Abstract
Objective
To better understand COVID-19 in newborns, we compared in-hospital illness severity indicators by COVID-19 status during birth hospitalization.
Study design
In a retrospective cohort of newborns born March–December 2020 in the Premier Healthcare Database Special COVID-19 Release, we classified COVID-19 status and severe illness indicators using ICD-CM-10 codes, laboratory data, and billing records. Illness severity indicators were compared by COVID-19 status, stratified by gestational age and race/ethnicity.
Result
Among 701,777 newborns, 209 had a COVID-19 diagnosis during the birth hospitalization. COVID-19 status differed significantly by race/ethnicity, gestational age, payor, and region. Late preterm/term newborns with COVID-19 had increased intensive care unit admission and sepsis risk; early preterm newborns with COVID-19 had increased risk for invasive ventilation. Risk for illness severity varied among racial/ethnic strata.
Conclusion
From March to December 2020, COVID-19 diagnosis in newborns was rare. More clinical data are needed to describe the risk profiles of newborns with COVID-19.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Few neonates (<28 days of age) with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) have been reported, and our understanding of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection and COVID-19 in neonates is limited. Early public health surveillance data suggested increased risk of more severe disease among infants (<1 year of age) compared with older children based on the increased rate of hospitalization among infants. In the United States, infants aged <1 year accounted for 62% of pediatric COVID-19 hospitalizations during February-April 2020, and infants aged <3 months accounted for 18.8% of pediatric COVID-19 hospitalizations during March–July 2020 [1, 2]. However, clinicians may have a lower risk threshold for hospital admission for infants, especially neonates, with symptoms consistent with SARS-CoV-2 infection; therefore, rate of hospitalization might not be an appropriate proxy for illness severity in this population [3, 4].
Emerging evidence suggests a low incidence of neonates infected with SARS-CoV-2 and neonates with SARS-CoV-2 infection have a relatively mild disease course, though severe disease (i.e., requiring intensive care and invasive ventilatory support) has been reported [5, 6]. A report of French national surveillance of children hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2 found that infants aged <90 days accounted for 37% of all pediatric COVID-19 hospitalizations; however, 97% of hospitalized infants aged <90 days did not have severe disease (defined as the need for ventilatory or hemodynamic support or death). Infants aged <90 days had the lowest rate of severe COVID-19 disease compared with older children (≥10 years) [7]. In a case series of infants who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 as outpatients in an emergency department in Greece and were admitted to a COVID-19 unit of the hospital, most patients had no symptoms besides hypertriglyceridemia, which occurred in only six of 14 infants; only one infant was reported to have mild respiratory distress [8]. These two studies reported 40% of hospitalized SARS-CoV-2 infected infants received antibiotics, suggesting that these infants may have been hospitalized due to a concern about potential bacterial infection before the source of their fever was known [7, 8].
Though transmission to neonates appears rare [9], it is still possible, and there are particular concerns for infants with immature immune systems. Due to the rarity of COVID-19 in newborns and the lack of studies with appropriate comparison groups, a knowledge gap exists related to the clinical severity of illness in newborns with COVID-19. By using a large U.S. electronic healthcare dataset, we sought to compare indicators of severe illness in newborns with and without COVID-19 diagnosed during the birth hospitalization.
Materials and methods
Data source
We performed a retrospective cohort analysis of birth hospitalizations using the Premier Healthcare Database Special COVID-19 Release (PHD-SR) (release date: March 29, 2021) (https://www.premierinc.com/). The PHD-SR is a “large, U.S. hospital-based, service-level, all-payer database that contains information on inpatient discharges, primarily from geographically diverse non-profit, non-governmental, community and teaching hospitals and health systems from rural and urban areas” that represents ~25% of annual U.S. inpatient admissions [10]. We included data from 609 hospitals reporting birth hospitalizations for newborns during March–December 2020.
