Abstract
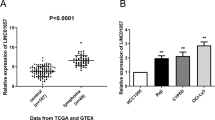
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have recently been reported to act as crucial regulators and prognostic biomarkers of human tumorigenesis. Based on microarray data, RP11-301G19.1 was previously identified as an upregulated lncRNA during B cell development. However, the effect of RP11-301G19.1 on multiple myeloma (MM) cells remains unclear. In the present study, the effects of RP11-301G19.1 on tumour progression were ascertained both in vitro and in vivo. Our results demonstrated that RP11-301G19.1 was upregulated in MM cell lines and that its downregulation inhibited the proliferation and cell cycle progression and promoted the apoptosis of MM cells. Bioinformatic analysis and luciferase reporter assay results revealed that RP11-301G19.1 can upregulate the miR-582-5p-targeted gene HMGB2 as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA). Furthermore, Western blot results indicated that RP11-301G19.1 knockdown decreased the levels of PI3K and AKT phosphorylation without affecting their total protein levels. Additionally, in a xenograft model of human MM, RP11-301G19.1 knockdown significantly inhibited tumour growth by downregulating HMGB2. Overall, our data demonstrated that RP11-301G19.1 is involved in MM cell proliferation by sponging miR-582-5p and may serve as a therapeutic target for MM.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Manasanch E, Munshi NC, Nooka AK, Rapoport AP, Smith EL, Vij R, et al. The Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer consensus statement on immunotherapy for the treatment of multiple myeloma. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8:e000734 https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2020-000734
Chiu E, Cabanero M, Sidhu G. Paradoxical stress fracture in a patient with multiple myeloma and bisphosphonate use. Cureus. 2020;12:e9837 https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.9837
Eckhert E, Hewitt R, Liedtke M. B-cell maturation antigen directed monoclonal antibody therapies for multiple myeloma. Immunotherapy. 2019;11:801–11. https://doi.org/10.2217/imt-2018-0199
Ntanasis-Stathopoulos I, Gavriatopoulou M, Kastritis E, Terpos E, Dimopoulos MA. Multiple myeloma: role of autologous transplantation. Cancer Treat Rev 2020;82:101929 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2019.101929
Chim CS, Kumar SK, Orlowski RZ, Cook G, Richardson PG, Gertz MA, et al. Management of relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma: novel agents, antibodies, immunotherapies and beyond. Leukemia 2018;32:252–62. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2017.329
Butova R, Vychytilova-Faltejskova P, Souckova A, Sevcikova S, Hajek R. Long non-coding RNAs in multiple myeloma. Noncoding RNA. 2019;5:13 https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna5010013
Sanchez Calle A, Kawamura Y, Yamamoto Y, Takeshita F, Ochiya T. Emerging roles of long non-coding RNA in cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018;109:2093–2100. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13642
Yang Y, Peng XW. The silencing of long non-coding RNA ANRIL suppresses invasion, and promotes apoptosis of retinoblastoma cells through the ATM-E2F1 signaling pathway. Biosci Rep. 2018;38:BSR20180558 https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20180558
Gao Y, Fang P, Li WJ, Zhang J, Wang GP, Jiang DF, et al. LncRNA NEAT1 sponges miR-214 to regulate M2 macrophage polarization by regulation of B7-H3 in multiple myeloma. Mol Immunol. 2020;117:20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2019.10.026
Chen X, Liu Y, Yang Z, Zhang J, Chen S, Cheng J. LINC01234 promotes multiple myeloma progression by regulating miR-124-3p/GRB2 axis. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11:6600–18
David A, Zocchi S, Talbot A, Choisy C, Ohnona A, Lion J, et al. The long non-coding RNA CRNDE regulates growth of multiple myeloma cells via an effect on IL6 signalling. Leukemia. 2020 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-020-01034-y
Lee YS, Dutta A. MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 2009;4:199–227. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pathol.4.110807.092222
Tang XJ, Wang W, Hann SS. Interactions among lncRNAs, miRNAs and mRNA in colorectal cancer. Biochimie 2019;163:58–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2019.05.010
Shen X, Kong S, Yang Q, Yin Q, Cong H, Wang X, et al. PCAT-1 promotes cell growth by sponging miR-129 via MAP3K7/NF-κB pathway in multiple myeloma. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24:3492–503. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15035
Yang N, Chen J, Zhang H, Wang X, Yao H, Peng Y, et al. LncRNA OIP5-AS1 loss-induced microRNA-410 accumulation regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by targeting KLF10 via activating PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway in multiple myeloma. Cell Death Dis 2017;8:e2975 https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.358
Petri A, Dybkær K, Bøgsted M, Thrue CA, Hagedorn PH, Schmitz A, et al. Long noncoding RNA expression during human B-cell development. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0138236 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0138236
Zhang X, Zhang Y, Yang J, Li S, Chen J. Upregulation of miR-582-5p inhibits cell proliferation, cell cycle progression and invasion by targeting Rab27a in human colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 2015;22:475–80. https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2015.44
Jin Y, Tao LP, Yao SC, Huang QK, Chen ZF, Sun YJ, et al. MicroRNA-582-5p suppressed gastric cancer cell proliferation via targeting AKT3. Eur Rev Med Pharm Sci. 2017;21:5112–20. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201711_13827
