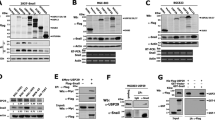
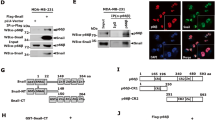
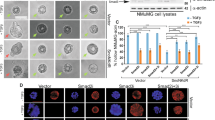
Abstract
The epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) that occurs during embryonic development has begun to attract attention as a potential mechanism for tumor cell metastasis. Snail is a well-known Zn-finger transcription factor that promotes EMT by repressing E-cadherin expression. It is known that Snail is phosphorylated by GSK3β and degraded by β-TrCP-mediated ubiquitination. Here we described another protein kinase, CK1, whose phosphorylation of Snail is required for the subsequent GSK3β phosphorylation. Specific inhibition or depletion of CK1ɛ inhibits the phosphorylation and degradation of Snail and promotes cell migration, suggesting a central role of CK1ɛ in the EMT process. Furthermore, our study uncovered distinct roles and steps of Snail phosphorylation by CK1ɛ and GSK3β. Taken together, we identified CK1ɛ as a new component of the Snail-mediated EMT process, providing insight into the mechanism of human cancer metastasis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberle H, Bauer A, Stappert J, Kispert A, Kemler R . (1997). Beta-catenin is a target for the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. EMBO J 16: 3797–3804.
Batlle E, Sancho E, Franci C, Dominguez D, Monfar M, Baulida J et al. (2000). The transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol 2: 84–89.
Behrens J, Jerchow BA, Wurtele M, Grimm J, Asbrand C, Wirtz R et al. (1998). Functional interaction of an axin homolog, conductin, with beta-catenin, APC, and GSK3beta. Science 280: 596–599.
Bilic J, Huang YL, Davidson G, Zimmermann T, Cruciat CM, Bienz M et al. (2007). Wnt induces LRP6 signalosomes and promotes dishevelled-dependent LRP6 phosphorylation. Science 316: 1619–1622.
Birchmeier W, Behrens J, Weidner KM, Frixen UH, Schipper J . (1991). Dominant and recessive genes involved in tumor cell invasion. Curr Opin Cell Biol 3: 832–840.
Cavallaro U, Christofori G . (2004). Cell adhesion and signalling by cadherins and Ig-CAMs in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 118–132.
Chu EY, Hens J, Andl T, Kairo A, Yamaguchi TP, Brisken C et al. (2004). Canonical WNT signaling promotes mammary placode development and is essential for initiation of mammary gland morphogenesis. Development 131: 4819–4829.
Cobb MH, Rosen OM . (1983). Description of a protein kinase derived from insulin-treated 3T3-L1 cells that catalyzes the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 and casein. J Biol Chem 258: 12472–12481.
Cowin P, Rowlands TM, Hatsell SJ . (2005). Cadherins and catenins in breast cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17: 499–508.
Dahlberg CL, Nguyen EZ, Goodlett D, Kimelman D . (2009). Interactions between Casein kinase Iepsilon (CKIepsilon) and two substrates from disparate signaling pathways reveal mechanisms for substrate-kinase specificity. PLoS ONE 4: e4766.
Dominguez D, Montserrat-Sentis B, Virgos-Soler A, Guaita S, Grueso J, Porta M et al. (2003). Phosphorylation regulates the subcellular location and activity of the snail transcriptional repressor. Mol Cell Biol 23: 5078–5089.
Frame S, Cohen P, Biondi RM . (2001). A common phosphate binding site explains the unique substrate specificity of GSK3 and its inactivation by phosphorylation. Mol Cell 7: 1321–1327.
Frescas D, Pagano M . (2008). Deregulated proteolysis by the F-box proteins SKP2 and beta-TrCP: tipping the scales of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 8: 438–449.
Gross SD, Anderson RA . (1998). Casein kinase I: spatial organization and positioning of a multifunctional protein kinase family. Cell Signal 10: 699–711.
Ha NC, Tonozuka T, Stamos JL, Choi HJ, Weis WI . (2004). Mechanism of phosphorylation-dependent binding of APC to beta-catenin and its role in beta-catenin degradation. Mol Cell 15: 511–521.
Ikenouchi J, Matsuda M, Furuse M, Tsukita S . (2003). Regulation of tight junctions during the epithelium-mesenchyme transition: direct repression of the gene expression of claudins/occludin by Snail. J Cell Sci 116: 1959–1967.
Jho EH, Zhang T, Domon C, Joo CK, Freund JN, Costantini F . (2002). Wnt/beta-catenin/Tcf signaling induces the transcription of Axin2, a negative regulator of the signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol 22: 1172–1183.
Kim MJ, Park BJ, Kang YS, Kim HJ, Park JH, Kang JW et al. (2003). Downregulation of FUSE-binding protein and c-myc by tRNA synthetase cofactor p38 is required for lung cell differentiation. Nat Genet 34: 330–336.
Kishida M, Hino S, Michiue T, Yamamoto H, Kishida S, Fukui A et al. (2001). Synergistic activation of the Wnt signaling pathway by Dvl and casein kinase Iepsilon. J Biol Chem 276: 33147–33155.
Knippschild U, Gocht A, Wolff S, Huber N, Lohler J, Stoter M . (2005). The casein kinase 1 family: participation in multiple cellular processes in eukaryotes. Cell Signal 17: 675–689.
Knippschild U, Milne DM, Campbell LE, DeMaggio AJ, Christenson E, Hoekstra MF et al. (1997). p53 is phosphorylated in vitro and in vivo by the delta and epsilon isoforms of casein kinase 1 and enhances the level of casein kinase 1 delta in response to topoisomerase-directed drugs. Oncogene 15: 1727–1736.
Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R, Thompson EW . (2006). The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: new insights in signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol 172: 973–981.
Lee SH, Lee SJ, Jung YS, Xu Y, Kang HS, Ha NC et al. (2009). Blocking of p53-Snail binding, promoted by oncogenic K-Ras, recovers p53 expression and function. Neoplasia 11: 22–31 and 6 pages following 31.
Liu C, Li Y, Semenov M, Han C, Baeg GH, Tan Y et al. (2002). Control of beta-catenin phosphorylation/degradation by a dual-kinase mechanism. Cell 108: 837–847.
Mashhoon N, DeMaggio AJ, Tereshko V, Bergmeier SC, Egli M, Hoekstra MF et al. (2000). Crystal structure of a conformation-selective casein kinase-1 inhibitor. J Biol Chem 275: 20052–20060.
Nieto MA . (2002). The snail superfamily of zinc-finger transcription factors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3: 155–166.
Orford K, Crockett C, Jensen JP, Weissman AM, Byers SW . (1997). Serine phosphorylation-regulated ubiquitination and degradation of beta-catenin. J Biol Chem 272: 24735–24738.
Pantel K, Brakenhoff RH . (2004). Dissecting the metastatic cascade. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 448–456.
Peinado H, Ballestar E, Esteller M, Cano A . (2004). Snail mediates E-cadherin repression by the recruitment of the Sin3A/histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1)/HDAC2 complex. Mol Cell Biol 24: 306–319.
Peinado H, Quintanilla M, Cano A . (2003). Transforming growth factor beta-1 induces snail transcription factor in epithelial cell lines: mechanisms for epithelial mesenchymal transitions. J Biol Chem 278: 21113–21123.
Peters JM, McKay RM, McKay JP, Graff JM . (1999). Casein kinase I transduces Wnt signals. Nature 401: 345–350.
Piao S, Lee SH, Kim H, Yum S, Stamos JL, Xu Y et al. (2008). Direct inhibition of GSK3beta by the phosphorylated cytoplasmic domain of LRP6 in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. PLoS ONE 3: e4046.
Reya T, Clevers H . (2005). Wnt signalling in stem cells and cancer. Nature 434: 843–850.
Sakanaka C, Leong P, Xu L, Harrison SD, Williams LT . (1999). Casein kinase iepsilon in the wnt pathway: regulation of beta-catenin function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 12548–12552.
Santos JA, Logarinho E, Tapia C, Allende CC, Allende JE, Sunkel CE . (1996). The casein kinase 1 alpha gene of Drosophila melanogaster is developmentally regulated and the kinase activity of the protein induced by DNA damage. J Cell Sci 109 (Pt 7): 1847–1856.
Schwarz-Romond T, Metcalfe C, Bienz M . (2007). Dynamic recruitment of axin by Dishevelled protein assemblies. J Cell Sci 120: 2402–2412.
Swiatek W, Tsai IC, Klimowski L, Pepler A, Barnette J, Yost HJ et al. (2004). Regulation of casein kinase I epsilon activity by Wnt signaling. J Biol Chem 279: 13011–13017.
Thiery JP . (2002). Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 442–454.
Tuazon PT, Traugh JA . (1991). Casein kinase I and II--multipotential serine protein kinases: structure, function, and regulation. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res 23: 123–164.
Winston JT, Strack P, Beer-Romero P, Chu CY, Elledge SJ, Harper JW . (1999). The SCFbeta-TRCP-ubiquitin ligase complex associates specifically with phosphorylated destruction motifs in IkappaBalpha and beta-catenin and stimulates IkappaBalpha ubiquitination in vitro. Genes Dev 13: 270–283.
Yook JI, Li XY, Ota I, Fearon ER, Weiss SJ . (2005). Wnt-dependent regulation of the E-cadherin repressor snail. J Biol Chem 280: 11740–11748.
Yook JI, Li XY, Ota I, Hu C, Kim HS, Kim NH et al. (2006). A Wnt-Axin2-GSK3beta cascade regulates Snail1 activity in breast cancer cells. Nat Cell Biol 8: 1398–1406.
Zhou BP, Deng J, Xia W, Xu J, Li YM, Gunduz M et al. (2004). Dual regulation of Snail by GSK-3beta-mediated phosphorylation in control of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Cell Biol 6: 931–940.
Zhou BP, Hung MC . (2005). Wnt, hedgehog and snail: sister pathways that control by GSK-3beta and beta-Trcp in the regulation of metastasis. Cell Cycle 4: 772–776.
Acknowledgements
We thank Xiao Ling Jin for assisting in DNA construction and protein purification. This study was supported by a grant from the National R&D Program for Cancer Control, Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family affairs, Republic of Korea (0920140).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Lee, SH., Kim, H. et al. Role of CK1 in GSK3β-mediated phosphorylation and degradation of Snail. Oncogene 29, 3124–3133 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.77
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.77
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Decidual stromal cells-derived exosomes incurred insufficient migration and invasion of trophoblast by disturbing of β-TrCP-mediated snail ubiquitination and degradation in unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion
European Journal of Medical Research (2024)
-
Targeting tumor-intrinsic PD-L1 suppresses the progression and aggressiveness of head and neck cancer by inhibiting GSK3β-dependent Snail degradation
Cellular Oncology (2023)
-
SIRT2 promotes the viability, invasion and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells by inhibiting the degradation of Snail
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
Silencing IKBKE inhibits the migration and invasion of glioblastoma by promoting Snail1 degradation
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2022)
-
Insights into the post-translational modification and its emerging role in shaping the tumor microenvironment
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2021)