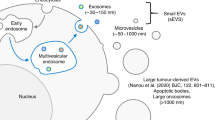
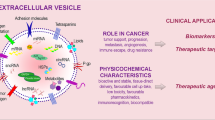
Abstract
To increase cancer patient survival and wellbeing, diagnostic assays need to be able to detect cases earlier, be applied more frequently, and preferably before symptoms develop. The expansion of blood biopsy technologies such as detection of circulating tumour cells and cell-free DNA has shown clinical promise for this. Extracellular vesicles released into the blood from tumour cells may offer a snapshot of the whole of the tumour. They represent a stable and multifaceted complex of a number of different types of molecules including DNA, RNA and protein. These represent biomarker targets that can be collected and analysed from blood samples, offering great potential for early diagnosis. In this review we discuss the benefits and challenges of the use of extracellular vesicles in this context and provide recommendations on where this developing field should focus their efforts to bring future success.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
N/A.
References
Cancer Research UK. Cancer Research UK Ovarian cancer survival statistics [Internet]. 2015. https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/statistics-by-cancer-type/ovarian-cancer/survival.
Torre LA, Trabert B, DeSantis CE, Miller KD, Samimi G, Runowicz CD, et al. Ovarian cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:284–96.
Cancer Research UK. Cancer Research UK Lung cancer survival statistics [Internet]. 2015. https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/statistics-by-cancer-type/lung-cancer/survival.
Hüsemann Y, Geigl JB, Schubert F, Musiani P, Meyer M, Burghart E, et al. Systemic spread is an early step in breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 2008;13:58–68.
Attiyeh FF, Jensen M, Huvos AG, Fracchia A. Axillary micrometastasis and macrometastasis in carcinoma of the breast. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1977;144:839–42.
World Health Organisation. World Heath Organisation Cancer Health Topics [Internet]. 2021. https://www.who.int/health-topics/cancer.
NHS. NHS Long Term Plan for Cancer [Internet]. 2021. https://www.longtermplan.nhs.uk/areas-of-work/cancer/.
England NHS. NHS Rapid Diagnostics Centres Vision and Implementation Specification [Internet]. 2021. https://www.england.nhs.uk/publication/rapid-diagnostic-centres-vision-and-2019-20-implementation-specification/.
Al-Nedawi K, Meehan B, Micallef J, Lhotak V, May L, Guha A, et al. Intercellular transfer of the oncogenic receptor EGFRvIII by microvesicles derived from tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:619–24.
Di Vizio D, Kim J, Hager MH, Morello M, Yang W, Lafargue CJ, et al. Oncosome formation in prostate cancer: association with a region of frequent chromosomal deletion in metastatic disease. Cancer Res. 2009;69:5601–9.
Zhang H, Freitas D, Kim HS, Fabijanic K, Li Z, Chen H, et al. Identification of distinct nanoparticles and subsets of extracellular vesicles by asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20:332–43.
Witwer KW, Buzás EI, Bemis LT, Bora A, Lässer C, Lötvall J, et al. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J Extracell Vesicles [Internet]. 2013. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v2i0.20360.
Théry C, Witwer KW, Aikawa E, Alcaraz MJ, Anderson JD, Andriantsitohaina R, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7:1535750.
Yáñez-Mó M, Siljander PR-M, Andreu Z, Zavec AB, Borràs FE, Buzas EI, et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:27066.
Becker A, Thakur BK, Weiss JM, Kim HS, Peinado H, Lyden D. Extracellular vesicles in cancer: cell-to-cell mediators of metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2016;30:836–48.
Caby M-P, Lankar D, Vincendeau-Scherrer C, Raposo G, Bonnerot C. Exosomal-like vesicles are present in human blood plasma. Int Immunol. 2005;17:879–87.
Deep G, Jain A, Kumar A, Agarwal C, Kim S, Leevy WM, et al. Exosomes secreted by prostate cancer cells under hypoxia promote matrix metalloproteinases activity at pre-metastatic niches. Mol Carcinog. 2020;59:323–32.
Jung T, Castellana D, Klingbeil P, Cuesta Hernández I, Vitacolonna M, Orlicky DJ, et al. CD44v6 dependence of premetastatic niche preparation by exosomes. Neoplasia. 2009;11:1093–105.
Rabinowits G, Gerçel-Taylor C, Day JM, Taylor DD, Kloecker GH. Exosomal microRNA: a diagnostic marker for lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009;10:42–6.
Hurwitz SN, Rider MA, Bundy JL, Liu X, Singh RK, Meckes DG Jr. Proteomic profiling of NCI-60 extracellular vesicles uncovers common protein cargo and cancer type-specific biomarkers. Oncotarget. 2016;7:86999–7015.
