Abstract
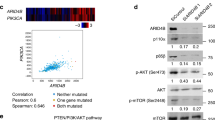
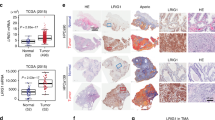
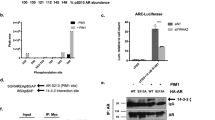
Activation and transcriptional reprogramming of AR in advanced prostate cancer frequently coincides with the loss of two tumor suppressors, INPP4B and PTEN, which are highly expressed in human and mouse prostate epithelium. While regulation of AR signaling by PTEN has been described by multiple groups, it is not known whether the loss of INPP4B affects AR activity. Using prostate cancer cell lines, we showed that INPP4B regulates AR transcriptional activity and the oncogenic signaling pathways Akt and PKC. Analysis of gene expression in prostate cancer patient cohorts showed a positive correlation between INPP4B expression and both AR mRNA levels and AR transcriptional output. Using an Inpp4b−/− mouse model, we demonstrated that INPP4B suppresses Akt and PKC signaling pathways and modulates AR transcriptional activity in normal mouse prostate. Remarkably, PTEN protein levels and phosphorylation of S380 were the same in Inpp4b−/− and WT males, suggesting that the observed changes were due exclusively to the loss of INPP4B. Our data show that INPP4B modulates AR activity in normal prostate and its loss contributes to the AR-dependent transcriptional profile in prostate cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fedele CG, Ooms LM, Ho M, Vieusseux J, O’Toole SA, Millar EK, et al. Inositol polyphosphate 4-phosphatase II regulates PI3K/Akt signaling and is lost in human basal-like breast cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:22231–6.
Gewinner C, Wang ZC, Richardson A, Teruya-Feldstein J, Etemadmoghadam D, Bowtell D, et al. Evidence that inositol polyphosphate 4-phosphatase type II is a tumor suppressor that inhibits PI3K signaling. Cancer Cell. 2009;16:115–25.
Hodgson MC, Shao LJ, Frolov A, Li R, Peterson LE, Ayala G, et al. Decreased expression and androgen regulation of the tumor suppressor gene INPP4B in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2011;71:572–82.
Hsu I, Yeh CR, Slavin S, Miyamoto H, Netto GJ, Tsai YC, et al. Estrogen receptor alpha prevents bladder cancer via INPP4B inhibited akt pathway in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget. 2014;5:7917–35.
Li Chew C, Lunardi A, Gulluni F, Ruan DT, Chen M, Salmena L, et al. In Vivo Role of INPP4B in tumor and metastasis suppression through regulation of PI3K-AKT signaling at endosomes. Cancer Discov. 2015;5:740–51.
Agoulnik IU, Hodgson MC, Bowden WA, Ittmann MM. INPP4B: the new kid on the PI3K block. Oncotarget. 2011;2:321–8.
Taylor BS, Schultz N, Hieronymus H, Gopalan A, Xiao Y, Carver BS, et al. Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer. Cancer Cell. 2010;18:11–22.
Kofuji S, Kimura H, Nakanishi H, Nanjo H, Takasuga S, Liu H, et al. INPP4B is a ptdins(3,4,5)p3 phosphatase that can act as a tumor suppressor. Cancer Discov. 2015;5:730–9.
Hodgson MC, Deryugina EI, Suarez E, Lopez SM, Lin D, Xue H, et al. INPP4B suppresses prostate cancer cell invasion. Cell Commun Signal. 2014;12:61.
Manning BD, Cantley LC. AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell. 2007;129:1261–74.
Chen M, Nowak DG, Trotman LC. Molecular pathways: PI3K pathway phosphatases as biomarkers for cancer prognosis and therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:3057–63.
Newton AC. Diacylglycerol’s affair with protein kinase C turns 25. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2004;25:175–7.
Newton AC. Regulation of the ABC kinases by phosphorylation: protein kinase C as a paradigm. Biochem J. 2003;370:11.
Creba JA, Downes CP, Hawkins PT, Brewster G, Michell RH, Kirk CJ. Rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in rat hepatocytes stimulated by vasopressin and other Ca2+-mobilizing hormones. Biochem J. 1983;212:15.
Nishizuka Y. The protein kinase c family and lipid mediators for transmembrane signaling and cell regulation. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2001;25:35–75.
