Abstract
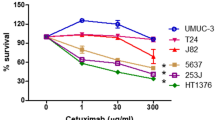
Monoclonal antibodies against the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) are effective cancer therapeutics, but tumors harboring RAS mutations are resistant. To functionally dissect RAS-mediated resistance, we have studied clinically approved anti-EGFR antibodies, cetuximab and panitumumab, in cancer models. Both antibodies were equally cytotoxic in vitro. However, cetuximab, which also triggers antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), was more effective than panitumumab in vivo. Oncogenic RAS neutralized the activity of both antibodies in vivo. Mechanistically, RAS upregulated BCL-XL in cancer cell lines and in primary colorectal cancers. Suppression of BCL-XL by short hairpin RNA or treatment with a BH3 mimetic overcame RAS-mediated antibody resistance. In conclusion, RAS-mutant tumors escape anti-EGFR antibody-mediated receptor blockade as well as ADCC in vivo. Pharmacological targeting of RAS effectors can restore sensitivity to antibody therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mayer A, Takimoto M, Fritz E, Schellander G, Kofler K, Ludwig H . The prognostic significance of proliferating cell nuclear antigen, epidermal growth factor receptor, and mdr gene expression in colorectal cancer. Cancer 1993; 71: 2454–2460.
Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, Khayat D, Bleiberg H, Santoro A et al. Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 337–345.
Jonker DJ, O'Callaghan CJ, Karapetis CS, Zalcberg JR, Tu D, Au HJ et al. Cetuximab for the treatment of colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: 2040–2048.
Amado RG, Wolf M, Peeters M, Van CE, Siena S, Freeman DJ et al. Wild-type KRAS is required for panitumumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 1626–1634.
Van CE, Peeters M, Siena S, Humblet Y, Hendlisz A, Neyns B et al. Open-label phase III trial of panitumumab plus best supportive care compared with best supportive care alone in patients with chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 1658–1664.
Vermorken JB, Mesia R, Rivera F, Remenar E, Kawecki A, Rottey S et al. Platinum-based chemotherapy plus cetuximab in head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 1116–1127.
Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Azarnia N, Shin DM, Cohen RB et al. Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med 2006; 354: 567–578.
Karapetis CS, Khambata-Ford S, Jonker DJ, O'Callaghan CJ, Tu D, Tebbutt NC et al. K-ras mutations and benefit from cetuximab in advanced colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 1757–1765.
Van CE, Kohne CH, Hitre E, Zaluski J, Chang CCR, Makhson A et al. Cetuximab and chemotherapy as initial treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2009; 360: 1408–1417.
Bokemeyer C, Bondarenko I, Makhson A, Hartmann JT, Aparicio J, de BF et al. Fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin with and without cetuximab in the first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 663–671.
De RW, Claes B, Bernasconi D, De SJ, Biesmans B, Fountzilas G et al. Effects of KRAS, BRAF, NRAS, and PIK3CA mutations on the efficacy of cetuximab plus chemotherapy in chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer: a retrospective consortium analysis. Lancet Oncol 2010; 11: 753–762.
Kurai J, Chikumi H, Hashimoto K, Yamaguchi K, Yamasaki A, Sako T et al. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity mediated by cetuximab against lung cancer cell lines. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13: 1552–1561.
Hara M, Nakanishi H, Tsujimura K, Matsui M, Yatabe Y, Manabe T et al. Interleukin-2 potentiation of cetuximab antitumor activity for epidermal growth factor receptor-overexpressing gastric cancer xenografts through antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Cancer Sci 2008; 99: 1471–1478.
Schneider-Merck T, Lammerts van Bueren JJ, Berger S, Rossen K, van Berkel PH, Derer S et al. Human IgG2 antibodies against epidermal growth factor receptor effectively trigger antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity but, in contrast to IgG1, only by cells of myeloid lineage. J Immunol 2010; 184: 512–520.
Bibeau F, Lopez-Crapez E, Di FF, Thezenas S, Ychou M, Blanchard F et al. Impact of Fc{gamma}RIIa-Fc{gamma}RIIIa polymorphisms and KRAS mutations on the clinical outcome of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab plus irinotecan. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 1122–1129.
Barriere J, Fischel J, Formento P, Renee N, Francoual MFJ, Chefour M et al. Cetuximab-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) against tumor cell lines characterized for EGFR expression and K-ras mutation. J Clin Oncol 2010; 27: e14583.
Kagi D, Ledermann B, Burki K, Seiler P, Odermatt B, Olsen KJ et al. Cytotoxicity mediated by T cells and natural killer cells is greatly impaired in perforin-deficient mice. Nature 1994; 369: 31–37.
Piloto O, Nguyen B, Huso D, Kim KT, Li Y, Witte L et al. IMC-EB10, an anti-FLT3 monoclonal antibody, prolongs survival and reduces nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient engraftment of some acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines and primary leukemic samples. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 4843–4851.
Strasser A, Harris AW, Vaux DL, Webb E, Bath ML, Adams JM et al. Abnormalities of the immune system induced by dysregulated bcl-2 expression in transgenic mice. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 1990; 166: 175–181.