Salvianti F, Gelmini S, Costanza F, Mancini I, Sonnati G, Simi L, et al. The pre-analytical phase of the liquid biopsy. N Biotechnol. 2020;55:19–29.
Ignatiadis M, Rack B, Rothé F, Riethdorf S, Decraene C, Bonnefoi H, et al. Liquid biopsy-based clinical research in early breast cancer: The EORTC 90091-10093 Treat CTC trial. Eur J Cancer. 2016;63:97–104.
Cheng L, Sharples RA, Scicluna BJ, Hill AF. Exosomes provide a protective and enriched source of miRNA for biomarker profiling compared to intracellular and cell-free blood. J Extracell Vesicles [Internet]. 2014. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v3.23743.
Jin Y, Chen K, Wang Z, Wang Y, Liu J, Lin L, et al. DNA in serum extracellular vesicles is stable under different storage conditions. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:753.
Dragovic RA, Gardiner C, Brooks AS, Tannetta DS, Ferguson DJP, Hole P, et al. Sizing and phenotyping of cellular vesicles using Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis. Nanomedicine. 2011;7:780–8.
Li M, Zeringer E, Barta T, Schageman J, Cheng A, Vlassov AV. Analysis of the RNA content of the exosomes derived from blood serum and urine and its potential as biomarkers. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci [Internet]. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2013.0502.
Nanou A, Miller MC, Zeune LL, de Wit S, Punt CJA, Groen HJM, et al. Tumour-derived extracellular vesicles in blood of metastatic cancer patients associate with overall survival. Br J Cancer. 2020;122:801–11.
Trapp E, Janni W, Schindlbeck C, Jückstock J, Andergassen U, de Gregorio A, et al. Presence of circulating tumor cells in high-risk early breast cancer during follow-up and prognosis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2019;111:380–7.
Buscail E, Alix-Panabières C, Quincy P, Cauvin T, Chauvet A, Degrandi O, et al. High clinical value of liquid biopsy to detect circulating tumor cells and tumor exosomes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients eligible for up-front surgery. Cancers [Internet]. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111656.
Malentacchi F, Pizzamiglio S, Verderio P, Pazzagli M, Orlando C, Ciniselli CM, et al. Influence of storage conditions and extraction methods on the quantity and quality of circulating cell-free DNA (ccfDNA): the SPIDIA-DNAplas External Quality Assessment experience. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2015;53:1935–42.
Castellanos-Rizaldos E, Grimm DG, Tadigotla V, Hurley J, Healy J, Neal PL, et al. Exosome-based detection of EGFR T790M in plasma from non-small cell lung cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:2944–50.
Möhrmann L, Huang HJ, Hong DS, Tsimberidou AM, Fu S, Piha-Paul SA, et al. Liquid biopsies using plasma exosomal nucleic acids and plasma cell-free DNA compared with clinical outcomes of patients with advanced cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:181–8.
Bernard V, Kim DU, San Lucas FA, Castillo J, Allenson K, Mulu FC, et al. Circulating nucleic acids are associated with outcomes of patients with pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:108–18.
Garcia-Murillas I, Chopra N, Comino-Méndez I, Beaney M, Tovey H, Cutts RJ, et al. Assessment of molecular relapse detection in early-stage breast cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5:1473–8.
Morad G, Carman CV, Hagedorn EJ, Perlin JR, Zon LI, Mustafaoglu N, et al. Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles breach the intact blood-brain barrier via transcytosis. ACS Nano. 2019;13:13853–65.
Thind A, Wilson C. Exosomal miRNAs as cancer biomarkers and therapeutic targets. J Extracell Vesicles. 2016;5:31292.
Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C. MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2008;110:13–21.
Skog J, Würdinger T, van Rijn S, Meijer DH, Gainche L, Sena-Esteves M, et al. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:1470–6.
Hu D, Zhan Y, Zhu K, Bai M, Han J, Si Y, et al. Plasma exosomal long non-coding RNAs serve as biomarkers for early detection of colorectal cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51:2704–15.
Li Y, Zhao J, Yu S, Wang Z, He X, Su Y, et al. Extracellular vesicles long RNA sequencing reveals abundant mRNA, circRNA, and lncRNA in human blood as potential biomarkers for cancer diagnosis. Clin Chem. 2019;65:798–808.
Xu J, Ji L, Liang Y, Wan Z, Zheng W, Song X, et al. CircRNA-SORE mediates sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by stabilizing YBX1. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5:298.