Cornford P, Evans J, Dodson A, Parsons K, Woolfenden A, Neoptolemos J, et al. Protein kinase C isoenzyme patterns characteristically modulated in early prostate cancer. Am J Pathol. 1999;154:137–44.
Balk SP. Androgen receptor as a target in androgen-independent prostate cancer. Urology. 2002;60(3Suppl 1):132–8.
Yeh S, Tsai M-Y, Xu Q, Mu X-M, Lardy H, Huang K-E, et al. Generation and characterization of androgen receptor knockout (ARKO) mice: An in vivo model for the study of androgen functions in selective tissues. PNAS, Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2002;99:6.
Nakazawa M, Antonarakis ES, Luo J. Androgen receptor splice variants in the era of enzalutamide and abiraterone. Horm Cancer. 2014;5:265–73.
Antonarakis ES, Lu C, Wang H, Luber B, Nakazawa M, Roeser JC, et al. AR-V7 and resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone in prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1028–38.
Guo Z, Yang X, Sun F, Jiang R, Linn DE, Chen H, et al. A novel androgen receptor splice variant is up-regulated during prostate cancer progression and promotes androgen depletion-resistant growth. Cancer Res. 2009;69:2305–13.
Hu R, Lu C, Mostaghel EA, Yegnasubramanian S, Gurel M, Tannahill C, et al. Distinct transcriptional programs mediated by the ligand-dependent full-length androgen receptor and its splice variants in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2012;72:3457–62.
Lin HK, Hu YC, Yang L, Altuwaijri S, Chen YT, Kang HY, et al. Suppression versus induction of androgen receptor functions by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway in prostate cancer LNCaP cells with different passage numbers. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:50902–7.
Lin HK, Yeh S, Kang HY, Chang C. Akt suppresses androgen-induced apoptosis by phosphorylating and inhibiting androgen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:7200–5.
Taneja SS, Ha S, Swenson NK, Huang HY, Lee P, Melamed J, et al. Cell-specific regulation of androgen receptor phosphorylation in vivo. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:40916–24.
Carver BS, Chapinski C, Wongvipat J, Hieronymus H, Chen Y, Chandarlapaty S, et al. Reciprocal feedback regulation of PI3K and androgen receptor signaling in PTEN-deficient prostate cancer. Cancer Cell. 2011;19:575–86.
Ponguta LA, Gregory CW, French FS, Wilson EM. Site-specific androgen receptor serine phosphorylation linked to epidermal growth factor-dependent growth of castration-recurrent prostate cancer. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:20989–1001.
Tatin F, Varon C, Genot E, Moreau V. A signalling cascade involving PKC, Src and Cdc42 regulates podosome assembly in cultured endothelial cells in response to phorbol ester. J Cell Sci. 2006;119(Pt 4):769–81.
Guo Z, Dai B, Jiang T, Xu K, Xie Y, Kim O, et al. Regulation of androgen receptor activity by tyrosine phosphorylation. Cancer Cell. 2006;10:309–19.
Karaca M, Liu Y, Zhang Z, De Silva D, Parker JS, Earp HS, et al. Mutation of androgen receptor N-terminal phosphorylation site Tyr-267 leads to inhibition of nuclear translocation and DNA binding. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0126270.
Benavides F, Blando J, Perez CJ, Garg R, Conti CJ, DiGiovanni J, et al. Transgenic overexpression of PKCepsilon in the mouse prostate induces preneoplastic lesions. Cell Cycle. 2011;10:268–77.
Hafeez BB, Zhong W, Weichert J, Dreckschmidt NE, Jamal MS, Verma AK. Genetic ablation of PKC epsilon inhibits prostate cancer development and metastasis in transgenic mouse model of prostate adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2011;71:2318–27.
Saporita AJ, Zhang Q, Navai N, Dincer Z, Hahn J, Cai X, et al. Identification and characterization of a ligand-regulated nuclear export signal in androgen receptor. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:41998–2005.
Lopez SM, Agoulnik AI, Zhang M, Peterson LE, Suarez E, Gandarillas GA, et al. Nuclear receptor corepressor 1 expression and output declines with prostate cancer progression. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:3937–49.
Xu K, Wu ZJ, Groner AC, He HH, Cai C, Lis RT, et al. EZH2 oncogenic activity in castration-resistant prostate cancer cells is Polycomb-independent. Science. 2012;338:1465–9.
