Abstract
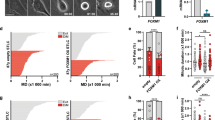
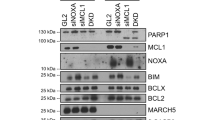
Mitotic microtubule (MT)-targeting drugs are widely used to treat cancer. The GTPase Ran regulates multiple processes, including mitotic spindle assembly, spindle pole formation and MT dynamics; Ran activity is therefore essential to formation of a functional mitotic apparatus. The RanBP1 protein, which binds Ran and regulates its interaction with effectors, is overexpressed in many cancer types. Several observations indicate that RanBP1 contributes to regulate the function of the mitotic apparatus: RanBP1 inactivation yields hyperstable MTs and induces apoptosis during mitosis, reminiscent of the effects of the MT-stabilizing drug taxol. Here we have investigated the influence of RanBP1 on spontaneous and taxol-induced apoptosis in transformed cells. We report that RanBP1 downregulation by RNA interference activates apoptosis in several transformed cell lines regardless of their p53 status, but not in the caspase-3-defective MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. Furthermore, RanBP1-interfered cells show an increased apoptotic response to taxol compared to their counterpart with normal or high RanBP1 levels, and this response is caspase-3 dependent. These results indicate that RanBP1 can modulate the outcome of MT-targeting therapeutic protocols.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Abe H, Kamai T, Shirataki H, Oyama T, Arai K, Yoshida K . (2008). High expression of Ran GTPase is associated with local invasion and metastasis of human clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 122: 2391–2397.
Allan LA, Clarke PR . (2007). Phosphorylation of caspase-9 by DCK1/cyclin B1 protects mitotic cells against apoptosis. Mol cell 26: 301–310.
Alli E, Bash-Babula J, Yang JM, Hait WN . (2002). Effect of stathmin on the sensitivity to antimicrotubule drugs in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 62: 6864–6869.
Altieri DC . (2008). Survivin, cancer networks and pathway-directed drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer 8: 61–70.
Anand S, Penrhyn-Lowe S, Venkitaraman AR . (2003). AURORA-A amplification overrides the mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint, inducing resistance to Taxol. Cancer Cell 3: 51–62.
Bacus SS, Gudkov AV, Lowe M, Lyass L, Yung Y, Komarov AP et al. (2001). Taxol-induced apoptosis depends on MAP kinase pathways (ERK and p38) and is independent of p53. Oncogene 20: 147–155.
Battistoni A, Guarguaglini G, Degrassi F, Pittoggi C, Palena A, Di Matteo G et al. (1997). Deregulated expression of the RanBP1 gene alters cell cycle progression in murine fibroblasts. J Cell Sci 110: 2345–2357.
Bhalla KN . (2003). Microtubule-targeted anticancer agents and apoptosis. Oncogene 22: 9075–9086.
Bhat KM, Setaluri V . (2007). Microtubule-associated proteins as targets in cancer chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 13: 2849–2854.
Bischoff FR, Krebber H, Smirnova E, Dong W, Ponstingl H . (1995). Co-activation of RanGTPase and inhibition of GTP dissociation by Ran-GTP binding protein RanBP1. EMBO J 14: 705–715.
Brito DA, Rieder CL . (2008). The ability to survive mitosis in the presence of microtubule poisons differs significantly between human nontransformed (RPE-1) and cancer (U2OS, HeLa) cells. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton (e-pub ahead of print 12 September 2008).
Carvalho A, Carmena M, Sambade C, Earnshaw WC, Wheatley SP . (2003). Survivin is required for stable checkpoint activation in taxol-treated HeLa cells. J Cell Sci 116: 2987–2998.
Ciciarello M, Mangiacasale R, Lavia P . (2007). Spatial control of mitosis by the GTPase Ran. Cell Mol Life Sci 64: 1891–1914.
Ciciarello M, Mangiacasale R, Thibier C, Guarguaglini G, Marchetti E, Di Fiore B et al. (2004). Importin beta is transported to spindle poles during mitosis and regulates Ran-dependent spindle assembly factors in mammalian cells. J Cell Sci 117: 6511–6522.
Clarke PR, Zhang C . (2008). Spatial and temporal coordination of mitosis by Ran GTPase. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9: 464–477.