Yuasa I, Ohno K, Hashimoto K, Iijima K, Yamashita K, Takeshita K. Carbohydrate-deficient glycoprotein syndrome: electrophoretic study of multiple serum glycoproteins. Brain Dev. 1995;17:13–9.
Kral J, Korenkova V, Novosadova V, Langerova L, Schneiderova M, Liska V, et al. Expression profile of miR-17/92 cluster is predictive of treatment response in rectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2018;39:1359–67.
Chen WW, Balaj L, Liau LM, Samuels ML, Kotsopoulos SK, Maguire CA, et al. BEAMing and droplet digital PCR analysis of mutant IDH1 mRNA in glioma patient serum and cerebrospinal fluid extracellular vesicles. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2013;2:e109.
Arroyo JD, Chevillet JR, Kroh EM, Ruf IK, Pritchard CC, Gibson DF, et al. Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011;108:5003–8.
Li K, Rodosthenous RS, Kashanchi F, Gingeras T, Gould SJ, Kuo LS, et al. Advances, challenges, and opportunities in extracellular RNA biology: insights from the NIH exRNA Strategic Workshop. JCI Insight [Internet]. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.98942.
Balaj L, Lessard R, Dai L, Cho Y-J, Pomeroy SL, Breakefield XO, et al. Tumour microvesicles contain retrotransposon elements and amplified oncogene sequences. Nat Commun. 2011;2:180.
Lázaro-Ibáñez E, Sanz-Garcia A, Visakorpi T, Escobedo-Lucea C, Siljander P, Ayuso-Sacido A, et al. Different gDNA content in the subpopulations of prostate cancer extracellular vesicles: apoptotic bodies, microvesicles, and exosomes. Prostate. 2014;74:1379–90.
Kahlert C, Melo SA, Protopopov A, Tang J, Seth S, Koch M, et al. Identification of double-stranded genomic DNA spanning all chromosomes with mutated KRAS and p53 DNA in the serum exosomes of patients with pancreatic cancer. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:3869–75.
Lee TH, Chennakrishnaiah S, Audemard E, Montermini L, Meehan B, Rak J. Oncogenic ras-driven cancer cell vesiculation leads to emission of double-stranded DNA capable of interacting with target cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;451:295–301.
Thakur BK, Zhang H, Becker A, Matei I, Huang Y, Costa-Silva B, et al. Double-stranded DNA in exosomes: a novel biomarker in cancer detection. Cell Res. 2014;24:766–9.
Yamamoto H, Watanabe Y, Oikawa R, Morita R, Yoshida Y, Maehata T, et al. BARHL2 methylation using gastric wash DNA or gastric juice exosomal DNA is a useful marker For early detection of gastric cancer in an H. pylori-independent manner. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2016;7:e184.
Moon P-G, Lee J-E, Cho Y-E, Lee SJ, Chae YS, Jung JH, et al. Fibronectin on circulating extracellular vesicles as a liquid biopsy to detect breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7:40189–99.
Melo SA, Luecke LB, Kahlert C, Fernandez AF, Gammon ST, Kaye J, et al. Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2015;523:177–82.
Niu L, Song X, Wang N, Xue L, Song X, Xie L. Tumor-derived exosomal proteins as diagnostic biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2019;110:433–42.
Mathivanan S, Lim JWE, Tauro BJ, Ji H, Moritz RL, Simpson RJ. Proteomics analysis of A33 immunoaffinity-purified exosomes released from the human colon tumor cell line LIM1215 reveals a tissue-specific protein signature. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010;9:197–208.
Mallegol J, van Niel G, Heyman M. Phenotypic and functional characterization of intestinal epithelial exosomes. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2005;35:11–6.
Yoh KE, Lowe CJ, Mahajan S, Suttmann R, Nguy T, Reichelt M, et al. Enrichment of circulating tumor-derived extracellular vesicles from human plasma. J Immunol Methods. 2021;490:112936.
Royo F, Théry C, Falcón-Pérez JM, Nieuwland R, Witwer KW. Methods for separation and characterization of extracellular vesicles: results of a worldwide survey performed by the ISEV rigor and standardization subcommittee. Cells [Internet]. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9091955.
Potts JL, Coppack SW, Fisher RM, Humphreys SM, Gibbons GF, Frayn KN. Impaired postprandial clearance of triacylglycerol-rich lipoproteins in adipose tissue in obese subjects. Am J Physiol. 1995;268:E588–94.
Scheer FAJL, Michelson AD, Frelinger AL 3rd, Evoniuk H, Kelly EE, McCarthy M, et al. The human endogenous circadian system causes greatest platelet activation during the biological morning independent of behaviors. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e24549.