Krause WC, Shafi AA, Nakka M, Weigel NL. Androgen receptor and its splice variant, AR-V7, differentially regulate FOXA1 sensitive genes in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014;54:49–59.
Sahu B, Laakso M, Ovaska K, Mirtti T, Lundin J, Rannikko A, et al. Dual role of FoxA1 in androgen receptor binding to chromatin, androgen signalling and prostate cancer. EMBO J. 2011;30:3962–76.
Wang D, Garcia-Bassets I, Benner C, Li W, Su X, Zhou Y, et al. Reprogramming transcription by distinct classes of enhancers functionally defined by eRNA. Nature. 2011;474:390–4.
Lupien M, Eeckhoute J, Meyer CA, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Li W, et al. FoxA1 translates epigenetic signatures into enhancer-driven lineage-specific transcription. Cell. 2008;132:958–70.
Gao N, Zhang J, Rao MA, Case TC, Mirosevich J, Wang Y, et al. The role of hepatocyte nuclear factor-3 alpha (Forkhead Box A1) and androgen receptor in transcriptional regulation of prostatic genes. Mol Endocrinol. 2003;17:1484–507.
Gao N, Ishii K, Mirosevich J, Kuwajima S, Oppenheimer SR, Roberts RL, et al. Forkhead box A1 regulates prostate ductal morphogenesis and promotes epithelial cell maturation. Development. 2005;132:3431–43.
He B, Lanz RB, Fiskus W, Geng C, Yi P, Hartig SM, et al. GATA2 facilitates steroid receptor coactivator recruitment to the androgen receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:18261–6.
Guo ST, Chi MN, Yang RH, Guo XY, Zan LK, Wang CY, et al. INPP4B is an oncogenic regulator in human colon cancer. Oncogene. 2016;35:3049–61.
Lopez SM, Hodgson MC, Packianathan C, Bingol-Ozakpinar O, Uras F, Rosen BP, et al. Determinants of the tumor suppressor INPP4B protein and lipid phosphatase activities. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;440:277–82.
Ferron M, Boudiffa M, Arsenault M, Rached M, Pata M, Giroux S, et al. Inositol polyphosphate 4-phosphatase B as a regulator of bone mass in mice and humans. Cell Metab. 2011;14:466–77.
Wang XD, Wang BE, Soriano R, Zha J, Zhang Z, Modrusan Z, et al. Expression profiling of the mouse prostate after castration and hormone replacement: implication of H-cadherin in prostate tumorigenesis. Differentiation. 2007;75:219–34.
Sun S, Sprenger CC, Vessella RL, Haugk K, Soriano K, Mostaghel EA, et al. Castration resistance in human prostate cancer is conferred by a frequently occurring androgen receptor splice variant. J Clin Invest. 2010;120:2715–30.
Shafi AA, Putluri V, Arnold JM, Tsouko E, Maity S, Roberts JM, et al. Differential regulation of metabolic pathways by androgen receptor (AR) and its constitutively active splice variant, AR-V7, in prostate cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2015;6:31997–2012.
Jenster G, Trapman J, Brinkmann AO. Nuclear import of the human androgen receptor. Biochem J. 1993;293(Pt 3):761–8.
Kooijman EE, King KE, Gangoda M, Gericke A. Ionization properties of phosphatidylinositol polyphosphates in mixed model membranes. Biochemistry. 2009;48:9360–71.
Kim J, Choi YL, Vallentin A, Hunrichs BS, Hellerstein MK, Peehl DM, et al. Centrosomal PKCbetaII and pericentrin are critical for human prostate cancer growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2008;68:6831–9.
Patek S, Willder J, Heng J, Taylor B, Horgan P, Leung H, et al. Androgen receptor phosphorylation status at serine 578 predicts poor outcome in prostate cancer patients. Oncotarget. 2017;8:4875–87.
Gavrielides MV, Gonzalez-Guerrico AM, Riobo NA, Kazanietz MG. Androgens regulate protein kinase Cdelta transcription and modulate its apoptotic function in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66:11792–801.
Henttu P, Vihko AP. The protein kinase C activator, phorbol ester, elicits disparate functional responses in androgen-sensitive and androgen-independent human prostatic cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;224:5.
Wu D, Foreman TL, Gregory CW, McJilton MA, Wescott GG, Ford OH, et al. Protein kinase Cε has the potential to advance the recurrence of human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2002;62:7.
