Abstract
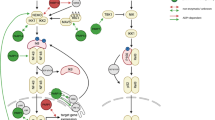
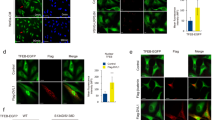
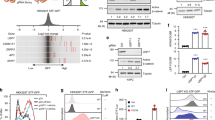
It has been shown that inhibition of GTPase-activating protein of ADP-ribosylation factor (Arf), ArfGAP, with a small molecule (QS11) results in synergistic activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. However, the role of Arf in Wnt/β-catenin signaling has not yet been elucidated. Here, we show that activation of Arf is essential for Wnt/β-catenin signaling. The level of the active form of Arf (Arf-GTP) transiently increased in the presence of Wnt, and this induction event was abrogated by blocking the interaction between Wnt and Frizzled (Fzd). In addition, knockdown of Fzds, Dvls or LRP6 blocked the Wnt-mediated activation of Arf. Consistently, depletion of Arf led to inhibition of Wnt-mediated membrane PtdIns (4,5)P2 (phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-bisphosphate) synthesis and LRP6 phosphorylation. Overall, our data suggest that transient activation of Arf modulates LRP6 phosphorylation for the transduction of Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
MacDonald BT, Tamai K, He X . Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell 2009; 17: 9–26.
Davidson G, Wu W, Shen J, Bilic J, Fenger U, Stannek P et al. Casein kinase 1 gamma couples Wnt receptor activation to cytoplasmic signal transduction. Nature 2005; 438: 867–872.
Tamai K, Zeng X, Liu C, Zhang X, Harada Y, Chang Z et al. A mechanism for Wnt coreceptor activation. Mol Cell 2004; 13: 149–156.
Zeng X, Tamai K, Doble B, Li S, Huang H, Habas R et al. A dual-kinase mechanism for Wnt co-receptor phosphorylation and activation. Nature 2005; 438: 873–877.
Clevers H . Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell 2006; 127: 469–480.
He X, Semenov M, Tamai K, Zeng XLDL . receptor-related proteins 5 and 6 in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: arrows point the way. Development 2004; 131: 1663–1677.
Logan CY, Nusse R . The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2004; 20: 781–810.
Zhang Q, Major MB, Takanashi S, Camp ND, Nishiya N, Peters EC et al. Small-molecule synergist of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 7444–7448.
Santy LC, Casanova JE . Activation of ARF6 by ARNO stimulates epithelial cell migration through downstream activation of both Rac1 and phospholipase D. J Cell Biol 2001; 154: 599–610.
Kahn RA, Cherfils J, Elias M, Lovering RC, Munro S, Schurmann A . Nomenclature for the human Arf family of GTP-binding proteins: ARF, ARL, and SAR proteins. J Cell Biol 2006; 172: 645–650.
D’Souza-Schorey C, Chavrier P . ARF proteins: roles in membrane traffic and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2006; 7: 347–358.
Gillingham AK, Munro S . The small G proteins of the Arf family and their regulators. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2007; 23: 579–611.
Shin HW, Nakayama K . Guanine nucleotide-exchange factors for arf GTPases: their diverse functions in membrane traffic. J Biochem 2004; 136: 761–767.
Pan W, Choi SC, Wang H, Qin Y, Volpicelli-Daley L, Swan L et al. Wnt3a-mediated formation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate regulates LRP6 phosphorylation. Science 2008; 321: 1350–1353.
Godi A, Pertile P, Meyers R, Marra P, Di Tullio G, Iurisci C et al. ARF mediates recruitment of PtdIns-4-OH kinase-beta and stimulates synthesis of PtdIns(4,5)P2 on the Golgi complex. Nat Cell Biol 1999; 1: 280–287.
Honda A, Nogami M, Yokozeki T, Yamazaki M, Nakamura H, Watanabe H et al. Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase alpha is a downstream effector of the small G protein ARF6 in membrane ruffle formation. Cell 1999; 99: 521–532.
Giguere P, Rochdi MD, Laroche G, Dupre E, Whorton MR, Sunahara RK et al. ARF6 activation by Galpha q signaling: Galpha q forms molecular complexes with ARNO and ARF6. Cell Signal 2006; 18: 1988–1994.
Hall B, McLean MA, Davis K, Casanova JE, Sligar SG, Schwartz MA . A fluorescence resonance energy transfer activation sensor for Arf6. Anal Biochem 2008; 374: 243–249.
Jackson CL, Casanova JE . Turning on ARF: the Sec7 family of guanine-nucleotide-exchange factors. Trends Cell Biol 2000; 10: 60–67.
MacDonald BT, Yokota C, Tamai K, Zeng X, He X . Wnt signal amplification via activity, cooperativity, and regulation of multiple intracellular PPPSP motifs in the Wnt co-receptor LRP6. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 16115–16123.