Yuana Y, Sturk A, Nieuwland R. Extracellular vesicles in physiological and pathological conditions. Blood Rev. 2013;27:31–9.
Heijnen HF, Schiel AE, Fijnheer R, Geuze HJ, Sixma JJ. Activated platelets release two types of membrane vesicles: microvesicles by surface shedding and exosomes derived from exocytosis of multivesicular bodies and alpha-granules. Blood. 1999;94:3791–9.
Arraud N, Linares R, Tan S, Gounou C, Pasquet J-M, Mornet S, et al. Extracellular vesicles from blood plasma: determination of their morphology, size, phenotype and concentration. J Thromb Haemost. 2014;12:614–27.
Ayers L, Kohler M, Harrison P, Sargent I, Dragovic R, Schaap M, et al. Measurement of circulating cell-derived microparticles by flow cytometry: sources of variability within the assay. Thromb Res. 2011;127:370–7.
Coumans FAW, Brisson AR, Buzas EI, Dignat-George F, Drees EEE, El-Andaloussi S, et al. Methodological guidelines to study extracellular vesicles. Circ Res. 2017;120:1632–48.
Palviainen M, Saraswat M, Varga Z, Kitka D, Neuvonen M, Puhka M, et al. Extracellular vesicles from human plasma and serum are carriers of extravesicular cargo-Implications for biomarker discovery. PLoS ONE. 2020;15:e0236439.
Kalra H, Adda CG, Liem M, Ang C-S, Mechler A, Simpson RJ, et al. Comparative proteomics evaluation of plasma exosome isolation techniques and assessment of the stability of exosomes in normal human blood plasma. Proteomics. 2013;13:3354–64.
Gorgens A, El Andaloussi S, Wiklander O and Corso G. Composition for extracellular vesicle storage and formulation [Internet]. 2021. https://patents.justia.com/patent/20210069254.
UK Biobank. UK Biobank [Internet]. 2021. https://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/.
Chevillet JR, Kang Q, Ruf IK, Briggs HA, Vojtech LN, Hughes SM, et al. Quantitative and stoichiometric analysis of the microRNA content of exosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:14888–93.
Johnsen KB, Gudbergsson JM, Andresen TL, Simonsen JB. What is the blood concentration of extracellular vesicles? Implications for the use of extracellular vesicles as blood-borne biomarkers of cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2019;1871:109–16.
Forootan A, Sjöback R, Björkman J, Sjögreen B, Linz L, Kubista M. Methods to determine limit of detection and limit of quantification in quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR). Biomol Detect Quantif. 2017;12:1–6.
Rupert DLM, Claudio V, Lässer C, Bally M. Methods for the physical characterization and quantification of extracellular vesicles in biological samples. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017;1861:3164–79.
Maas SLN, de Vrij J, van der Vlist EJ, Geragousian B, van Bloois L, Mastrobattista E, et al. Possibilities and limitations of current technologies for quantification of biological extracellular vesicles and synthetic mimics. J Control Release. 2015;200:87–96.
Emons H. The “RM family”—Identification of all of its members. Accredit Qual Assur. 2006;10:690–1.
Valkonen S, van der Pol E, Böing A, Yuana Y, Yliperttula M, Nieuwland R, et al. Biological reference materials for extracellular vesicle studies. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017;98:4–16.
Geeurickx E, Tulkens J, Dhondt B, Van Deun J, Lippens L, Vergauwen G, et al. The generation and use of recombinant extracellular vesicles as biological reference material. Nat Commun. 2019;10:3288.
Geeurickx E, Hendrix A. Targets, pitfalls and reference materials for liquid biopsy tests in cancer diagnostics. Mol Asp Med. 2020;72:100828.
Geeurickx E, Lippens L, Rappu P, De Geest BG, De Wever O, Hendrix A. Recombinant extracellular vesicles as biological reference material for method development, data normalization and assessment of (pre-)analytical variables. Nat Protoc. 2021;16:603–33.
Ferguson S, Weissleder R. Modeling EV kinetics for use in early cancer detection. Adv Biosyst. 2020;4:e1900305.
Kowal J, Arras G, Colombo M, Jouve M, Morath JP, Primdal-Bengtson B, et al. Proteomic comparison defines novel markers to characterize heterogeneous populations of extracellular vesicle subtypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113:E968–77.
Martínez-Greene JA, Hernández-Ortega K, Quiroz-Baez R, Resendis-Antonio O, Pichardo-Casas I, Sinclair DA, et al. Quantitative proteomic analysis of extracellular vesicle subgroups isolated by an optimized method combining polymer-based precipitation and size exclusion chromatography. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10:e12087.