Darne C, Veyssiere G, Jean C. Phorbol ester causes ligand-independent activation of the androgen receptor. Eur J Biochem. 1998;256:9.
Mediwala SN, Sun H, Szafran AT, Hartig SM, Sonpavde G, Hayes TG, et al. The activity of the androgen receptor variant AR-V7 is regulated by FOXO1 in a PTEN-PI3K-AKT-dependent way. Prostate. 2013;73:267–77.
Li Y, Xie N, Gleave ME, Rennie PS, Dong X. AR-v7 protein expression is regulated by protein kinase and phosphatase. Oncotarget. 2015;6:12.
Garabedian MJ, Logan SK. Atypical regulation of SRC-3. Trends Biochem Sci. 2008;33:301–4.
Wu RC, Feng Q, Lonard DM, O’Malley BW. SRC-3 coactivator functional lifetime is regulated by a phospho-dependent ubiquitin time clock. Cell. 2007;129:1125–40.
Jo YS, Ryu D, Maida A, Wang X, Evans RM, Schoonjans K, et al. Phosphorylation of the nuclear receptor corepressor 1 by protein kinase B switches its corepressor targets in the liver in mice. Hepatology. 2015;62:1606–18.
Mahajan K, Challa S, Coppola D, Lawrence H, Luo Y, Gevariya H, et al. Effect of Ack1 tyrosine kinase inhibitor on ligand-independent androgen receptor activity. Prostate. 2010;70:1274–85.
Mahajan K, Coppola D, Challa S, Fang B, Chen YA, Zhu W, et al. Ack1 mediated AKT/PKB tyrosine 176 phosphorylation regulates its activation. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e9646.
Mulholland DJ, Tran LM, Li Y, Cai H, Morim A, Wang S, et al. Cell autonomous role of PTEN in regulating castration-resistant prostate cancer growth. Cancer Cell. 2011;19:792–804.
Wang S, Gao J, Lei Q, Rozengurt N, Pritchard C, Thomas JJGV, et al. Prostate-specific deletion of the murine Pten tumor suppressor gene leads to metastatic prostate cancer. Cancer Cell. 2003;4:209–21.
Lokody IB, Francis JC, Gardiner JR, Erler JT, Swain A. Pten regulates epithelial cytodifferentiation during prostate development. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0129470.
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:15545–50.
Hieronymus H, Lamb J, Ross KN, Peng XP, Clement C, Rodina A, et al. Gene expression signature-based chemical genomic prediction identifies a novel class of HSP90 pathway modulators. Cancer Cell. 2006;10:321–30.
Nelson PS, Clegg N, Arnold H, Ferguson C, Bonham M, White J, et al. The program of androgen-responsive genes in neoplastic prostate epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:11890–5.
Cancer Genome Atlas Research N. The molecular taxonomy of primary prostate. Cancer Cell. 2015;163:1011–25.
Zhang M, Krause WC, Agoulnik IU. Techniques for evaluation of AR transcriptional output and recruitment to DNA. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1786:219–36.
Hodgson MC, Vanostran G, Alghamdi S, Poppiti RJ, Agoulnik AI, Agoulnik IU. Reduced androgen receptor expression accelerates the onset of ERBB2 induced breast tumors in female mice. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e60455.
Guedes LB, Morais CL, Almutairi F, Haffner MC, Zheng Q, Isaacs JT, et al. Analytic validation of RNA in situ hybridization (RISH) for AR and AR-V7 expression in human prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:4651–63.
Hodgson MC, Deryugina EI, Suarez E, Lopez SM, Lin D, Xue H, et al. INPP4B suppresses prostate cancer cell invasion. Cell Commun Signal. 2014;12:61.
Funding
This work was supported by NCI grant R15 CA179287-01A1 (IUA), NCI grant P30CA125123 (CC), CPRIT grant RP150648 (NLW, CC), and CPRIT grant RP170005 (CC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Suarez, E., Vasquez, J.L. et al. Inositol polyphosphate 4-phosphatase type II regulation of androgen receptor activity. Oncogene 38, 1121–1135 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0498-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0498-3
This article is cited by
-
Cistrome and transcriptome analysis identifies unique androgen receptor (AR) and AR-V7 splice variant chromatin binding and transcriptional activities
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
INPP4B protects from metabolic syndrome and associated disorders
Communications Biology (2021)