Abstract
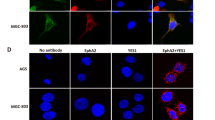
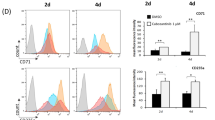
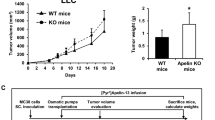
Erythropoietin (Epo) is widely used clinically to treat anemia associated with various clinical conditions including cancer. Data from several clinical trials suggest significant adverse effect of Epo treatment on cancer patient survival. However, controversy exists whether Epo receptor (EpoR) is functional in cancer cells. In this study, we demonstrated that EpoR mRNA expression was detectable in 90.1% of 65 melanoma cell lines, and increased copy number of the Epo and EpoR loci occurred in 30 and 24.6% of 130 primary melanomas, respectively. EpoR knockdown in melanoma cells resulted in diminished ERK phosphorylation in response to Epo stimulation, decreased cell proliferation and increased response to the inhibitory effect of hypoxia and cisplatin in vitro. EpoR knockdown significantly decreased melanoma xenograft size and tumor invasion in vivo. On the contrary, constitutive activation of EpoR activated cell proliferation pathways in melanoma cells and resulted in increased cell proliferation and resistance to hypoxia and cisplatin treatment in vitro. EpoR activation resulted in significantly larger xenografts with increased tumor invasion of surrounding tissue in vivo. Daily administration of recombinant Epo fails to stimulate melanoma growth in vivo, but the treatment increased vascular size in the xenografts. Increased local recurrence after excision of the primary tumors was observed after Epo treatment. Epo induced angiogenesis in Matrigel plug assays, and neutralization of Epo secreted by melanoma cells results in decreased angiogenesis. These data support that EpoR is functional in melanoma and EpoR activation may promote melanoma progression, and suggest that Epo may stimulate angiogenesis and increase survival of melanoma cells under hypoxic condition in vivo.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acs G, Acs P, Beckwith SM, Pitts RL, Clements E, Wong K et al. (2001). Erythropoietin and erythropoietin receptor expression in human cancer. Cancer Res 61: 3561–3565.
Acs G, Chen M, Xu X, Acs P, Verma A, Koch CJ . (2004a). Autocrine erythropoietin signaling inhibits hypoxia-induced apoptosis in human breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett 214: 243–251.
Acs G, Xu X, Chu C, Acs P, Verma A . (2004b). Prognostic significance of erythropoietin expression in human endometrial carcinoma. Cancer 100: 2376–2386.
Arcasoy MO . (2008). Erythropoiesis-stimulating agent use in cancer: preclinical and clinical perspectives. Clin Cancer Res 14: 4685–4690.
Arcasoy MO, Amin K, Chou SC, Haroon ZA, Varia M, Raleigh JA . (2005). Erythropoietin and erythropoietin receptor expression in head and neck cancer: relationship to tumor hypoxia. Clin Cancer Res 11: 20–27.
Arcasoy MO, Amin K, Karayal AF, Chou SC, Raleigh JA, Varia MA et al. (2002). Functional significance of erythropoietin receptor expression in breast cancer. Lab Invest 82: 911–918.
Arcasoy MO, Jiang X, Haroon ZA . (2003). Expression of erythropoietin receptor splice variants in human cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 307: 999–1007.
Belda-Iniesta C, Perona R, Carpeno JC, Cejas P, Casado E, Manguan-Garcia C et al. (2007). Human recombinant erythropoietin does not promote cancer growth in presence of functional receptors expressed in cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther 6: 1600–1605.
Bennett CL, Silver SM, Djulbegovic B, Samaras AT, Blau CA, Gleason KJ et al. (2008). Venous thromboembolism and mortality associated with recombinant erythropoietin and darbepoetin administration for the treatment of cancer-associated anemia. JAMA 299: 914–924.
Blau CA . (2007). Erythropoietin in cancer: presumption of innocence? Stem Cells 25: 2094–2097.
Bohlius J, Schmidlin K, Brillant C, Schwarzer G, Trelle S, Seidenfeld J et al. (2009). Erythropoietin or darbepoetin for patients with cancer—meta-analysis based on individual patient data. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, CD007303.
Carlin S, Khan N, Ku T, Longo VA, Larson SM, Smith-Jones PM . (2010). Molecular targeting of carbonic anhydrase IX in mice with hypoxic HT29 colorectal tumor xenografts. PLoS One 5: e10857.