Study population
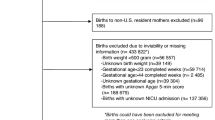
Birth hospitalizations were identified using International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) diagnostic codes (Supplementary Table). During March–December 2020, 704,779 birth hospitalizations were reported in the PHD-SR. We excluded one birth that occurred at a hospital with no patients diagnosed with COVID-19 in-hospital; 2,566 out-of-hospital births; and 435 duplicate birth records from 217 newborns. The resulting study sample included 701,777 births.
Measures and outcomes
COVID-19 during the birth hospitalization was based on documented ICD-10-CM code U07.1 (COVID-19, virus identified) during April–December 2020, ICD-10-CM code B97.29 (Other coronavirus as the cause of disease classified elsewhere) during March–April 2020 (before the COVID-19–specific U07.1 code was introduced) [11], or positive RNA laboratory test results for SARS-CoV-2 (available for a small portion of hospitals that reported laboratory data).
The following indicators of severe illness were assessed using ICD-10-CM and Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes: respiratory complications (pneumonia or respiratory distress), sepsis, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, invasive and noninvasive mechanical ventilation, and all-cause 30-day readmission to the same hospital system. ICU admission was defined as admission to an intensive care or step-down unit and identified using the hospital chargemaster records. Mechanical ventilation was identified through a combination of the hospital chargemaster records, ICD-10-CM procedure codes, and CPT codes and coded to represent the highest level of ventilatory support received (invasive vs noninvasive). Readmission was defined as any subsequent hospitalization in the same hospital system within 30 days of the birth hospitalization discharge. Respiratory complications and sepsis [12] were identified from ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes (Supplementary Table).
Newborn demographics (sex, race/ethnicity, and payor) and health characteristics (gestational age, small for gestational age, congenital anomalies, birth trauma, and discharge status) were described along with hospital characteristics (urbanicity and U.S. census region). Race and ethnicity were collected separately in the PHD-SR, but combined for this analysis: non-Hispanic White, non-Hispanic Black, Hispanic, and non-Hispanic Other/Unknown. Newborns who had unknown Hispanic origin were assumed to be non-Hispanic if race was available. The non-Hispanic Other/Unknown category includes persons who reported a race other than Black or White, including American Indian/Alaska Native, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, persons of more than one race, and persons with missing race. Gestational age and small for gestational age were defined using ICD-10-CM codes found on the newborn health record. Gestational weeks at the time of delivery are reported through ICD-10-CM codes for preterm newborns; newborns without an ICD-10-CM code for preterm birth were assumed to be born full-term (Supplementary Table). Gestational age strata of early preterm (<34 gestational weeks) and late preterm/full term (≥34 gestational weeks) were chosen to reflect the critical threshold at which the majority of infants would not routinely receive respiratory support nor require admission to an ICU after birth for prematurity [13, 14].
To define underlying health conditions (congenital anomalies and birth trauma), we used the Chronic Classification Software Refined (CCSR) to aggregate ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes into meaningful categories, which were then clinically reviewed (KW) to determine categories of conditions of interest that would reliably be identified at the birth hospitalization for newborns. The CCSR algorithm was developed and validated by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Congenital anomalies, both major and minor, include cardiac and circulatory, digestive, genitourinary, respiratory, and nervous system congenital anomalies as well as congenital malformations of eye, ear, face, or neck; musculoskeletal congenital conditions; and other and unspecified congenital anomalies. Birth trauma included birth injuries to the scalp, skeleton, or central or peripheral nervous system as well as intracranial laceration and hemorrhage due to birth injury (Supplementary Table 1) [15].
Discharge status was identified from the patient discharge status codes (home; other care [includes discharge/transfer to other facility]; other/unknown [left against medical advice, still a patient, and information not available]; and death/discharge to hospice). Respiratory complications (pneumonia or respiratory distress) and sepsis were defined using ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes (Supplementary Table).