Wong HC, Bourdelas A, Krauss A, Lee HJ, Shao Y, Wu D et al. Direct binding of the PDZ domain of Dishevelled to a conserved internal sequence in the C-terminal region of Frizzled. Mol Cell 2003; 12: 1251–1260.
Hsieh JC, Rattner A, Smallwood PM, Nathans J . Biochemical characterization of Wnt-frizzled interactions using a soluble, biologically active vertebrate Wnt protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 3546–3551.
Bilic J, Huang YL, Davidson G, Zimmermann T, Cruciat CM, Bienz M et al. Wnt induces LRP6 signalosomes and promotes dishevelled-dependent LRP6 phosphorylation. Science 2007; 316: 1619–1622.
Perez-Mansilla B, Ha VL, Justin N, Wilkins AJ, Carpenter CL, Thomas GM . The differential regulation of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinases and phospholipase D1 by ADP-ribosylation factors 1 and 6. Biochim Biophys Acta 2006; 1761: 1429–1442.
Nishioka T, Aoki K, Hikake K, Yoshizaki H, Kiyokawa E, Matsuda M . Rapid turnover rate of phosphoinositides at the front of migrating MDCK cells. Mol Biol Cell 2008; 19: 4213–4223.
Suzuki T, Kanai Y, Hara T, Sasaki J, Sasaki T, Kohara M et al. Crucial role of the small GTPase ARF6 in hepatic cord formation during liver development. Mol Cell Biol 2006; 26: 6149–6156.
Willert K, Shibamoto S, Nusse R . Wnt-induced dephosphorylation of axin releases beta-catenin from the axin complex. Genes Dev 1999; 13: 1768–1773.
Li VS, Ng SS, Boersema PJ, Low TY, Karthaus WR, Gerlach JP et al. Wnt Signaling through Inhibition of beta-Catenin Degradation in an Intact Axin1 Complex. Cell 2012; 149: 1245–1256.
Liu X, Rubin JS, Kimmel AR . Rapid Wnt-induced changes in GSK3beta associations that regulate beta-catenin stabilization are mediated by Galpha proteins. Curr Biol 2005; 15: 1989–1997.
Wu X, Tu X, Joeng KS, Hilton MJ, Williams DA, Long F . Rac1 activation controls nuclear localization of beta-catenin during canonical Wnt signaling. Cell 2008; 133: 340–353.
Kumari S, Mayor S . ARF1 is directly involved in dynamin-independent endocytosis. Nat Cell Biol 2008; 10: 30–41.
Naslavsky N, Weigert R, Donaldson JG . Characterization of a nonclathrin endocytic pathway: membrane cargo and lipid requirements. Mol Biol Cell 2004; 15: 3542–3552.
Gagliardi M, Piddini E, Vincent JP . Endocytosis: a positive or a negative influence on Wnt signalling? Traffic 2008; 9: 1–9.
Yamamoto H, Komekado H, Kikuchi A . Caveolin is necessary for Wnt-3a-dependent internalization of LRP6 and accumulation of beta-catenin. Dev Cell 2006; 11: 213–223.
Sakane H, Yamamoto H, Kikuchi A . LRP6 is internalized by Dkk1 to suppress its phosphorylation in the lipid raft and is recycled for reuse. J Cell Sci 2010; 123 (Pt 3): 360–368.
Nishida K, Yamasaki S, Hasegawa A, Iwamatsu A, Koseki H, Hirano T . Gab2 via PI-3K, regulates ARF1 in FcepsilonRI-mediated granule translocation and mast cell degranulation. J Immunol 2011; 187: 932–941.
Sawano A, Miyawaki A . Directed evolution of green fluorescent protein by a new versatile PCR strategy for site-directed and semi-random mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res 2000; 28: E78.
Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R . A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science 2002; 296: 550–553.
Tiscornia G, Singer O, Ikawa M, Verma IM . A general method for gene knockdown in mice by using lentiviral vectors expressing small interfering RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 1844–1848.
Heo WD, Inoue T, Park WS, Kim ML, Park BO, Wandless TJ et al. PI(3,4,5)P3 and PI(4,5)P2 lipids target proteins with polybasic clusters to the plasma membrane. Science 2006; 314: 1458–1461.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2006-2004046 and 2012R1A2A2A01012472 to E-HJ; 2010-0029206 to I-SK; 2011-0003980 to S-YK). WK, TK, and MK were supported by the Brain Korea 21 program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, W., Kim, S., Kim, T. et al. ADP-ribosylation factors 1 and 6 regulate Wnt/β-catenin signaling via control of LRP6 phosphorylation. Oncogene 32, 3390–3396 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.373
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.373