Constantinescu SN, Ghaffari S, Lodish HF . (1999). The erythropoietin receptor: structure, activation and intracellular signal transduction. Trends Endocrinol Metab 10: 18–23.
Curtin JA, Fridlyand J, Kageshita T, Patel HN, Busam KJ, Kutzner H et al. (2005). Distinct sets of genetic alterations in melanoma. N Engl J Med 353: 2135–2147.
Daniel RJ, Groves RW . (2002). Increased migration of murine keratinocytes under hypoxia is mediated by induction of urokinase plasminogen activator. J Invest Dermatol 119: 1304–1309.
Fu P, Jiang X, Arcasoy MO . (2009). Constitutively active erythropoietin receptor expression in breast cancer cells promotes cellular proliferation and migration through a MAP-kinase dependent pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 379: 696–701.
Hardee ME, Cao Y, Fu P, Jiang X, Zhao Y, Rabbani ZN et al. (2007). Erythropoietin blockade inhibits the induction of tumor angiogenesis and progression. PLoS One 2: e549.
Henke M, Laszig R, Rube C, Schafer U, Haase KD, Schilcher B et al. (2003). Erythropoietin to treat head and neck cancer patients with anaemia undergoing radiotherapy: randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 362: 1255–1260.
Jelkmann W, Bohlius J, Hallek M, Sytkowski AJ . (2008). The erythropoietin receptor in normal and cancer tissues. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 67: 39–61.
Jeong JY, Hoxhaj G, Socha AL, Sytkowski AJ, Feldman L . (2009). An erythropoietin autocrine/paracrine axis modulates the growth and survival of human prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 7: 1150–1157.
Knabe W, Siren AL, Ehrenreich H, Kuhn HJ . (2005). Expression patterns of erythropoietin and its receptor in the developing spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia. Anat Embryol (Berl) 210: 209–219.
Koritzinsky M, Wouters BG . (2007). Hypoxia and regulation of messenger RNA translation. Methods Enzymol 435: 247–273.
Kumar SM, Acs G, Fang D, Herlyn M, Elder DE, Xu X . (2005). Functional erythropoietin autocrine loop in melanoma. Am J Pathol 166: 823–830.
Kumar SM, Yu H, Edwards R, Chen L, Kazianis S, Brafford P et al. (2007). Mutant V600E BRAF increases hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha expression in melanoma. Cancer Res 67: 3177–3184.
Lai SY, Childs EE, Xi S, Coppelli FM, Gooding WE, Wells A et al. (2005). Erythropoietin-mediated activation of JAK-STAT signaling contributes to cellular invasion in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene 24: 4442–4449.
LaMontagne KR, Butler J, Marshall DJ, Tullai J, Gechtman Z, Hall C et al. (2006). Recombinant epoetins do not stimulate tumor growth in erythropoietin receptor-positive breast carcinoma models. Mol Cancer Ther 5: 347–355.
Ley CD, Olsen MW, Lund EL, Kristjansen PE . (2004). Angiogenic synergy of bFGF and VEGF is antagonized by angiopoietin-2 in a modified in vivo Matrigel assay. Microvasc Res 68: 161–168.
Leyland-Jones B, Semiglazov V, Pawlicki M, Pienkowski T, Tjulandin S, Manikhas G et al. (2005). Maintaining normal hemoglobin levels with epoetin alfa in mainly nonanemic patients with metastatic breast cancer receiving first-line chemotherapy: a survival study. J Clin Oncol 23: 5960–5972.
Lin WM, Baker AC, Beroukhim R, Winckler W, Feng W, Marmion JM et al. (2008). Modeling genomic diversity and tumor dependency in malignant melanoma. Cancer Res 68: 664–673.
Mirmohammadsadegh A, Marini A, Gustrau A, Delia D, Nambiar S, Hassan M et al. (2010). Role of erythropoietin receptor expression in malignant melanoma. J Invest Dermatol 130: 201–210.
Mohyeldin A, Lu H, Dalgard C, Lai SY, Cohen N, Acs G et al. (2005). Erythropoietin signaling promotes invasiveness of human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Neoplasia 7: 537–543.
Noguchi CT, Wang L, Rogers HM, Teng R, Jia Y . (2008). Survival and proliferative roles of erythropoietin beyond the erythroid lineage. Expert Rev Mol Med 10: e36.
Okazaki T, Ebihara S, Asada M, Yamanda S, Niu K, Arai H . (2008). Erythropoietin promotes the growth of tumors lacking its receptor and decreases survival of tumor-bearing mice by enhancing angiogenesis. Neoplasia 10: 932–939.
