Abstract
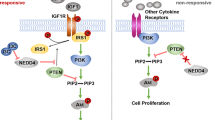
ING3 is a potential candidate tumor-suppressor gene that has been implicated in the pathogenesis of various cancers, however the exact role and mechanism of ING3 in gastric cancer (GC) remains elusive. In this study, the low expression of ING3 was validated in GC tissues and various GC cell lines. Overexpression of ING3 by transfection with pEGFP-ING3 plasmids inhibited cell proliferation in SGC-7901 and BGC-825 cells, concomitant with the decrease in the expression of PCNA, a marker for cell proliferation. Furthermore, overexpression of ING3-induced cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase. Meanwhile, elevation of ING3 distinctly aggravated cell apoptosis and increased Bax and Caspase-3 expression, but decreased Bcl-2 expression. Moreover, ING3 upregulation inhibited the activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway by reducing the expressions of p-PI3K and p-Akt in GC cells. Notably, preconditioning with IGF-1, a PI3K/Akt agonist, reversed the suppressive effects of ING3 overexpression on GC cell growth, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Furthermore, IGF-1 attenuated the inhibitory effect of excessive ING3 on CyclinD1 expression. Taken together, these results suggest ING3 may function as a tumor-suppressor gene in the progression of GC. Therefore, ING3 could serve as a potential therapeutic strategy for the treatment of GC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feng Y, Li L, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Liang Y, Lv J, et al. Hematopoietic pre-B cell leukemia transcription factor interacting protein is overexpressed in gastric cancer and promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Cancer Sci. 2015;106:1313–22.
Xu Y, Zhao F, Wang Z, Song Y, Luo Y, Zhang X, et al. MicroRNA-335 acts as a metastasis suppressor in gastric cancer by targeting Bcl-w and specificity protein 1. Oncogene. 2012;31:1398–407.
Guo H, Xia B. Collapsin response mediator protein 4 isoforms (CRMP4a and CRMP4b) have opposite effects on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:565.
Wadhwa R, Taketa T, Sudo K, Blum MA, Ajani JA. Modern oncological approaches to gastric adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2013;42:359–69.
Gunduz E, Gunduz M, Beder LB, Tamamura R, Nagatsuka H, Nagai N. Inhibitor of growth (ING) family: an emerging molecular target for cancer therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2008;17:275–84.
Li Y, Chen H, Hardy TM, Tollefsbol TO. Epigenetic regulation of multiple tumor-related genes leads to suppression of breast tumorigenesis by dietary genistein. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e54369–e54369.
Unoki M, Kumamoto K, Takenoshita S, Harris CC. Reviewing the current classification of inhibitor of growth family proteins. Cancer Sci. 2009;100:1173–9.
Unoki M, Kumamoto K, Harris CC. ING proteins as potential anticancer drug targets. Curr Drug Targets. 2009;10:442–54.
Almami A, Hegazy SA, Nabbi A, Alshalalfa M, Salman A, Abou-Ouf H, et al. ING3 is associated with increased cell invasion and lethal outcome in ERG-negative prostate cancer patients. Tumour Biol. 2016;37:9731–8.
He GH, Helbing CC, Wagner MJ, Sensen CW, Riabowol K. Phylogenetic analysis of the ING family of PHD finger proteins. Mol Biol Evol. 2005;22:104–16.
Gunduz M, Beder LB, Gunduz E, Nagatsuka H, Fukushima K, Pehlivan D, et al. Downregulation of ING3 mRNA expression predicts poor prognosis in head and neck cancer. Cancer Sci. 2008;99:531–8.
Wang Y, Dai DL, Martinka M, Li G. Prognostic significance of nuclear ING3 expression in human cutaneous melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:4111–6.
Yang HY, Liu HL, Tian LT, Song RP, Song X, Yin DL, et al. Expression and prognostic value of ING3 in human primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp Biol Med. 2012;237:352–61.
Lu M, Chen F, Wang Q, Wang K, Pan Q, Zhang X. Downregulation of inhibitor of growth 3 is correlated with tumorigenesis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2012;4:47–52.
Nabbi A, McClurg UL, Thalappilly S, Almami A, Mobahat M, Bismar TA, et al. ING3 promotes prostate cancer growth by activating the androgen receptor. BMC Med. 2017;15:103.