De Luca A, Mangiacasale R, Severino A, Malquori L, Baldi A, Palena A et al. (2003). E1A deregulates the centrosome cycle in a Ran GTPase-dependent manner. Cancer Res 63: 1430–1437.
Di Fiore B, Ciciarello M, Lavia P . (2004). Mitotic functions of the Ran GTPase network: the importance of being in the right place at the right time. Cell Cycle 3: 305–313.
Di Fiore B, Ciciarello M, Mangiacasale R, Palena A, Tassin AM, Cundari E et al. (2003). Mammalian RanBP1 regulates centrosome cohesion during mitosis. J Cell Sci 116: 3399–3411.
Di Fiore B, Guarguaglini G, Palena A, Kerkhoven RM, Bernards R, Lavia P . (1999). Two E2F sites control growth-regulated and cell cycle-regulated transcription of the Htf9-a/RanBP1 gene through functionally distinct mechanisms. J Biol 274: 10339–10348.
Di Matteo G, Fuschi P, Zerfass K, Moretti S, Ricordy R, Cenciarelli C et al. (1995). Transcriptional control of the Htf9-A/RanBP-1 gene during the cell cycle. Cell Growth Differ 6: 1213–1224.
Gascoigne KE, Taylor SS . (2008). Cancer cells display profound intra- and interline variation following prolonged exposure to antimitotic drugs. Cancer cell 14: 111–122.
Giodini A, Kallio MJ, Wall NR, Gorbsky GJ, Tognin S, Marchisio PC et al. (2002). Regulation of microtubule stability and mitotic progression by survivin. Cancer Res 62: 2462–2467.
Goerlich D, Seewald MJ, Ribbeck K . (2003). Characterization of Ran-driven cargo transport and the RanGTPase system by kinetic measurements and computer simulation. EMBO J 22: 1088–1100.
Guarguaglini G, Renzi L, D’Ottavio F, Di Fiore B, Casenghi M, Cundari E et al. (2000). Regulated Ran-binding protein 1 activity is required for organization and function of the mitotic spindle in mammalian cells in vivo. Cell Growth Differ 11: 455–465.
Hata T, Furukawa T, Sunamura M, Egawa S, Motoi F, Ohmura N et al. (2005). RNA interference targeting aurora kinase a suppresses tumor growth and enhances the taxane chemosensitivity in human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 65: 2899–2905.
Holland AJ, Cleveland DW . (2008). Beyond genetics: surprising determinants of cell fate in antitumor drugs. Cancer Cell 14: 103–105.
Huang J, Raff JW . (1999). The disappearance of cyclin B at the end of mitosis is regulated spatially in Drosophila cells. EMBO J 18: 2184–2195.
Iancu C, Mistry SJ, Arkin S, Atweh GF . (2000). Taxol and anti-stathmin therapy: a synergistic combination that targets the mitotic spindle. Cancer Res 60: 3537–3541.
Iancu C, Mistry SJ, Arkin S, Wallenstein S, Atweh GF . (2001). Effects of stathmin inhibition on the mitotic spindle. J Cell Sci 114: 909–916.
Ibrado AM, Kim CN, Bhalla K . (1998). Temporal relationship of CDK1 activation and mitotic arrest to cytosolic accumulation of cytochrome c and caspase-3 activity during taxol-induced apoptosis of human AML HL-60 cells. Leukemia 12: 1930–1936.
Impens F, Van Damme P, Demol H, Van Damme J, Vandekerckhove J, Gevaert K . (2008). Mechanistic insight into taxol-induced cell death. Oncogene 27: 4580–4591.
Ishida S, Huang E, Zuzan H, Spang R, Leone G, West M et al. (2001). Role for E2F in control of both DNA replication and mitotic functions as revealed from DNA microarray analysis. Mol Cell Biol 21: 4684–4699.
Jackson JR, Patrick DR, Dar MM, Huang PS . (2007). Targeted anti-mitotic therapies: can we improve on tubulin agents? Nat Rev Cancer 7: 107–117.
Jiang Y, Zhang Y, Lees E, Seghezzi W . (2003). AuroraA overexpression overrides the mitotic spindle checkpoint triggered by nocodazole, a microtubule destabilizer. Oncogene 22: 8293–8301.
Jordan MA, Wilson L . (2004). Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 253–265.