Pearson chi-squared tests were used to assess differences in infant and hospital characteristics by COVID-19 diagnosis. Median length of stay was calculated overall and by gestational age and ICU admission. Levene’s test for homogeneity of variance was used to verify the assumption of equal variance. Wilcoxon rank sum tests were used to compare length of stay by COVID-19 status for the different gestational age and ICU admission strata. Poisson regression models with robust standard errors were used to calculate relative risks for outcomes, accounting for within-hospital correlation. Relative risks were estimated and stratified by gestational age then further stratified by race/ethnicity (non-Hispanic White, non-Hispanic Black, Hispanic, and non-Hispanic Other/Unknown). A priori significance level was set to p < 0.05. All analyses were performed in SAS® 9.4 (SAS Institute, Cary NC). Analytic code is available upon request to the first author.
To assess whether our results were sensitive to how we categorized race and ethnicity when Hispanic origin was unknown, we also tested categorizing newborns with unknown Hispanic origin as “Other/Unknown” and as “Hispanic” for the combined race/ethnicity variable. Relative risks were recalculated using the alternative definitions of race/ethnicity.
This activity was reviewed by CDC and was conducted consistent with applicable federal law and CDC policy; the activity was determined to meet the requirements of public health surveillance as defined in 45 CFR 46.102(l)(2).
Results
Among 701,777 newborns in 609 U.S. hospitals from March to December 2020, 49.0% were non-Hispanic White; 46.5% used Medicaid as the payor for the birth hospitalization; and 9.2% were born preterm (<37 gestational weeks). Most newborns (97.1%) were discharged home, and a small portion were transferred to other facilities (2.5%), died/were discharged to hospice (0.3%), or had another/unknown discharge status (0.1%). Overall, 87.0% of births occurred in urban hospitals and 45.2% in the Southern region of the United States (Table 1).
Overall, 209 (0.03%) newborns had a documented COVID-19 diagnosis during the birth hospitalization. A higher proportion of newborns with COVID-19 were Hispanic (27.3% vs. 15.1%), had Medicaid as the payor (56.0% vs. 46.5%), and were born preterm (<37 gestational weeks) (23.4% vs. 9.2%) compared to those without COVID-19. Compared with newborns without COVID-19, newborns with COVID-19 were also more frequently born early preterm (<34 gestational weeks) (11.0% vs. 2.4%) and were more frequently born in the Midwest (30.6% vs. 22.1%) and less frequently born in the West (12.4% vs. 18.4%). No differences in small for gestational age, congenital anomalies, or birth trauma were observed by COVID-19 status (Table 1). Overall, 69.9% of newborns with COVID-19 and 86.6% of newborns without COVID-19 at birth hospitalization had no indicators of severe illness (p = <0.0001).
In late preterm/term newborns, the risks for sepsis [adjusted risk ratio (aRR): 3.98; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.95–8.12] and ICU admission (aRR: 2.22; 95% CI: 1.27–3.86) were elevated in newborns with COVID-19 compared with those without a COVID-19 diagnosis, but 77.4% of late preterm/term newborns with COVID and 88.6% without COVID had no indicators of severe illness (p = <0.0001). Early preterm newborns (<34 gestational weeks) with COVID-19 were at greater risk for invasive ventilation compared with those without COVID-19 (aRR: 1.48; 95% CI: 1.16–1.89). (Fig. 1). Only 8.7% of early preterm newborns with COVID and 8.5% of those without COVID had no indicators of severe illness (p = 0.97).
Abbreviations: COVID-19 coronavirus disease 2019, CI confidence interval, ICU intensive care unit, RR risk ratio; adjusted RR adjusted risk ratio, uRR unadjusted risk ratio. *Denominators for each gestational age strata were: 21 for early preterm (<34 weeks) COVID-19; 188 for late preterm/full term (≥34 weeks) COVID-19; 12,193 for early preterm No COVID-19; and 689,375 late preterm/full term No COVID-19. **Premier Healthcare Database, 609 hospitals with delivery hospitalizations. †Outcomes are not mutually exclusive. §Adjusted for hospital to account for within facility correlation.
