uc002mbe.2 mediates trichostatin-induced apoptosis of liver cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013;85:1761–9.
Jiang M, Huang O, Xie Z, Wu S, Zhang X, Shen A, et al. A novel long non-coding RNA-ARA: adriamycin resistance associated. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014;87:254–83.
Atmadibrata B, Liu PY, Sokolowski N, Zhang L, Wong M, Tee AE, et al. The novel long noncoding RNA linc00467 promotes cell survival but is down-regulated by N-Myc. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e88112.
Chang Y, Yang L. LINC00467 promotes cell proliferation and stemness in lung adenocarcinoma by sponging miR-4779 and miR-7978. J Cell Biochem. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29510.
Li Z, Liu J, Chen H, Zhang Y, Shi H, Huang L, et al. Ferritin Light Chain (FTL) competes with long noncoding RNA Linc00467 for miR-133b binding site to regulate chemoresistance and metastasis of colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgz181.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97.
Wijnhoven BPL, Michael MZ, Watson DI. MicroRNAs and cancer. BJS. 2007;94:23–30.
Wang Y, Cao J, Zhang S, Sun L, Nan Y, Yao H, et al. MicroRNA-802 induces hepatitis B virus replication and replication through regulating SMARCE1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:783.
Chen EB, Zhou ZJ, Xiao K, Zhu GQ, Yang Y, Wang B, et al. The miR-561-5p/CX3CL1 signaling axis regulates pulmonary metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma involving CX3CR1+ natural killer cells infiltration. Theranostics. 2019;9:4779–94.
Pan Y, Robertson G, Pedersen L, Lim E, Hernandez-Herrera A, Rowat AC, et al. Correction: miR-509-3p is clinically significant and strongly attenuates cellular migration and multi-cellular spheroids in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8:17406.
Chen W, Du J, Li X, Su J, Huang Y, Ding N, et al. miR-509-3p promotes cisplatin-induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells through the regulation of anti-apoptotic genes. Pharmacogenomics. 2017;18:1671–82.
Du P, Luan X, Liao Y, Mu Y, Yuan Y, Xu J, et al. MicroRNA-509-3p inhibits cell proliferation and invasion via downregulation of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis in glioma. Oncol Lett. 2018;15:1307–12.
Kasahara R, Nakaigawa N, Kobayashi K. Complete response to sorafenib rechallenge in a patient with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Case Rep Oncol Med. 2017;2017:2648471.
Ehrhardt M, Craveiro RB, Velz J, Olschewski M, Casati A, Schönberger S, et al. The FDA approved PI3K inhibitor GDC-0941 enhances in vitro the anti-neoplastic efficacy of Axitinib against c-myc-amplified high-risk medulloblastoma. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22:2153–61.
Chen B, Zhao Q, Guan L, Lv H, Bie L, Huang J, et al. Long non-coding RNA NNT-AS1 sponges miR-424/E2F1 to promote the tumorigenesis and cell cycle progression of gastric cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22:4751–9
Chang S, Chen B, Wang X, Wu K, Sun Y. Long non-coding RNA XIST regulates PTEN expression by sponging miR-181a and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression. BMC cancer. 2017;17:248.
Garofalo M, Jeon YJ, Nuovo GJ, Middleton J, Secchiero P, Joshi P, et al. Correction: MiR-34a/c-dependent PDGFR-α/β downregulation inhibits tumorigenesis and enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in lung cancer. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0131729.
Peng Y, Guo JJ, Liu YM, Wu XL. MicroRNA-34A inhibits the growth, invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer by targeting PDGFR and MET expression. Biosci Rep. 2014;34:e00112.
Zhu K, Pan Q, Zhang X, Kong LQ, Fan J, Dai Z, et al. MiR-146a enhances angiogenic activity of endothelial cells in hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting PDGFRA expression. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34:2071–9.
Li GC, Xin L, Wang YS, Chen Y. Long intervening noncoding 00467 RNA contributes to tumorigenesis by acting as a competing endogenous RNA against miR-107 in cervical cancer cells. Am J Pathol. 2019;189:2293–310.
Labeur TA, van Vugt JLA, Ten Cate DWG, Takkenberg RB, JNM IJ, Groot Koerkamp B, et al. Body composition is an independent predictor of outcome in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib. Liver Cancer. 2019;8:255–70.
Labeur TA, Berhane S, Edeline J. Improved survival prediction and comparison of prognostic models for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib. Liver Int. 2020;40:215–28.
Fondevila F, Mendez-Blanco C. Anti-tumoral activity of single and combined regorafenib treatments in preclinical models of liver and gastrointestinal cancers. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51:109.
Li W, Wang Q, Feng Q, Wang F, Yan Q, Gao SJ, et al. Oncogenic KSHV-encoded interferon regulatory factor upregulates HMGB2 and CMPK1 expression to promote cell invasion by disrupting a complex lncRNA-OIP5-AS1/miR-218-5p network. PLoS Pathog. 2019;15:e1007578.
Tian W, Du Y, Ma Y, Gu L, Zhou J, Deng D. MALAT1-miR663a negative feedback loop in colon cancer cell functions through direct miRNA-lncRNA binding. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:857.
Xu J, Meng Q, Li X, Yang H, Xu J, Gao N, et al. Long non-coding RNA MIR17HG promotes colorectal cancer progression via miR-17-5p. Cancer Res. 2019;79:4882–95.
Acknowledgements
Thank you for all participators in this study.
Funding
This study was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (NO.: LH2019H077).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WL designed this study. WL and YH contributed to experiments and interpretation. WC, WM, and QF were responsible for the collection of experimental materials. HT and HG took charge of statistical analysis. WL, JZ, and PY wrote the article. Each author conduced to this study and provided valuable advice for this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., He, Y., Chen, W. et al. Knockdown of LINC00467 contributed to Axitinib sensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma through miR-509-3p/PDGFRA axis. Gene Ther 28, 634–645 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41434-020-0137-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41434-020-0137-9
This article is cited by
-
Machine learning-based disulfidptosis-related lncRNA signature predicts prognosis, immune infiltration and drug sensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
LINC00467 mediates the 5-fluorouracil resistance in breast cancer cells
In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Animal (2024)
-
A review on the role of LINC00467 in the carcinogenesis
Cancer Cell International (2022)
-
LINC00467: an oncogenic long noncoding RNA
Cancer Cell International (2022)