Kalab P, Heald R . (2008). The RanGTP gradient—a GPS for the mitotic spindle. J Cell Sci 121: 1577–1586.
Kim M, Murphy K, Liu F, Parker SE, Dowling ML, Baff W et al. (2005). Caspase-mediated specific cleavage of BubR1 is a determinant of mitotic progression. Mol Cell Biol 25: 9232–9248.
Koffa MD, Casanova CM, Santarella R, Kocher T, Wilm M, Mattaj IW . (2006). HURP is part of a Ran-dependent complex involved in spindle formation. Curr Biol 16: 743–754.
Kops GJ, Weaver BA, Cleveland DW . (2005). On the road to cancer: aneuploidy and the mitotic checkpoint. Nat Rev Cancer 5: 773–785.
Kurisetty VV, Johnston PG, Johnston N, Erwin P, Crowe P, Fernig DG et al. (2008). Ran GTPase is an effector of the invasive/metastatic phenotype induced by osteopontin. Oncogene 27: 7139–7149.
Li HY, Ng WP, Wong CH, Iglesias PA, Zheng Y . (2007). Coordination of chromosome alignment and mitotic progression by the chromosome-based Ran signal. Cell Cycle 6: 1886–1895.
Lu KH, Lue KH, Chou MC, Chung JG . (2005). Paclitaxel induces apoptosis via caspase-3 activation in human osteogenic sarcoma cells (U-2 OS). J Orthop Res 23: 988–994.
Lu Z, Xu S . (2006). ERK1/2 MAP kinases in cell survival and apoptosis. IUBMB Life 58: 621–631.
McGrogan BT, Gilmartin B, Carney DN, McCann A . (2008). Taxanes, microtubules and chemoresistant breast cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1785: 96–132.
Mollinedo F, Gajate C . (2003). Microtubules, microtubule-interfering agents and apoptosis. Apoptosis 8: 413–450.
Nicholson DW, Ali A, Thornberry NA, Vaillancourt JP, Ding CK, Gallant M et al. (1995). Identification and inhibition of the ICE/CED-3 protease necessary for mammalian apoptosis. Nature 376: 37–43.
Ofir R, Seidman R, Rabinski T, Krup M, Yavelsky V, Weinstein Y et al. (2002). Taxol-induced apoptosis in human SKOV3 ovarian and MCF7 breast carcinoma cells is caspase-3 and caspase-9 independent. Cell Death Differ 9: 636–642.
Ouspenski II, Mueller UW, Matynia A, Sazer S, Elledge SJ, Brinkley BR . (1995). Ran-binding protein-1 is an essential component of the Ran/RCC1 molecular switch system in budding yeast. J Biol Chem 270: 1975–1978.
Oyaizu H, Adachi Y, Taketani S, Tokunaga R, Fukuhara S, Ikehara S . (1999). A crucial role of caspase 3 and caspase 8 in paclitaxel-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol Res Commun 2: 36–41.
Pérez de Castro I, de Cárcer G, Malumbres M . (2007). A census of mitotic cancer genes: new insights into tumor cell biology and cancer therapy. Carcinogenesis 28: 899–912.
Plafker K, Macara IG . (2000). Facilitated nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of the Ran binding protein RanBP1. Mol Cell Biol 20: 3510–3521.
Rensen WM, Mangiacasale R, Ciciarello M, Lavia P . (2008). The GTPase Ran: regulation of cell life and potential roles in cell transformation. Front Biosci 13: 4097–4121.
Shi J, Orth JD, Mitchison T . (2008). Cell type variation in responses to antimitotic drugs that target microtubules and kinesin-5. Cancer Res 68: 3269–3276.
Sillje HH, Nagel S, Korner R, Nigg EA . (2006). HURP is a Ran-importin beta-regulated protein that stabilizes kinetochore microtubules in the vicinity of chromosomes. Curr Biol 16: 731–742.
Spänkuch B, Heim S, Kurunci-Csacsko E, Lindenau C, Yuan J, Kaufmann M et al. (2006). Down-regulation of Polo-like kinase 1 elevates drug sensitivity of breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 66: 5836–5846.
Spänkuch B, Kurunci-Csacsko E, Kaufmann M, Strebhardt K . (2007). Rational combinations of siRNAs targeting Plk1 with breast cancer drugs. Oncogene 26: 5793–5807.