Among late preterm/term newborns, Hispanic newborns with COVID-19 had greater risk for respiratory complications (aRR: 2.54; 95% CI: 1.36–4.76) and ICU admission (aRR: 2.96; 95% CI:1.25–7.01) compared with Hispanic newborns without COVID-19. Non-Hispanic “Other/Unknown” race newborns with COVID-19 had elevated risks for ICU admission (aRR: 3.40; 95% CI:1.40–8.28), and non-Hispanic White late preterm/term newborns with COVID-19 had elevated risks for sepsis relative to those without COVID-19 (aRR: 4.83; 95% CI:1.74–13.4) (Fig. 2). Among early preterm newborns with COVID-19, non-Hispanic Black newborns with COVID-19 were at increased risk for respiratory complications (aRR: 1.36; 95% CI: 1.27–1.47) and any mechanical ventilation (aRR: 1.40; 95% CI: 1.23–1.61). Early preterm Hispanic newborns with COVID-19 were at higher risk for invasive ventilation (aRR: 1.78; 95% CI: 1.22–2.60), and non-Hispanic “Other/Unknown” race newborns with COVID-19 had elevated risks for respiratory complications (aRR: 1.39; 95% CI: 1.25–1.54), sepsis (aRR: 5.43; 95% CI: 2.75–10.7), any ventilation (aRR: 1.34; 95% CI: 1.22–1.47) and invasive ventilation (aRR: 2.27; 95% CI: 1.45–3.56) (Fig. 3).
Abbreviations: COVID-19 coronavirus disease 2019, CI confidence interval, ICU intensive care unit, RR risk ratio, adjusted RR adjusted risk ratio, uRR unadjusted risk ratio. Denominators for each race/ethnicity strata were: 77 for White COVID-19; 336450 for White no COVID-19; 27 for Black COVID-19; 88489 for Black no COVID-19; 50 for Hispanic COVID-19; 103747 for Hispanic no COVID-19; 32 for “Other/Unknown” COVID-19; 155965 for “Other/Unknown” no COVID-19. ||Premier Healthcare Database, 609 hospitals with delivery hospitalizations. *The non-Hispanic Other/Unknown category includes persons who reported a race other than Black or White, including American Indian/Alaska Native, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, persons of more than one race, and persons with missing race. †Outcomes are not mutually exclusive. §Adjusted for hospital to account for within facility correlation.
Abbreviations: COVID-19 coronavirus disease 2019, CI confidence interval, ICU intensive care unit, RR risk ratio, adjusted RR adjusted risk ratio; uRR unadjusted risk ratio. Denominators for each race/ethnicity strata were: 9 for White COVID-19; 7022 for White no COVID-19; 4 for Black COVID-19; 3842 for Black no COVID-19; 7 for Hispanic COVID-19; 2477 for Hispanic no COVID-19; 3 for “Other/Unknown” COVID-19; 3576 for “Other/Unknown” no COVID-19. *Premier Healthcare Database, 609 hospitals with delivery hospitalizations. **The non-Hispanic Other/Unknown category includes persons who reported a race other than Black or White, including American Indian/Alaska Native, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, persons of more than one race, and persons with missing race. †Outcomes are not mutually exclusive. §Adjusted for hospital to account for within facility correlation.
Overall, for newborns admitted to the ICU, median length of stay was significantly longer for those with COVID-19 [19.0 days, interquartile range (IQR): 6.0–40.0 days] than for those without COVID-19 (8.0 days, IQR: 3.0–19.0 days). The pattern for median length of stay was consistent regardless of gestational age (p < 0.0001) (Table 2).