Bordanaba-Florit G, Royo F, Kruglik SG, Falcón-Pérez JM. Using single-vesicle technologies to unravel the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. Nat Protoc. 2021;16:3163–85.
Sina AAI, Vaidyanathan R, Dey S, Carrascosa LG, Shiddiky MJA, Trau M. Real time and label free profiling of clinically relevant exosomes. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30460.
Rojalin T, Koster HJ, Liu J, Mizenko RR, Tran D, Wachsmann-Hogiu S, et al. Hybrid nanoplasmonic porous biomaterial scaffold for liquid biopsy diagnostics using extracellular vesicles. ACS Sens. 2020;5:2820–33.
Lu J, Pang J, Chen Y, Dong Q, Sheng J, Luo Y, et al. Application of microfluidic chips in separation and analysis of extracellular vesicles in liquid biopsy for cancer. Micromachines (Basel) [Internet]. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10060390.
Reátegui E, van der Vos KE, Lai CP, Zeinali M, Atai NA, Aldikacti B, et al. Engineered nanointerfaces for microfluidic isolation and molecular profiling of tumor-specific extracellular vesicles. Nat Commun. 2018;9:175.
Mizutani K, Terazawa R, Kameyama K, Kato T, Horie K, Tsuchiya T, et al. Isolation of prostate cancer-related exosomes. Anticancer Res. 2014;34:3419–23.
Lopez CA, Daaboul GG, Vedula RS, Ozkumur E, Bergstein DA, Geisbert TW, et al. Label-free multiplexed virus detection using spectral reflectance imaging. Biosens Bioelectron. 2011;26:3432–7.
Fraikin J-L, Teesalu T, McKenney CM, Ruoslahti E, Cleland AN. A high-throughput label-free nanoparticle analyser. Nat Nanotechnol. 2011;6:308–13.
Tian Y, Gong M, Hu Y, Liu H, Zhang W, Zhang M, et al. Quality and efficiency assessment of six extracellular vesicle isolation methods by nano-flow cytometry. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020;9:1697028.
Arab T, Mallick ER, Huang Y, Dong L, Liao Z, Zhao Z, et al. Characterization of extracellular vesicles and synthetic nanoparticles with four orthogonal single-particle analysis platforms. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10:e12079.
Lobb RJ, Becker M, Wen SW, Wong CSF, Wiegmans AP, Leimgruber A, et al. Optimized exosome isolation protocol for cell culture supernatant and human plasma. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:27031.
Vagner T, Spinelli C, Minciacchi VR, Balaj L, Zandian M, Conley A, et al. Large extracellular vesicles carry most of the tumour DNA circulating in prostate cancer patient plasma. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7:1505403.
Dragovic RA, Southcombe JH, Tannetta DS, Redman CWG, Sargent IL. Multicolor flow cytometry and nanoparticle tracking analysis of extracellular vesicles in the plasma of normal pregnant and pre-eclamptic women. Biol Reprod. 2013;89:151.
Rozenblatt-Rosen O, Stubbington MJT, Regev A, Teichmann SA. The Human Cell Atlas: from vision to reality. Nature. 2017;550:451–3.
Turnbull C, Scott RH, Thomas E, Jones L, Murugaesu N, Pretty FB, et al. The 100 000 Genomes Project: bringing whole genome sequencing to the NHS. BMJ. 2018;361:k1687.
Gao GF, Parker JS, Reynolds SM, Silva TC, Wang L-B, Zhou W, et al. Before and after: comparison of legacy and harmonized TCGA genomic data commons’ data. Cell Syst. 2019;9:24–34.
Acknowledgements
None
Funding
RP, PS and DC are supported by UKRI. All supported by Oxford Brookes University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All helped write and edit the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
RP, EB, SB and DC have shares in MetaGuideX Ltd. PS declares no conflict of interest. DC has share options in Evox Therapeutics, working on exosome therapeutics.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
N/A.
Consent for publication
N/A.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pink, R.C., Beaman, EM., Samuel, P. et al. Utilising extracellular vesicles for early cancer diagnostics: benefits, challenges and recommendations for the future. Br J Cancer 126, 323–330 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-021-01668-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-021-01668-4
This article is cited by
-
Advanced extracellular vesicle bioinformatic nanomaterials: from enrichment, decoding to clinical diagnostics
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2023)
-
Single test-based diagnosis of multiple cancer types using Exosome-SERS-AI for early stage cancers
Nature Communications (2023)