Tanaka E, Hashimoto Y, Ito T, Kondo K, Higashiyama M, Tsunoda S et al. (2007). The suppression of aurora-A/STK15/BTAK expression enhances chemosensitivity to docetaxel in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 13: 1331–1340.
Tedeschi A, Ciciarello M, Mangiacasale R, Roscioli E, Rensen WM, Lavia P . (2007). RANBP1 localizes a subset of mitotic regulatory factors on spindle microtubules and regulates chromosome segregation in human cells. J Cell Sci 120: 3748–3761.
Tewari M, Quan LT, O’Rourke K, Desnoyers S, Zeng Z, Beidler DR et al. (1995). Yama/CPP32 beta, a mammalian homolog of CED-3, is a CrmA-inhibitable protease that cleaves the death substrate poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Cell 81: 801–809.
Verde F, Dogterom M, Stelzer E, Karsenti E, Leibler S . (1992). Control of microtubule dynamics and length by cyclin A- and cyclin B-dependent kinases in Xenopus egg extracts. J Cell Biol 118: 1097–1108.
Wang TH, Popp DM, Wang HS, Saitoh M, Mural JG, Henley DC et al. (1999). Microtubule dysfunction induced by paclitaxel initiates apoptosis through both c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-dependent and -independent pathways in ovarian cancer cells. J Biol chem 274: 8208–8216.
Weaver BA, Cleveland DW . (2005). Decoding the links between mitosis, cancer, and chemotherapy: the mitotic checkpoint, adaptation, and cell death. Cancer 8: 7–12.
Weaver BA, Cleveland DW . (2007). Aneuploidy: instigator and inhibitor of tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 67: 10103–10105.
Wieder T, Essmann F, Prokop A, Schmelz K, Schulze-Osthoff K, Beyaert R et al. (2001). Activation of caspase-8 in drug-induced apoptosis of B-lymphoid cells is independent of CD95/Fas receptor-ligand interaction and occurs downstream of caspase-3. Blood 97: 1378–1387.
Wong J, Fang G . (2006). HURP controls spindle dynamics to promote proper interkinetochore tension and efficient kinetochore capture. J Cell Biol 173: 879–891.
Xia F, Canovas PM, Guadagno TM, Altieri DC . (2008b). A survivin–Ran complex regulates spindle formation in tumor cells. Mol Cell Biol 28: 5299–5311.
Xia F, Lee CW, Altieri DC . (2008a). Tumor cell dependence on Ran-GTP-directed mitosis. Cancer Res 68: 1826–1833.
Yamada HY, Gorbsky GJ . (2006). Spindle checkpoint function and cellular sensitivity to antimitotic drugs. Mol Cancer Ther 5: 2963–2969.
Yang XH, Sladek TL, Liu X, Butler BR, Froelich CJ, Thor AD . (2001). Reconstitution of caspase 3 sensitizes MCF-7 breast cancer cells to doxorubicin- and etoposide-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 61: 348–354.
Yuan J, Krämer A, Matthess Y, Yan R, Spänkuch B, Gätje R et al. (2006). Stable gene silencing of cyclin B1 in tumor cells increases susceptibility to taxol and leads to growth arrest in vivo. Oncogene 25: 1753–1762.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Christopher J Froelich (Northwestern University Medical School, Evanston, IL) for gifting the MCF-7/casp-3 cell line. We also thank Dr Giulia Guarguaglini for discussions and advice. This work was supported by the Italian Association for Cancer Research (AIRC) and by MIUR-FIRB (grant RBIN04T7MT). WMR and MC were supported by AIRC, ER and RM by MIUR-FIRB research contracts.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rensen, W., Roscioli, E., Tedeschi, A. et al. RanBP1 downregulation sensitizes cancer cells to taxol in a caspase-3-dependent manner. Oncogene 28, 1748–1758 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.24
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.24
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
RANBP1 promotes colorectal cancer progression by regulating pre-miRNA nuclear export via a positive feedback loop with YAP
Oncogene (2022)
-
SGK1 affects RAN/RANBP1/RANGAP1 via SP1 to play a critical role in pre-miRNA nuclear export: a new route of epigenomic regulation
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Sgk1 enhances RANBP1 transcript levels and decreases taxol sensitivity in RKO colon carcinoma cells
Oncogene (2013)