Sensitivity analysis
When newborns with missing ethnicity were classified as Hispanic in the combined race/ethnicity variable, race/ethnicity no longer differed significantly by COVID-19 status (Table SA1). Among late preterm/term, Hispanic newborns were no longer at greater risk for respiratory complications or ICU admission, but their risk for sepsis was elevated (aRR: 4.94; CI 95%: 1.95–12.53). The risk for sepsis in non-Hispanic White newborns was no longer significant. The elevated risk for ICU admission (aRR: 2.65; CI 95%: 1.03–6.84) in non-Hispanic Black newborns reached the level of significance, and non-Hispanic “Other/Unknown” race newborns had increased risks for respiratory complications (aRR: 3.03; CI 95%: 1.04–8.84) and noninvasive ventilation (aRR: 4.25; CI 95%: 1.33–13.58) (Table SA2). Among early preterm, Hispanic newborns with COVID-19 had increased risks for respiratory complications (aRR: 1.24; CI 95%: 1.04–1.48), sepsis (aRR: 2.64; CI 95%: 1.17–5.95), any ventilation (aRR: 1.21; CI 95%: 1.01–1.44), and invasive ventilation (aRR: 1.71; CI 95%: 1.32–2.23). In non-Hispanic “Other/Unknown” race newborns, ICU admission was elevated (aRR: 1.05; CI 95%: 1.04–1.07) (Table SA2).
When newborns with missing ethnicity were classified as “non-Hispanic Other/Unknown” in the combined race/ethnicity variable, among late preterm/term, non-Hispanic White newborns with COVID-19 were no longer at an increased risk for sepsis (aRR: 2.12; 95% CI: 0.41–11.00), and non-Hispanic Black newborns were at an increased risk for ICU admission (aRR: 2.65; 95% CI: 1.03–6.84). The increased risk for ICU admission among newborns of “Other/Unknown” race/ethnicity was no longer statistically significant (aRR: 1.98; 95% CI: 0.73–5.39). Among early preterm, newborns of “Other/Unknown” race/ethnicity were at a slightly increased risk for ICU admission (aRR: 1.06; 95% CI:1.02–1.10) (Table SA3).
Discussion
In our cohort of 701,777 newborns, 0.03% (209) had a documented COVID-19 diagnosis during their birth hospitalization. Our results add data on newborns with a documented COVID-19 diagnosis at their birth hospitalization during March–December 2020. We observed that early preterm newborns with COVID-19 had an increased risk for invasive ventilation, and late preterm/term newborns had increased risks for ICU admission and sepsis when compared with newborns without COVID-19; no other elevated risks were observed. Overall, COVID-19 diagnosis during birth hospitalization was rare, and when it did occur, most late preterm/term newborns did not have respiratory complications or require ventilatory support.
Although few newborns had documentation of COVID-19, variations in testing practices throughout the course of the pandemic likely influenced identification of neonates with COVID-19. Testing all infants born to mothers with COVID-19 is recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) [16, 17]; however, universal screening for COVID-19 of mothers admitted for delivery depends on the local prevalence of COVID-19 and testing capacity. Therefore, 0.03% likely represents the minimum percentage of newborns with COVID-19 during the birth hospitalization in our sample.
We observed significantly more preterm newborns with COVID-19 relative to those without COVID-19; further, more newborns with COVID-19 were born early preterm. Though the rate of preterm birth appears to be higher in infants born to mothers with COVID-19 [9, 18, 19] the relationship between maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection and preterm birth requires further investigation. Prior studies have described higher percent positivity for SARS-CoV-2 infection among preterm newborns compared with term newborns [20]. It might be that preterm newborns are more susceptible to COVID-19 due to immature immunity or lung development. It is also possible that preterm newborns admitted to the ICU are more frequently tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection due to testing protocols on ICU admission.
Among late preterm/term newborns, the risks of ICU admission and sepsis were elevated for newborns with a COVID-19 diagnosis compared with those without, and among early preterm newborns, the risk for invasive ventilation was elevated. The elevated risk of ICU admission for gestationally older newborns may reflect hospital infection, prevention, and control practices and policies for caring for newborns with COVID-19 (e.g., recommendations against rooming-in and isolation in negative pressure room). This association was not observed in gestationally younger newborns likely due to the overall need for a higher level of care (i.e., NICU admission) for early preterm infants [14]. A systematic review reported increased odds of NICU admission for infants born to mothers with COVID-19 (odds ratio: 4.89; 95% CI: 1.87–12.81) regardless of gestational age [18]. The reason for ICU admission is not captured in the PHD-SR. Given the low sensitivity of sepsis ICD-10-CM codes [21] in combination with other evidence supporting that many infants aged <90 days with COVID-19 present with fever, we postulate the elevated risk of sepsis may be reflective of fevers among newborns with COVID-19. This could include culture-positive as well as presumed cases of sepsis. Further clinical data would be needed to assess the risk of sepsis among neonates.