Li J, Gao J, Tian W, Li Y, Zhang J. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 drives gastric cancer progression by regulating HMGB2 modulating the miR-1297. Cancer Cell Int. 2017;17:44 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-017-0408-8
Han Q, Xu L, Lin W, Yao X, Jiang M, Zhou R, et al. Long noncoding RNA CRCMSL suppresses tumor invasive and metastasis in colorectal carcinoma through nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of HMGB2. Oncogene. 2019;38:3019–32. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0614-4
Pu J, Tan C, Shao Z, Wu X, Zhang Y, Xu Z, et al. Long noncoding RNA PART1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via targeting miR-590-3p/HMGB2 axis. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:9203–11. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S259962
Stros M, Ozaki T, Bacikova A, Kageyama H, Nakagawara A. HMGB1 and HMGB2 cell-specifically down-regulate the p53- and p73-dependent sequence-specific transactivation from the human Bax gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:7157–64. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110233200
National Research Council (US) Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. 8th ed. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2011. p. 11–104
Wang L, Park HJ, Dasari S, Wang S, Kocher JP, Li W. CPAT: Coding-Potential Assessment Tool using an alignment-free logistic regression model. Nucleic Acids Res 2013;41:e74 https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt006
Chen H, Li M, Xu N, Ng N, Sanchez E, Soof CM, et al. Serum B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) reduces binding of anti-BCMA antibody to multiple myeloma cells. Leuk Res. 2019;81:62–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2019.04.008
Liu D, Qiu M, Jiang L, Liu K. Long noncoding RNA HOXB-AS1 is upregulated in endometrial carcinoma and sponged miR-149-3p to upregulate Wnt10b. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020;19:1533033820967462 https://doi.org/10.1177/1533033820967462
Li QY, Chen L, Hu N, Zhao H. Long non-coding RNA FEZF1-AS1 promotes cell growth in multiple myeloma via miR-610/Akt3 axis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;103:1727–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.094
Handa H, Honma K, Oda T, Kobayashi N, Kuroda Y, Kimura-Masuda K, et al. Long noncoding RNA PVT1 is regulated by bromodomain protein BRD4 in multiple myeloma and is associated with disease progression. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:E7121 https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197121
Wang Y, Wang H, Ruan J, Zheng W, Yang Z, Pan W. Long non-coding RNA OIP5-AS1 suppresses multiple myeloma progression by sponging miR-27a-3p to activate TSC1 expression. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:155 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-01234-7
Pan Y, Zhang Y, Liu W, Huang Y, Shen X, Jing R, et al. LncRNA H19 overexpression induces bortezomib resistance in multiple myeloma by targeting MCL-1 via miR-29b-3p. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:106 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-1219-0
Yang X, Huang H, Wang X, Liu H, Liu H, Lin Z. Knockdown of lncRNA SNHG16 suppresses multiple myeloma cell proliferation by sponging miR-342-3p. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:38 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-1118-1
Li L, Ma L. Upregulation of miR-582-5p regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by targeting AKT3 in human endometrial carcinoma. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018;25:965–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs
Liu J, Liu S, Deng X, Rao J, Huang K, Xu G, et al. MicroRNA-582-5p suppresses non-small cell lung cancer cells growth and invasion via downregulating NOTCH1. PLoS ONE. 2019;14:e0217652 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0217652
Wang LL, Zhang M. miR-582-5p is a potential prognostic marker in human non-small cell lung cancer and functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting MAP3K2. Eur Rev Med Pharm Sci. 2018;22:7760–7. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201811_16397
Xu CH, Xiao LM, Liu Y, Chen LK, Zheng SY, Zeng EM, et al. The lncRNA HOXA11-AS promotes glioma cell growth and metastasis by targeting miR-130a-5p/HMGB2. Eur Rev Med Pharm Sci. 2019;23:241–52. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201901_16770
Wu ZB, Cai L, Lin SJ, Xiong ZK, Lu JL, Mao Y, et al. High-mobility group box 2 is associated with prognosis of glioblastoma by promoting cell viability, invasion, and chemotherapeutic resistance. Neuro Oncol 2013;15:1264–75. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/not078
Zhang P, Lu Y, Gao S. High-mobility group box 2 promoted proliferation of cervical cancer cells by activating AKT signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120:17345–53. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28998
Funding
This study was supported by the Graduate Research and Innovation Projects of Jiangsu Province (KYCX19_0114).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Luo, Y., Zhang, L. et al. The LncRNA RP11-301G19.1/miR-582-5p/HMGB2 axis modulates the proliferation and apoptosis of multiple myeloma cancer cells via the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway. Cancer Gene Ther 29, 292–303 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-021-00309-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-021-00309-5
This article is cited by
-
Single-cell and spatial architecture of primary liver cancer
Communications Biology (2023)
-
Ablation of VLA4 in multiple myeloma cells redirects tumor spread and prolongs survival
Scientific Reports (2022)