Paragh G, Kumar SM, Rakosy Z, Choi SC, Xu X, Acs G . (2009). RNA interference-mediated inhibition of erythropoietin receptor expression suppresses tumor growth and invasiveness in A2780 human ovarian carcinoma cells. Am J Pathol 174: 1504–1514.
Pharr PN, Hankins D, Hofbauer A, Lodish HF, Longmore GD . (1993). Expression of a constitutively active erythropoietin receptor in primary hematopoietic progenitors abrogates erythropoietin dependence and enhances erythroid colony-forming unit, erythroid burst-forming unit, and granulocyte/macrophage progenitor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 938–942.
Reynolds CP, Sun BC, DeClerck YA, Moats RA . (2005). Assessing growth and response to therapy in murine tumor models. Methods Mol Med 111: 335–350.
Seaman ME, Peirce SM, Kelly K . (2011). Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. PLoS One 6: e20807.
Sinclair AM, Todd MD, Forsythe K, Knox SJ, Elliott S, Begley CG . (2007). Expression and function of erythropoietin receptors in tumors: implications for the use of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents in cancer patients. Cancer 110: 477–488.
Sytkowski AJ . (2007). Does erythropoietin have a dark side? Epo signaling and cancer cells. Sci STKE 2007: e38.
Tovari J, Gilly R, Raso E, Paku S, Bereczky B, Varga N et al. (2005). Recombinant human erythropoietin alpha targets intratumoral blood vessels, improving chemotherapy in human xenograft models. Cancer Res 65: 7186–7193.
Tovari J, Pirker R, Timar J, Ostoros G, Kovacs G, Dome B . (2008). Erythropoietin in cancer: an update. Curr Mol Med 8: 481–491.
Tsai PT, Ohab JJ, Kertesz N, Groszer M, Matter C, Gao J et al. (2006). A critical role of erythropoietin receptor in neurogenesis and post-stroke recovery. J Neurosci 26: 1269–1274.
Um M, Gross AW, Lodish HF . (2007). A ‘classical’ homodimeric erythropoietin receptor is essential for the antiapoptotic effects of erythropoietin on differentiated neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y and pheochromocytoma PC-12 cells. Cell Signal 19: 634–645.
Wouters BG, Koritzinsky M . (2008). Hypoxia signalling through mTOR and the unfolded protein response in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 8: 851–864.
Wright GL, Hanlon P, Amin K, Steenbergen C, Murphy E, Arcasoy MO . (2004). Erythropoietin receptor expression in adult rat cardiomyocytes is associated with an acute cardioprotective effect for recombinant erythropoietin during ischemia-reperfusion injury. FASEB J 18: 1031–1033.
Wu H, Klingmuller U, Besmer P, Lodish HF . (1995). Interaction of the erythropoietin and stem-cell-factor receptors. Nature 377: 242–246.
Yates CM, Patel A, Oakley K, Helms A, Tuttle RM, Francis GL . (2006). Erythropoietin in thyroid cancer. J Endocrinol Invest 29: 320–329.
Yu T, Ye H, Chen Z, Ziober BL, Zhou X . (2008). Dimension reduction and mixed-effects model for microarray meta-analysis of cancer. Front Biosci 13: 2714–2720.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to M Herlyn from the Wistar Institute for providing melanoma cell lines. Financial support was provided by CA-093372, CA-116103, AR-054593 and Melanoma Research Foundation (to X Xu) and CA-100844 (to MO Arcasoy).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Zhang, G., Bastian, B. et al. Erythropoietin receptor contributes to melanoma cell survival in vivo. Oncogene 31, 1649–1660 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.366
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.366
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
VE-Cadherin Disassembly and Cell Contractility in the Endothelium are Necessary for Barrier Disruption Induced by Tumor Cells
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
The lack of CD131 and the inhibition of Neuro-2a growth by carbamylated erythropoietin
Cell Biology and Toxicology (2015)
-
Effects of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents on fatigue- and anaemia-related symptoms in cancer patients: systematic review and meta-analyses of published and unpublished data
British Journal of Cancer (2014)
-
Characterization of the erythropoietin/erythropoietin receptor axis in a rat model of liver damage and cholangiocarcinoma development
Histochemistry and Cell Biology (2013)
-
Erythropoietin-driven signalling and cell migration mediated by polyADP-ribosylation
British Journal of Cancer (2012)