Inequality in obstetric and prenatal care in the United States leads to racial and ethnic disparities in maternal morbidity and mortality as well as infant mortality, low birth weight, and preterm birth [22,23,24]. Newborns are not exempt from racial inequities that exist in healthcare; healthcare provider recognition of sepsis and approaches to treatment as well as patient access to healthcare services influence disparate racial outcomes in children [25], and early-onset sepsis disproportionately impacts non-Hispanic Black and preterm infants [26]. Differences in NICU quality of care have been found to disadvantage infants of color [27]. Consequently, we further stratified our results to examine risk for the illness severity indicators by race/ethnicity.
Our race-stratified risks were sensitive to the method of classifying race and ethnicity in the presence of missing data. The PHD-SR is subject to the limitations in the completeness and precision of race and ethnicity in administrative data sources [28,29,30]. In our sample, race was missing for 12.6% of newborns, and ethnicity was missing for 25.8% of newborns. Because missingness in race and ethnicity may occur nonrandomly in COVID-19 data [31], combined with the limitations of race and ethnicity in administrative data sources, our results might be subject to misclassification bias. Though early preterm newborns of other or unknown race/ethnicity had increased risk for respiratory complications, sepsis, any ventilation, and invasive ventilation, the heterogeneity of this strata of newborns limits the extrapolation of the findings to other populations. This categorization of race/ethnicity represents newborns with missing race/ethnicity as well as those from racial and ethnic backgrounds for which the number of cases were too small to describe alone, including Asian, Pacific Islander, and American Indian/Alaska Native newborns. Further study using data with larger samples of racial and ethnic minorities are needed to better understand the risk for severe illness from COVID-19 for newborns of racial and ethnic minorities.
Our results represent a cautious description of the risks for severe disease from COVID-19 in newborns during March 2020–December 2020; replication and further study in datasets with more granular clinical information are merited. The present study is subject to several additional limitations. First, our cohort was derived from a period of time when early variants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus were circulating. Future studies may examine changes in illness severity indicators during different periods with emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. Second, because infant and maternal health records cannot be linked in the PHD-SR, maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection status, maternal age, and cause of preterm birth or pregnancy complications that may place resulting infants at risk of these markers of illness severity are unknown. Third, because linkage across different hospital systems is not possible in the PHD-SR limiting our ability to link birth hospitalizations with subsequent care received from other providers, we focus solely on birth hospitalization; these results may not be generalizable to all neonates and older infants. As such, our estimates represent the minimum risk for same hospital readmission within 30 days. Fourth, our analysis relies on ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes as the primary identifier for COVID-19 (in combination with laboratory testing where available) as well as to define some illness severity indicators (respiratory complications and sepsis). The U07.1 code, used since March 2020, has been found to be highly specific and sensitive, and the more inclusive B07.29 code was only used to identify cases in March for this analysis [32]. ICD-10-CM codes used to define sepsis (Supplementary Table) are undercoded in administrative data, and our results may be underestimated [21]. Fifth, because newborns born to mothers with SARS-CoV-2 infection may not be tested for SARS-CoV-2 in addition to the limited availability of laboratory data in the PHD-SR, our study has likely underascertained newborns with COVID-19 [20]. Further, testing may be more frequent in infants who are symptomatic, thus biasing our results to sicker newborns.
Despite these limitations, we have described the risk for in-hospital illness severity indicators for newborns with COVID-19 with a robust comparison group of noninfected newborns using a large database of electronic health records from geographically diverse hospitals across the United States. Further study is needed to understand how maternity care practices and implementation and adherence to infection prevention and control practices influence the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in newborns.