Li D, Qu X, Hou K, Zhang Y, Dong Q, Teng Y, et al. PI3K/Akt is involved in bufalin-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. Anti Cancer Drugs. 2009;20:59–64.
Yuan ZQ, Sun M, Feldman RI, Wang G, Ma X, Jiang C, et al. Frequent activation of AKT2 and induction of apoptosis by inhibition of phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase/Akt pathway in human ovarian cancer. Oncogene. 2000;19:2324–30.
Harashima N, Inao T, Imamura R, Okano S, Suda T, Harada M. Roles of the PI3K/Akt pathway and autophagy in TLR3 signaling-induced apoptosis and growth arrest of human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2012;61:667–76.
Lu XX, Cao LY, Chen X, Xiao J, Zou Y, Chen Q. PTEN inhibits cell proliferation, promotes cell apoptosis, and induces cell cycle arrest via downregulating the PI3K/AKT/HTERT pathway in lung adenocarcinoma A549 Cells. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:1–8.
Zheng HC, Sun JM, Wei ZL, Yang XF, Zhang YC, Xin Y. Expression of Fas ligand and caspase-3 contributes to formation of immune escape in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2003;9:1415–20.
Wu JH, Yao YL, Gu T, Wang ZY, Pu XY, Sun WW, et al. MiR-421 regulates apoptosis of BGC-823 gastric cancer cells by targeting caspase-3. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15:5463–8.
Fadlelmola FM, Zhou M, Leeuw RJD, Dosanjh NS, Harmer K, Huntsman D, et al. Sub-megabase resolution tiling (SMRT) array-based comparative genomic hybridization profiling reveals novel gains and losses of chromosomal regions in Hodgkin Lymphoma and Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma cell lines. Mol Cancer. 2008;7:2.
Wang Y, Li G. ING3 promotes UV-induced apoptosis via Fas/Caspase-8 pathway in melanoma cells. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:11887–93.
Czyzewska J, Guzińska-Ustymowicz K, Pryczynicz A, Kemona A, Bandurski R. Immunohistochemical evaluation of Ki-67, PCNA and MCM2 proteins proliferation index (PI) in advanced gastric cancer. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2009;47:289–96.
Zhou RP, Chen G, Shen ZL, Pan LQ. Cinobufacin suppresses cell proliferation via miR-494 in BGC- 823 gastric cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15:1241–5.
Peso LD. Apoptosis and cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 2000;2:180–90.
Hu YQ, Wang J, Wu JH. Administration of resveratrol enhances cell-cycle arrest followed by apoptosis in DMBA-induced skin carcinogenesis in male Wistar rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016;20:2935–46.
Luo J, Manning BD, Cantley LC. Targeting the PI3K-Akt pathway in human cancer: rationale and promise. Cancer Cell. 2003;4:257–62.
Hennessy BT, Smith DL, Ram PT, Lu Y, Mills GB. Exploiting the PI3K/AKT pathway for cancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4:988–1004.
Dreesen O, Brivanlou AH. Signaling pathways in cancer and embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Rev. 2007;3:7–17.
Wu YR, Qi HJ, Deng DF, Luo YY, Yang SL. MicroRNA-21 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and resistance to apoptosis through PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in esophageal cancer. Tumor Biol. 2016;37:12061–70.
Chang F, Lee JT, Navolanic PM, Steelman LS, Shelton JG, Blalock WL, et al. Involvement of PI3K|[sol]|Akt pathway in cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and neoplastic transformation: a target for cancer chemotherapy. Leukemia. 2003;17:590–603.
Zhou C, Qiu L, Sun Y, Healey S, Wanebo H, Kouttab N, et al. Inhibition of EGFR/PI3K/AKT cell survival pathway promotes TSA’s effect on cell death and migration in human ovarian cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2006;29:269–78.
Singh BN, Kumar D, Shankar S, Srivastava RK. Rottlerin induces autophagy which leads to apoptotic cell death through inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in human pancreatic cancer stem cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;84:1154–63.
Acknowledgements
Financial support was provided by the Foundation of the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University (2011BS018, 2012BS0113), Heilongjiang Postdoctoral Research Starting Foundation (LBH-Q14122), Heilongjiang Natural Science Foundation of China (H201349).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, S., Wang, L., Zhang, C. et al. Inhibitor of growth 3 induces cell death by regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by blocking the PI3K/AKT pathway. Cancer Gene Ther 25, 240–247 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-018-0023-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-018-0023-4