Knudson CM, Tung KS, Tourtellotte WG, Brown GA, Korsmeyer SJ . Bax-deficient mice with lymphoid hyperplasia and male germ cell death. Science 1995; 270: 96–99.
Yoshida H, Kong YY, Yoshida R, Elia AJ, Hakem A, Hakem R et al. Apaf1 is required for mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis and brain development. Cell 1998; 94: 739–750.
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 2004; 304: 1497–1500.
Huber C, Bobek N, Kuball J, Thaler S, Hoffarth S, Huber C et al. Inhibitors of apoptosis confer resistance to tumour suppression by adoptively transplanted cytotoxic T-lymphocytes in vitro and in vivo. Cell Death Differ 2005; 12: 317–325.
Marques CA, Hahnel PS, Wolfel C, Thaler S, Huber C, Theobald M et al. An immune escape screen reveals Cdc42 as regulator of cancer susceptibility to lymphocyte-mediated tumor suppression. Blood 2008; 111: 1413–1419.
Hahnel PS, Thaler S, Antunes E, Huber C, Theobald M, Schuler M et al. signaling sensitizes cancer to cellular immunotherapy. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 3899–3906.
Oltersdorf T, Elmore SW, Shoemaker AR, Armstrong RC, Augeri DJ, Belli BA et al. An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature 2005; 435: 677–681.
van Delft MF, Wei AH, Mason KD, Vandenberg CJ, Chen L, Czabotar PE et al. The BH3 mimetic ABT-737 targets selective Bcl-2 proteins and efficiently induces apoptosis via Bak/Bax if Mcl-1 is neutralized. Cancer Cell 2006; 10: 389–399.
Wesarg E, Hoffarth S, Wiewrodt R, Kroll M, Biesterfeld S, Huber C et al. Targeting BCL-2 family proteins to overcome drug resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer 2007; 121: 2387–2394.
Shultz LD, Schweitzer PA, Christianson SW, Gott B, Schweitzer IB, Tennent B et al. Multiple defects in innate and adaptive immunologic function in NOD/LtSz-scid mice. J Immunol 1995; 154: 180–191.
Ravi R, Fuchs EJ, Jain A, Pham V, Yoshimura K, Prouser T et al. Resistance of cancers to immunologic cytotoxicity and adoptive immunotherapy via X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein expression and coexisting defects in mitochondrial death signaling. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 1730–1739.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011; 144: 646–674.
Schuler M, Maurer U, Goldstein JC, Breitenbucher F, Hoffarth S, Waterhouse NJ et al. p53 triggers apoptosis in oncogene-expressing fibroblasts by the induction of Noxa and mitochondrial Bax translocation. Cell Death Differ 2003; 10: 451–460.
Kasper S, Breitenbuecher F, Heidel F, Hoffarth S, Markova B, Schuler M et al. Targeting MCL-1 sensitizes FLT3-ITD-positive leukemias to cytotoxic therapies. Blood Cancer J 2012; 2: e60.
Remmele W, Stegner HE . [Recommendation for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast cancer tissue]. Pathologe 1987; 8: 138–140.
Acknowledgements
We thank Sandra Hoffarth, Sarah-Luise Stergar, Kirsten Bruderek, Jeannette Markowetz, Anna Even, Miriam Backs, Ali Sak, Sabine Harde and the staff of the Central Animal Facility, and the Pathology and Molecular Pathology Laboratories, University Hospital Essen, for their support. Robert Coffey, Roman Thomas, Hyatt Balke-Want, Scott W Lowe, Gary P Nolan and Abbott are acknowledged for providing reagents. This work was funded by grants from the Wilhelm Sander-Stiftung (2005.136.3, MS), the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SCHU 1541/5-1, MS), Mercator Research Center Ruhr-MERCUR (An-2011-0031, SK) a CESAR Research Fellowship (SK), the Wiedenfeld-Stiftung (SK) and the IFORES program of the Medical Faculty of the University Duisburg-Essen (MS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Martin Schuler has served as consultant to Amgen; Tanja Trarbach has received research funding, consulting and speaker honoraria from Merck Serono and Amgen. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kasper, S., Breitenbuecher, F., Reis, H. et al. Oncogenic RAS simultaneously protects against anti-EGFR antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and EGFR signaling blockade. Oncogene 32, 2873–2881 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.302
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.302
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
BCL-XL PROTAC degrader DT2216 synergizes with sotorasib in preclinical models of KRASG12C-mutated cancers
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2022)
-
Signaling pathways in intestinal homeostasis and colorectal cancer: KRAS at centre stage
Cell Communication and Signaling (2021)
-
Rab5C enhances resistance to ionizing radiation in rectal cancer
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2019)
-
GC1118, a novel anti-EGFR antibody, has potent KRAS mutation-independent antitumor activity compared with cetuximab in gastric cancer
Gastric Cancer (2019)
-
Restoring PUMA induction overcomes KRAS-mediated resistance to anti-EGFR antibodies in colorectal cancer
Oncogene (2018)