Conclusions
From March to December 2020, COVID-19 diagnosis in newborns was rare. Our results suggest that late preterm/term newborns with a COVID-19 diagnosis might not have elevated risks for respiratory complications or mechanical ventilation, but may be at increased risk for sepsis and ICU admission; early preterm infants with COVID-19 might not be at an increased risk for respiratory complications and ICU admission, but may be at increased risk for invasive ventilation. The trends we observed for specific race/ethnicity categories requires replication in studies with granular clinical data. Further, future studies may examine changes in the risk profile of newborns with COVID-19.
Disclaimer
The findings and conclusions in this report are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official position of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention nor the U.S. Public Health Service Commissioned Corps.
References
Kim L, Whitaker M, O’Halloran A, Kambhampati A, Chai SJ, Reingold A, et al. Hospitalization rates and characteristics of children aged <18 years hospitalized with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 — COVID-NET, 14 states, March 1–July 25, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:1081–8.
CDC COVID-19 Response Team. . Coronavirus disease 2019 in children — United States, February 12–April 2, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:422–6.
Biondi EA, Byington CL. Evaluation and management of febrile, well-appearing young infants. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2015;29:575–85.
Biondi EA, McCulloh R, Staggs VS, Garber M, Hall M, Arana J, et al. Reducing variability in the infant sepsis evaluation (REVISE): a national quality initiative. Pediatrics.2019;144:e2018–201.
Chi H, Chiu NC, Tai YL, Chang HY, Lin CH, Sung YH, et al. Clinical features of neonates born to mothers with coronavirus disease-2019: a systematic review of 105 neonates. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2021;54:69–76.
Kim DH. Clinical implications of coronavirus disease 2019 in neonates. Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64:157–64.
Ouldali N, Yang DD, Madhi F, Levy M, Gaschignard J, Craiu I, et al. Factors associated with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection. Pediatrics. 2021;147:e2020023432.
Spoulou V, Noni M, Koukou D, Kossyvakis A, Michos A. Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in neonates and young infants. Eur J Pediatr. 2021;180:3041–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-021-04042-x
Mullins E, Hudak ML, Banerjee J, Getzlaff T, Townson J, Barnette K, et al. Pregnancy and neonatal outcomes of COVID-19: co-reporting of common outcomes from PAN-COVID and AAP SONPM registries. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2021;57:573–81.
Premier Healthcare Database (COVID-19): data that informs and performs: Premier Applied Sciences®, Premier; 2020 [p. 3]. Available from: https://learn.premierinc.com/white-papers/premier-healthcaredatabase.
New ICD-10-CM code for the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19), April 1, 2020 [press release]. 2020.
Gedeborg R, Furebring M, Michaëlsson K. Diagnosis-dependent misclassification of infections using administrative data variably affected incidence and mortality estimates in ICU patients. J Clin Epidemiol. 2007;60:155. e1–11
Wilson A, Gardner MN, Armstrong MA, Folck BF, Escobar GJ. Neonatal assisted ventilation: predictors, frequency, and duration in a mature managed care organization. Pediatrics.2000;105:822–30.
American Academy of Pediatrics. Levels of neonatal care. Pediatrics.2012;130:587–97.
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP). HCUP Chronic Condition Indicator [Available from: https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/toolssoftware/ccsr/ccs_refined.jsp.
Centers for Disease Control & Prevention. Evaluation and management considerations for neonates at risk for COVID-19: Testing reccomendations [Web page]. [updated December 8, 2020. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/caring-for-newborns.html#testing-recommendations.
American Academy of PediatricsFAQs: management of infants born to mothers with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 [updated February 11, 2021. Available from: https://services.aap.org/en/pages/2019-novel-coronavirus-covid-19-infections/clinical-guidance/faqs-management-of-infants-born-to-covid-19-mothers/.
Allotey J, Stallings E, Bonet M, Yap M, Chatterjee S, Kew T, et al. Clinical manifestations, risk factors, and maternal and perinatal outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 in pregnancy: living systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ.2020;370:m3320.
Matar R, Alrahmani L, Monzer N, Debiane LG, Berbari E, Fares J, et al. Clinical presentation and outcomes of pregnant women with coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 2021;72:521–33.
Olsen EOM, Roth NM, Aveni K, Sizemore L, Nestoridi E, Siebman S, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infections among neonates born to women with SARS-CoV-2 infection: maternal, pregnancy and birth characteristics. ResearchSquare. 2021. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-491688/v1.
Jolley RJ, Sawka KJ, Yergens DW, Quan H, Jetté N, Doig CJ. Validity of administrative data in recording sepsis: a systematic review. Crit Care.2015;19:139.
Chambers BD, Arega HA, Arabia SE, Taylor B, Barron RG, Gates B, et al. Black women’s perspectives on structural racism across the reproductive lifespan: a conceptual framework for measurement development. Matern Child Health J. 2021;25:402–13.
Scott KA, Britton L, McLemore MR. The ethics of perinatal care for black women: dismantling the structural racism in “mother blame” narratives. J Perinat Neonatal Nurs. 2019;33:108–15.
Gadson A, Akpovi E, Mehta PK. Exploring the social determinants of racial/ethnic disparities in prenatal care utilization and maternal outcome. Semin Perinatol. 2017;41:308–17.
Mitchell HK, Reddy A, Montoya-Williams D, Harhay M, Fowler JC, Yehya N. Hospital outcomes for children with severe sepsis in the USA by race or ethnicity and insurance status: a population-based, retrospective cohort study. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2021;5:103–12.
Weston EJ, Pondo T, Lewis MM, Martell-Cleary P, Morin C, Jewell B, et al. The burden of invasive early-onset neonatal sepsis in the United States, 2005-2008. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011;30:937–41.
Sigurdson K, Mitchell B, Liu J, Morton C, Gould JB, Lee HC, et al. Racial/ethnic disparities in neonatal intensive care: a systematic review. Pediatrics. 2019;144:e20183114.
Jarrín OF, Nyandege AN, Grafova IB, Dong X, Lin H. Validity of race and ethnicity codes in Medicare administrative data compared with gold-standard self-reported race collected during routine home health care visits. Med Care. 2020;58:e1–8.
Smith N, Iyer RL, Langer-Gould A, Getahun DT, Strickland D, Jacobsen SJ, et al. Health plan administrative records versus birth certificate records: quality of race and ethnicity information in children. BMC Health Serv Res. 2010;10:316.
Polubriaginof FCG, Ryan P, Salmasian H, Shapiro AW, Perotte A, Safford MM, et al. Challenges with quality of race and ethnicity data in observational databases. J Am Med Inf Assoc. 2019;26:730–6.
Labgold K, Hamid S, Shah S, Gandhi NR, Chamberlain A, Khan F, et al. Estimating the unknown: greater racial and ethnic disparities in COVID-19 burden after accounting for missing race and ethnicity data. Epidemiology. 2021;32:157–61.
Kadri SS, Gundrum J, Warner S, Cao Z, Babiker A, Klompas M, et al. Uptake and accuracy of the diagnosis code for COVID-19 among US hospitalizations. JAMA.2020;324:2553–4.
Acknowledgements
This project was supported in part by an appointment to the Research Participation Program at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention administered by the Oak Ridge Institute for Science and Education through an interagency agreement between the U.S. Department of Energy and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BW conceptualized and designed the study, carried out analyses, drafted the initial paper, and reviewed and revised the paper. DC replicated all analyses and reviewed and revised the paper. KW, CLD, RS, JYK, SG, and SE assisted with and approved study design and reviewed and revised the paper. All authors approved the final paper as submitted and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wallace, B., Chang, D., Woodworth, K. et al. Illness severity indicators in newborns by COVID-19 status in the United States, March–December 2020. J Perinatol 42, 446–453 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-021-01243-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-021-01243-y
This article is cited by
-
Critical care among newborns with and without a COVID-19 diagnosis, May 2020–February 2022
Journal of Perinatology (2023)